Hip dysplasia is a condition where the hip joint does not develop properly, leading to instability and potential dislocation. This disorder can cause pain, limited mobility, and osteoarthritis if left untreated. While it can affect individuals of all ages, it is most commonly diagnosed in infants and young adults. Germany has emerged as a top destination for innovative and effective treatments, offering advanced medical care for patients with hip dysplasia.
Hip dysplasia varies in severity and can be categorized into different types:
Congenital Hip Dysplasia: Present at birth and detected in infancy.
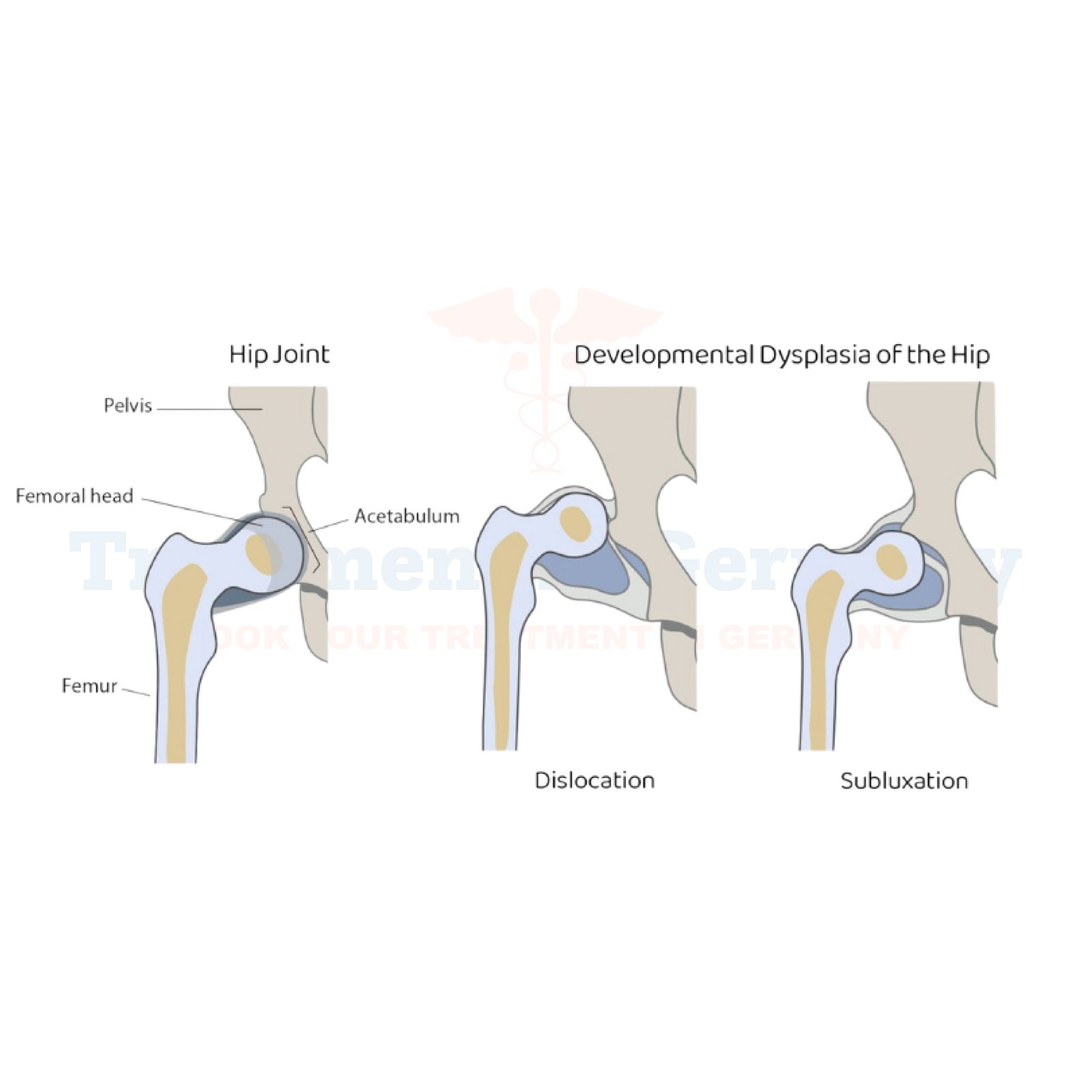
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH): Occurs as a child grows, affecting hip stability.
Acquired Hip Dysplasia: Develops later in life due to trauma or degenerative changes.
Risk Factors of Hip Dysplasia
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing hip dysplasia, including:
Genetics: Family history of hip dysplasia increases risk.
Breech Birth Position: Babies born in a breech position have a higher likelihood of hip instability.
Firstborn Children: More common in firstborns due to less room in the womb.
Sex: Females are more likely to develop hip dysplasia than males.
Swaddling Practices: Tight swaddling of infants may contribute to improper hip development.
Obesity: Excess weight puts additional strain on hip joints.
Diabetes and High Cholesterol (Hyperlipidemia): Metabolic disorders that may affect joint health.
Symptoms of Hip Dysplasia
The severity of symptoms varies, but common indicators include:
Hip Pain: Discomfort in the hip, groin, or thigh area.
Limping or Uneven Gait: A noticeable difference in leg length or walking pattern.
Clicking or Popping Sounds: Audible signs of joint instability.
Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty in hip movement, particularly in infants.
Early-Onset Arthritis: Increased risk of osteoarthritis due to joint misalignment.
Diagnosis and Diagnostic Tools
Early and accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. German hospitals use advanced diagnostic methods, including:
Physical Examination: Evaluates joint stability and movement.
X-rays: Determines the degree of hip displacement.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides detailed images of soft tissues and joint structures.
CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: Helps in complex cases requiring surgical planning.
Ultrasound: Commonly used for diagnosing infants and young children.
Blood Tests: To rule out autoimmune diseases and metabolic conditions affecting joint health.
Treatment in Germany
Germany is renowned for its cutting-edge medical technology and highly skilled specialists in orthopedic treatments. Various treatment options include:
Bracing (for Infants): Pavlik harness or other devices to correct hip alignment.
Physical Therapy: Strengthens muscles and improves joint function.
Pain Relievers and Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Manage pain and inflammation.
Minimally Invasive Surgery: Procedures like periacetabular osteotomy (PAO) to realign the hip joint.
Total Hip Replacement (THR): Recommended for severe cases or advanced arthritis.
Regenerative Medicine: Use of stem cell therapy for joint preservation.
Complementary Therapies: Alternative treatments like acupuncture and hydrotherapy for pain relief.
Innovative Therapies in Germany
Germany is at the forefront of pioneering medical research and treatments, offering advanced therapies for hip dysplasia:
Stem Cell Therapy: Used for regenerating damaged joint cartilage and reducing inflammation.
TACE (Transarterial Chemoembolization): Although primarily used for cancer treatments, research is ongoing for its application in inflammatory joint diseases.
Dendritic Cell Therapy: An emerging treatment in the field of regenerative medicine, with potential applications in autoimmune-related joint damage.
3D-Printed Implants: Custom-made hip implants designed to fit individual patients for improved mobility and comfort.
Robot-Assisted Surgery: Enhancing precision in hip realignment and replacement surgeries.
Why is it Preferable to Get Treatment in Germany?
Germany has established itself as a leader in hip dysplasia treatment due to:
Innovative Treatment Methods: Utilization of the latest technologies in hip preservation.
Experienced Specialists: Highly trained orthopedic surgeons with extensive expertise.
World-Class Hospitals: Equipped with advanced surgical and rehabilitation facilities.
Personalized Treatment Plans: Customized therapies for each patient’s needs.
Comprehensive Rehabilitation Programs: Ensuring long-term mobility and function.
Affordable Medical Packages: Competitive pricing for international patients.
Success Rate: High success rates in hip preservation and replacement surgeries.
Solutions and Prevention
While some cases of hip dysplasia are unavoidable, preventive measures can reduce the risk:
Routine Screenings for Newborns: Early detection helps in effective intervention.
Proper Swaddling Techniques: Allowing natural hip movement in infants.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Reduces strain on the hip joints.
Regular Exercise: Strengthens muscles around the hip for better support.
Early Treatment for Symptoms: Seeking medical attention at the first sign of discomfort.
Dietary Changes: Proper nutrition to support joint health and prevent metabolic disorders.
Conclusion
Hip dysplasia can lead to serious mobility issues if left untreated, but Germany offers world-class treatment options for patients of all ages. With highly skilled surgeons, innovative therapies, and state-of-the-art hospitals, Germany remains a premier destination for hip dysplasia care. By taking preventive measures and seeking timely treatment, individuals can maintain hip health and prevent long-term complications.
If you or a loved one is considering treatment for hip dysplasia, Germany offers some of the most advanced and effective options available today. The combination of expert doctors, modern hospitals, and innovative treatment approaches ensures the best possible outcomes for patients dealing with hip dysplasia.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
