Hematomas are described as a general health concern related to the pooling of blood outside the actions of blood vessels resulting from injuries or conditions. While small hematomas, which include bruises, normally do not require medical treatment, large hematomas should be treated urgently.
Hematoma is treatable in any of Germany’s health facilities and Germany is among the best countries to get this treatment due to enhanced technology used by experienced doctors.
A hematoma is a collection of blood or hemorrhage in body tissues because of a violation in a blood vessel. Pain can occur anywhere and might be due to the tumor pressing on surrounding structures such as nerves.
When this occurs, one is likely to develop paresthesia (tingling sensation), numbness, nerve pain, or paralysis. Hematomas may be localized and spontaneous and have no complications but may be severe and warrant treatment by a doctor.
Different Types of Hematomas
Hematomas can be developed in many areas of the body tissue. They all require certain management based on the site of the burn and the degree of burn.
Breast Hematomas
They occur within the breast, commonly caused by an injury or surgical procedure. Although they are normally benign, they require surveillance to check whether any of these cells are malignant.
Cephalohematomas
Cephalohematomas are seen in newborns and they occur during childbirth as the result of pressure or impact. They are usually asymptomatic but should be closely observed for signs of trouble.
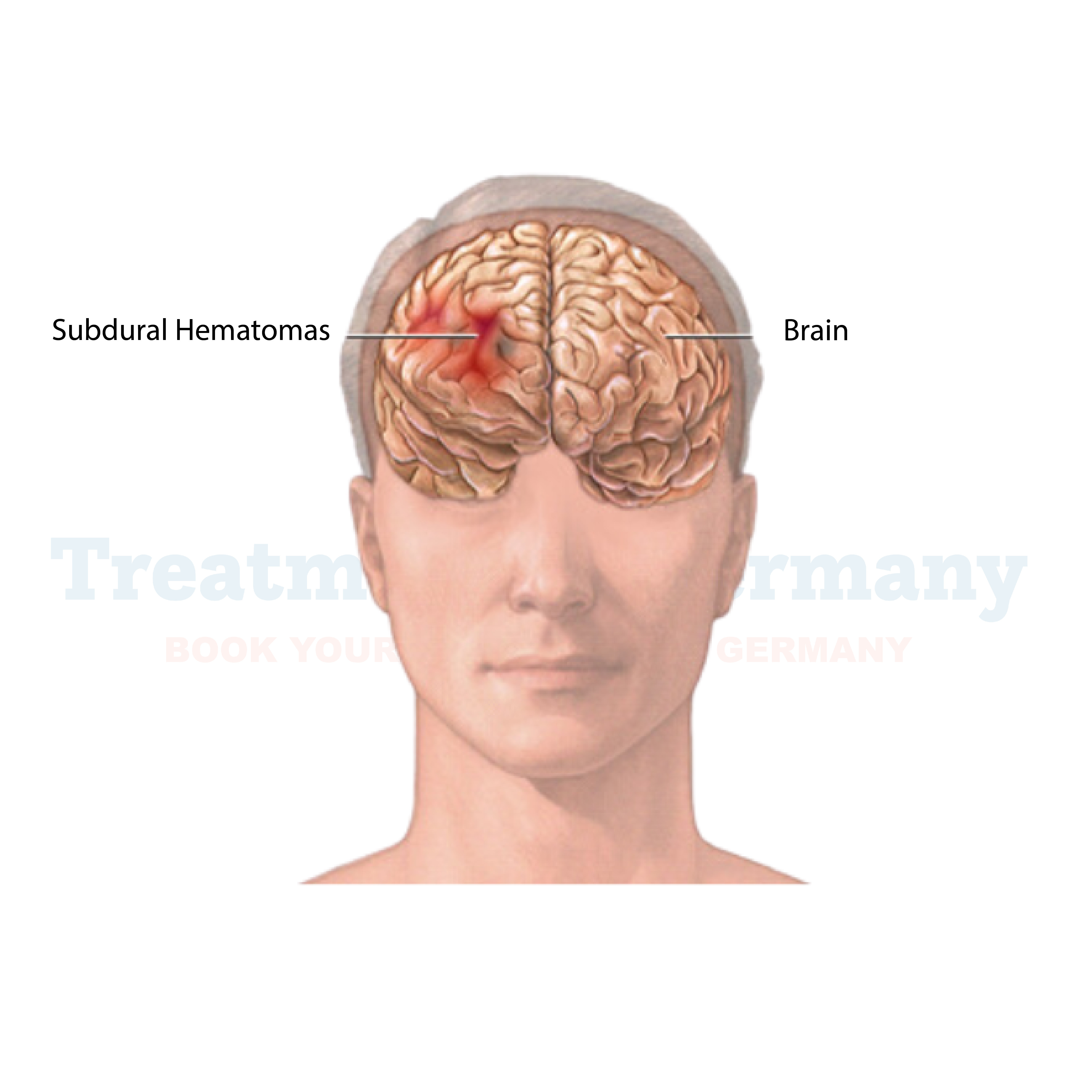
These types form inside the skull and may be fatal. Subdural hemorrhages are collections of blood beneath the dura mater, while epidural hemorrhages develop in between the skull and the outermost layer of the brain. They both can cause hazardous complications like seizures, coma, and severe headaches.
Hemoperitoneum
The type of hematoma indicated here is the one where clotted blood accumulates in the abdominal cavity. Most of the time it occurs as a result of an injury or when tissues of organs have been torn apart.
Rectus Sheath Hematomas
They happen close to the abdominal muscles and many a time are confused with other abdominal issues. They are normally diagnosed by ultrasound.
Sub-chorionic Hematomas
These are characteristic of pregnancy and refer to bleeding at the site of the uterus and the placenta. They are usually not serious and can be asymptomatic but can be dangerous to the mother and baby if not treated.
Symptoms of Hematomas
The manifestations of hematomas depend on their size and the area of the body they become a part of.
Common Symptoms
When there are signs of petechiae (red pinpoint rashes) conflation to bruises, purpura, or any other visible skin discoloration.
Severe Symptoms
Cardiac dyspnea, which includes tachypnea, which is having a large number of breaths per minute, which is having a small number of breaths in a minute.
What Causes Hematomas?
The following are the causes of hematomas:
Injuries and Trauma
Medical Conditions
Hematoma Diagnosis in Germany
There are highly developed diagnostics in Germany to identify a hematoma effectively and with high accuracy.
Physical Examination
The doctor assesses the symptoms in the area by feeling for the warmth, redness, hardness, and pain. Internal injuries can be checked using a stethoscope by putting various tubes into the stomach.
Imaging Tests
Hematomas Treatment Options in Germany
Non-surgical and surgical treatment of hematomas is presented at a high level in Germany.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Surgical Treatments
Recovery and Outlook
The nature and intensity of a hematoma determine how quickly it heals. Bruises and other minor hematomas usually go away in a few weeks. Other complications include subdural hematomas and brain bleeds, which may take a client several months to heal and sometimes need rehabilitation services. Treatments that help the patients normalize function, like physical and speech therapy, among others.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should you look for when suspecting a severe hematoma?
With large hematomas, symptoms might include numbness, weakness, paralysis, and a sudden severe headache. If any of these happen, you should consult your doctor.
Can hematomas heal naturally?
Small areas of hemorrhage are typical and most of the time they last for a few days and heal on their own. They might be larger or represent some sort of threat that demands handling with special types of therapy, including drainage or surgery.
How are hematomas diagnosed?
MRI, CT scans, and ultrasound are some of the imaging tests that doctors utilize to diagnose and stage hematomas.
Can hematomas be fatal?
Yes, especially those intracranial or intra-abdominal, for instance, and subdural hematoma. Emergency treatment is required in most cases.
Why Hematoma Treatment in Germany?
Germany has highly advanced healthcare facilities and some of the best brains in this field to provide effective treatments for all types of hematomas.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
