What is Hirsutism?
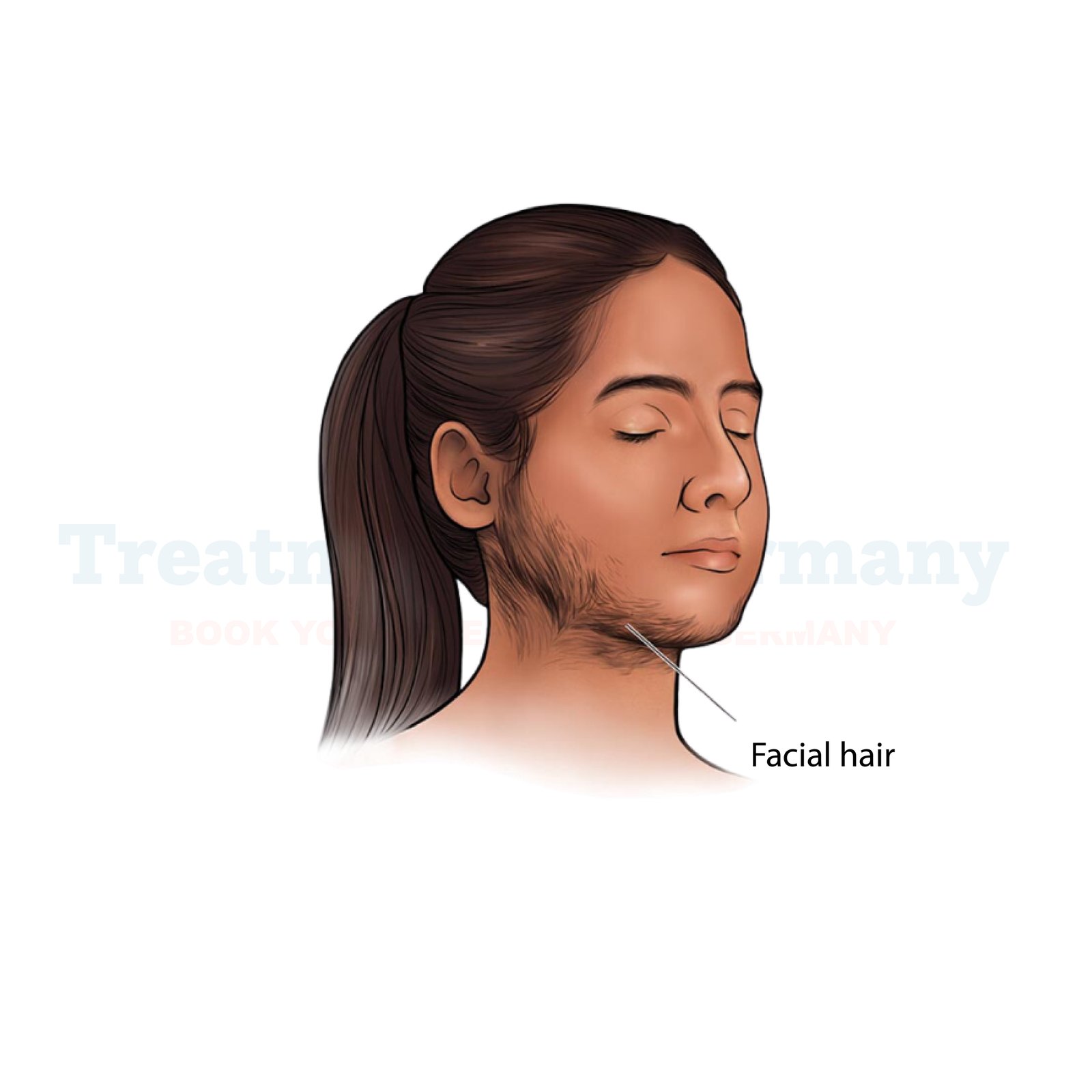
Hirsutism is a medical condition characterized by excessive hair growth in areas where hair is normally absent or minimal, particularly in women.
This excessive hair growth often occurs in a male pattern, such as on the face, chest, back, or abdomen. While some degree of hair growth is normal for everyone, hirsutism involves hair that is thicker, darker, and coarser than usual.
Side Effects of Hirsutism:
Aside from the physical discomfort and self-consciousness that may arise from excessive hair growth, hirsutism can also have psychological effects. Many individuals with hirsutism experience decreased self-esteem, anxiety, and depression due to the social stigma associated with the condition.
Additionally, hirsutism can sometimes be a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which may lead to further health complications if left untreated.
How is Hirsutism Diagnosed?
Diagnosing hirsutism typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist, gynecologist, or endocrinologist.
The diagnosis process may include a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and possibly laboratory tests to assess hormone levels and rule out underlying medical conditions.
Additionally, imaging studies, such as ultrasound, may be recommended to evaluate the ovaries and adrenal glands.
Potential Treatments of Hirsutism:
Treatment options for hirsutism aim to reduce excessive hair growth and manage any underlying medical conditions contributing to the condition. The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the severity of symptoms, underlying causes, and patient preferences.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
