What is Histiocytosis?
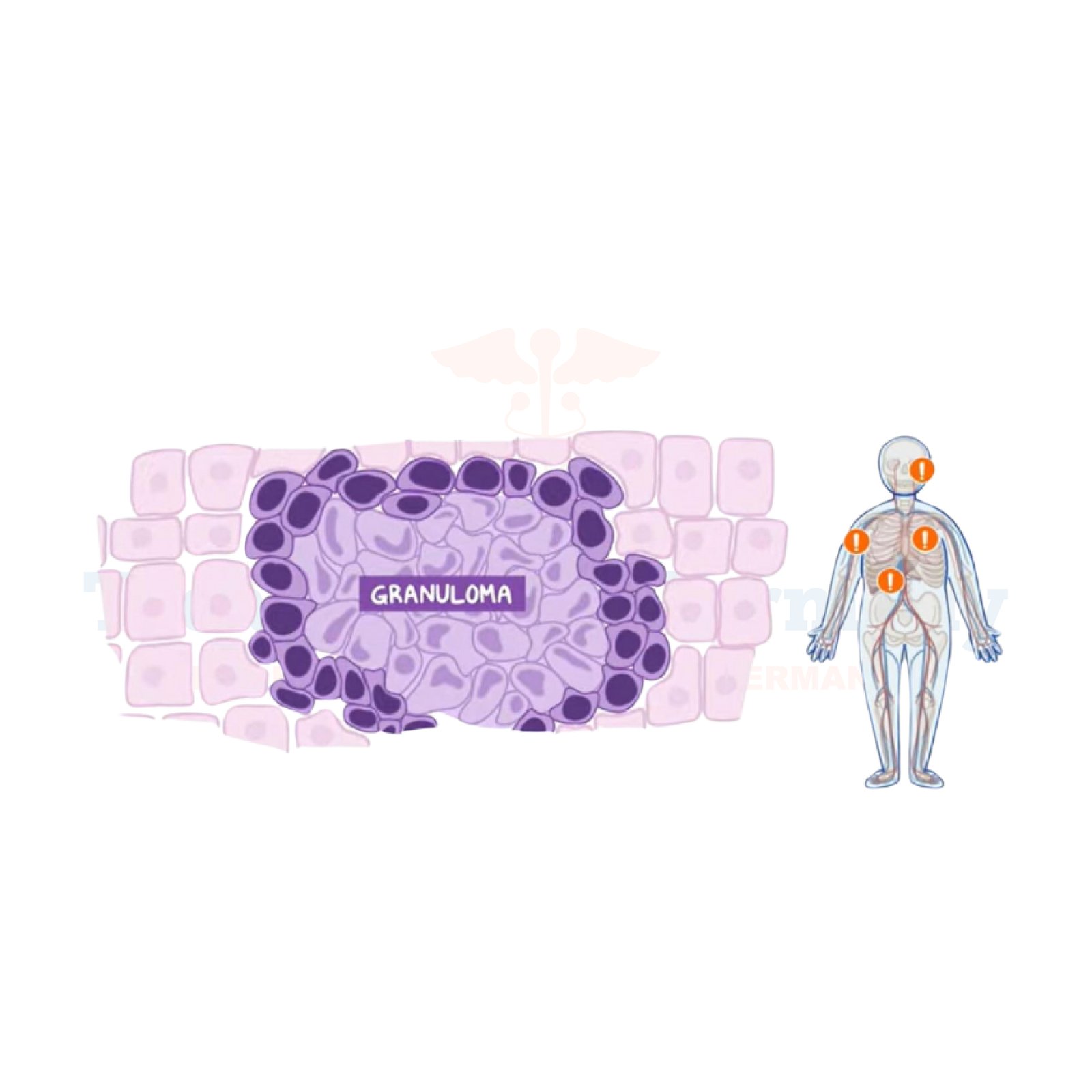
Histiocytosis, also known as histiocytic disorders, refers to a group of rare diseases characterized by an abnormal increase in the number of certain immune cells called histiocytes.
These cells are normally involved in fighting infection and performing other immune system functions. However, in histiocytosis, these cells multiply uncontrollably and accumulate in various parts of the body, leading to the formation of tumors or tissue damage.
There are different types of histiocytosis, including Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) which primarily affects children, and non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis which is less common and affects both children and adults.
Side Effects of Histiocytosis
The symptoms and side effects of histiocytosis can vary widely depending on the type and location of the disease. Common symptoms may include:
In severe cases, histiocytosis can affect multiple organs and systems, leading to serious complications if not treated promptly.
How is Histiocytosis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing histiocytosis typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, imaging studies (such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs), and biopsy of affected tissues.
Blood tests and other laboratory tests may also be performed to assess organ function and rule out other conditions.
Potential Treatment of Histiocytosis
Treatment for histiocytosis depends on the type and severity of the disease, as well as the organs involved. Common approaches include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
