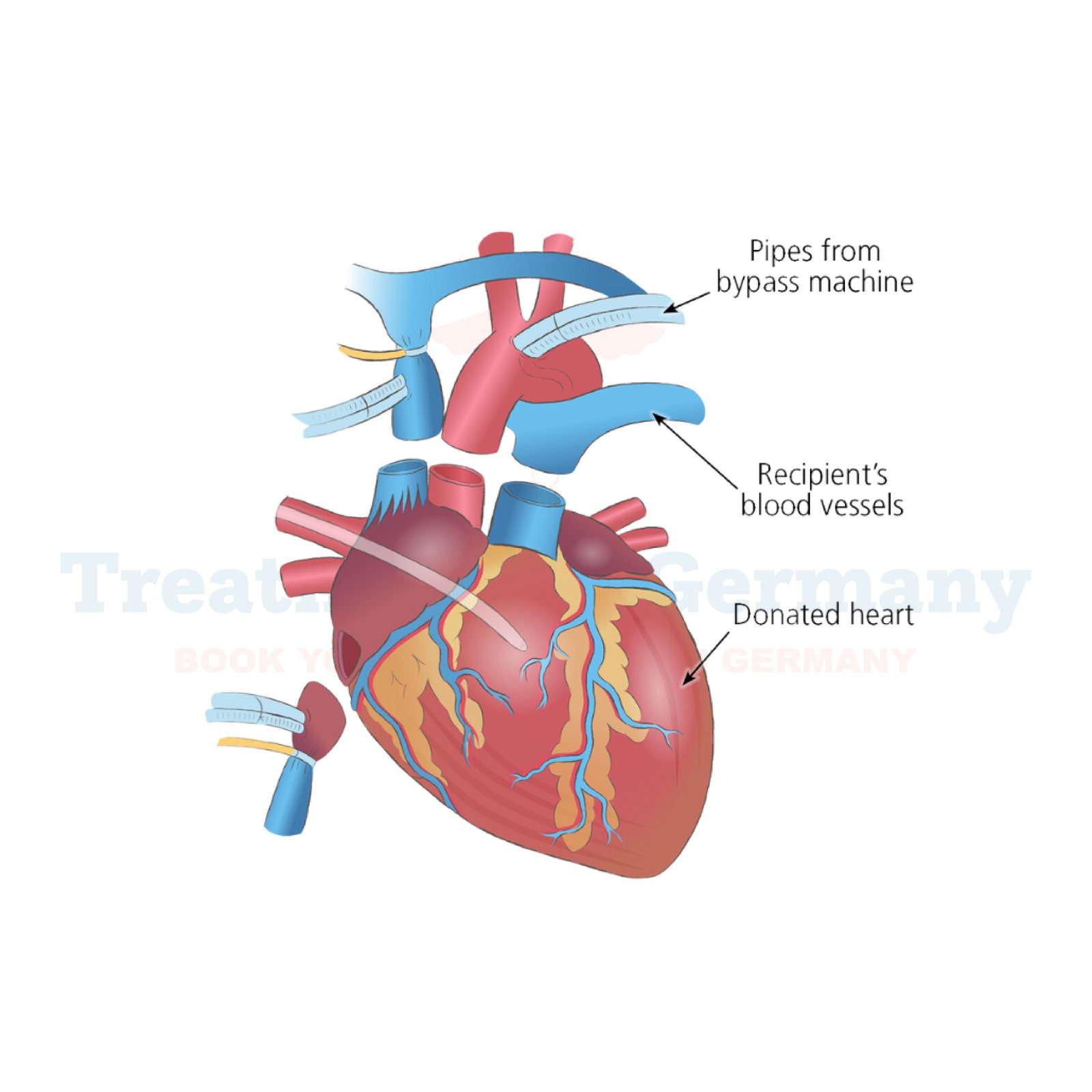
What is Heart Transplantation?
Heart transplantation is a surgical procedure where a diseased or failing heart is replaced with a healthy heart from a donor.
This procedure is typically recommended for patients with end-stage heart failure or severe coronary artery disease that cannot be effectively managed with other treatments.
In Germany, heart transplantation is performed by highly specialized cardiac surgeons and medical teams in leading hospitals equipped with advanced facilities for such complex surgeries.
Side Effects of Heart Transplantation
While heart transplantation can significantly improve quality of life and survival rates for eligible patients, it also carries certain risks and potential side effects. Some common side effects include:
- Rejection: The recipient’s immune system may recognize the transplanted heart as foreign and attempt to attack it. This can be managed with immunosuppressive medications, but regular monitoring is crucial to detect and treat rejection early.
- Infection: Due to the immunosuppressive medications required to prevent rejection, patients are more susceptible to infections. Careful monitoring and preventive measures are essential.
- Medication Side Effects: Drugs used to suppress the immune system can cause side effects such as weight gain, diabetes, high blood pressure, and osteoporosis.
- Post-Surgical Complications: Like any major surgery, there is a risk of bleeding, blood clots, and complications related to anesthesia.
How is Heart Transplantation Diagnosed?
The decision to undergo heart transplantation is made after a thorough evaluation by a multidisciplinary team of cardiologists, surgeons, transplant coordinators, and other specialists. Diagnostic tests and assessments typically include:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: To assess overall health and severity of heart disease.
- Diagnostic Tests: Such as echocardiogram, cardiac catheterization, electrocardiogram (ECG), and blood tests to evaluate heart function and overall health.
- Psychosocial Evaluation: To assess readiness for the emotional and lifestyle changes associated with transplantation.
- Blood Tests for Tissue Typing: To match the recipient with a suitable donor.
Potential Treatments for Heart Transplantation
In Germany, heart transplantation is considered a last resort when other treatments for heart failure have been ineffective. Potential treatments may include:
- Medical Management: Optimizing medications to manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
- Surgical Interventions: Such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or implantation of ventricular assist devices (VADs) as a bridge to transplantation.
- Lifestyle Changes: Including diet, exercise, and smoking cessation to improve overall health and heart function.
- Transplant Evaluation and Listing: Once deemed a suitable candidate, the patient is placed on a national waiting list for a suitable donor heart.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
