What is Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS)?
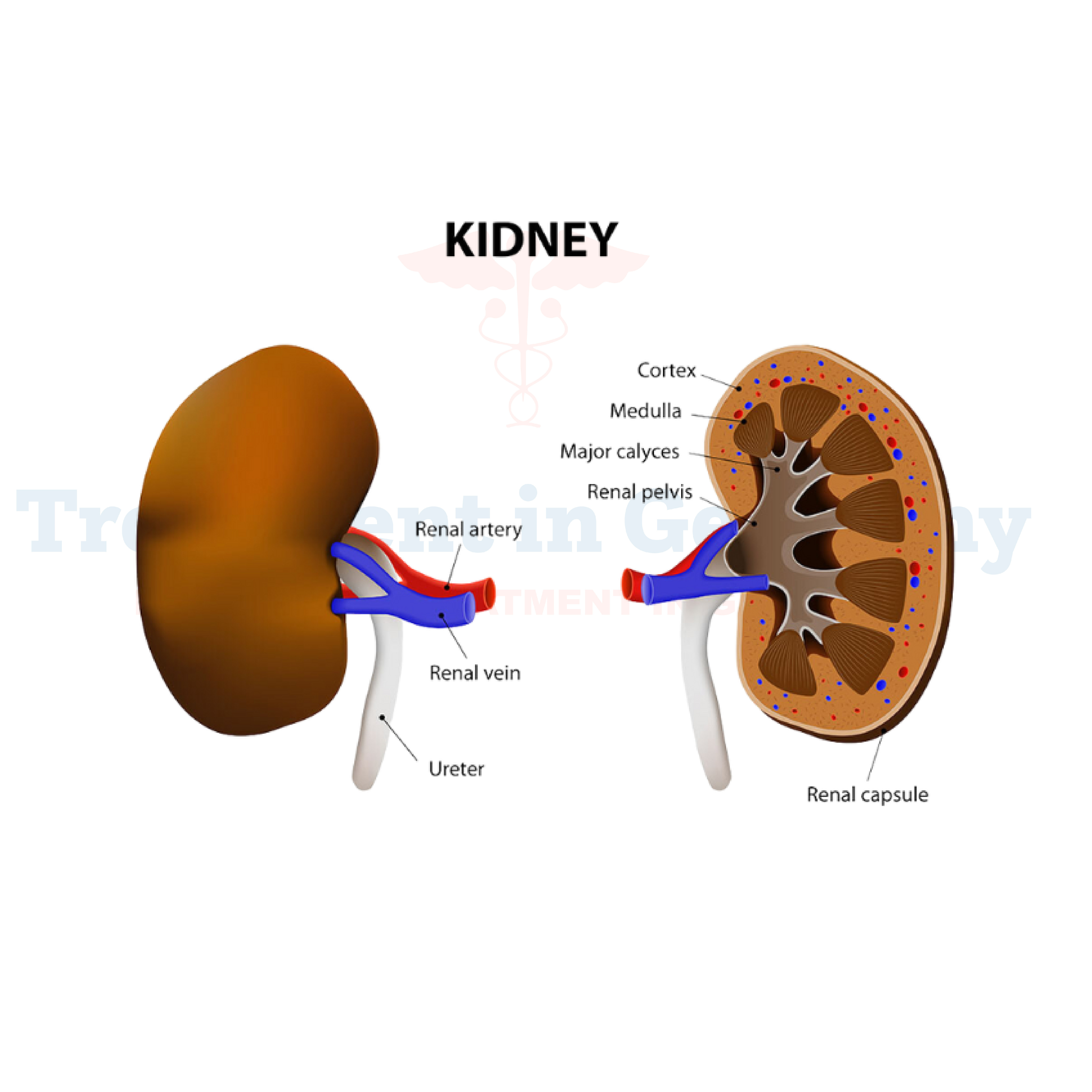
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS) is a rare but serious condition characterized by the destruction of red blood cells, acute kidney injury, and low platelet count. This syndrome primarily affects children under the age of 5, although adults can also develop it. In most cases, HUS is caused by infection with certain strains of Escherichia coli (E. coli), particularly serotype O157:H7, which produce toxins that damage blood vessels, leading to the symptoms associated with HUS.
Side effects of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS):
The symptoms of HUS can vary in severity but commonly include:
- Bloody diarrhea: This is often the first sign of HUS and is caused by the toxins produced by certain strains of E. coli.
- Decreased urine output: As the kidneys are affected, urine production may decrease or stop altogether.
- Fatigue and weakness: Due to anemia resulting from the destruction of red blood cells.
- Pale skin: Another indication of anemia.
- Bruising and easy bleeding: Due to low platelet count.
- Swelling: Particularly noticeable in the face, hands, and feet due to fluid retention.
How is Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS) diagnosed?
Diagnosing Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Healthcare providers may order the following tests:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): To assess levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Kidney Function Tests: Such as serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels to evaluate kidney function.
- Stool Culture: To identify the presence of E. coli bacteria and determine the strain responsible for the infection.
- Peripheral Blood Smear: To examine the blood under a microscope for signs of red blood cell destruction.
- Coagulation Studies: To assess clotting function.
Additionally, imaging tests such as ultrasound or CT scans may be performed to evaluate kidney function and identify any abnormalities in the organs.
Potential treatments of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS):
Treatment for HUS typically involves supportive care to manage symptoms and complications. This may include:
- Fluid and Electrolyte Management: To maintain hydration and electrolyte balance, particularly if kidney function is impaired.
- Blood Transfusions: To replace red blood cells and platelets lost due to destruction or bleeding.
- Dialysis: In cases of severe kidney failure, dialysis may be necessary to remove waste products and excess fluid from the blood.
- Medications: Antibiotics are generally not recommended for treating HUS, but certain medications may be used to manage symptoms such as hypertension or seizures.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
