Hydrocephalus is a condition where excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up in the brain’s ventricles, causing increased pressure. If left untreated, it can result in serious symptoms such as gait difficulties, bladder control challenges, and cognitive problems. Germany is renowned for its advanced medical facilities and expertise in treating hydrocephalus, particularly through the use of cutting-edge shunt placement techniques.
German neurosurgeons employ state-of-the-art technology and minimally invasive procedures to ensure precise placement of shunts, which help drain excess cerebrospinal fluid and alleviate symptoms effectively. Patients benefit from Germany’s multidisciplinary approach, combining neurology, radiology, and rehabilitation services to ensure thorough and holistic care. Germany is globally recognized for its advanced medical technology, expert neurosurgeons, and pioneering treatments, making it a top destination for hydrocephalus treatment.
There are various types of hydrocephalus that may develop at any stage of life. Understanding the condition is the first crucial step toward effective treatment.
Causes of Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus can arise from various factors including:
Blockages preventing proper CSF flow
Brain infections such as meningitis
Head injury or trauma
Brain tumors or abnormalities
Genetic conditions affecting CSF absorption
Symptoms of Hydrocephalus
Recognizing the symptoms early can aid in timely diagnosis and treatment. These symptoms may include:
General Symptoms in All Age Groups:
Persistent headache
Nausea followed by vomiting
Blurred or double vision
Drowsiness or lethargy
For Adults:
For Infants and Children:
Enlarged head size
Nausea, Vomiting and irritability
Delays in developmental milestones
Advanced Diagnosis & Diagnostic Tools
Germany’s medical centers utilize state-of-the-art diagnostic tools to confirm hydrocephalus accurately:
Hydrocephalus Shunt Placement Treatment in Germany
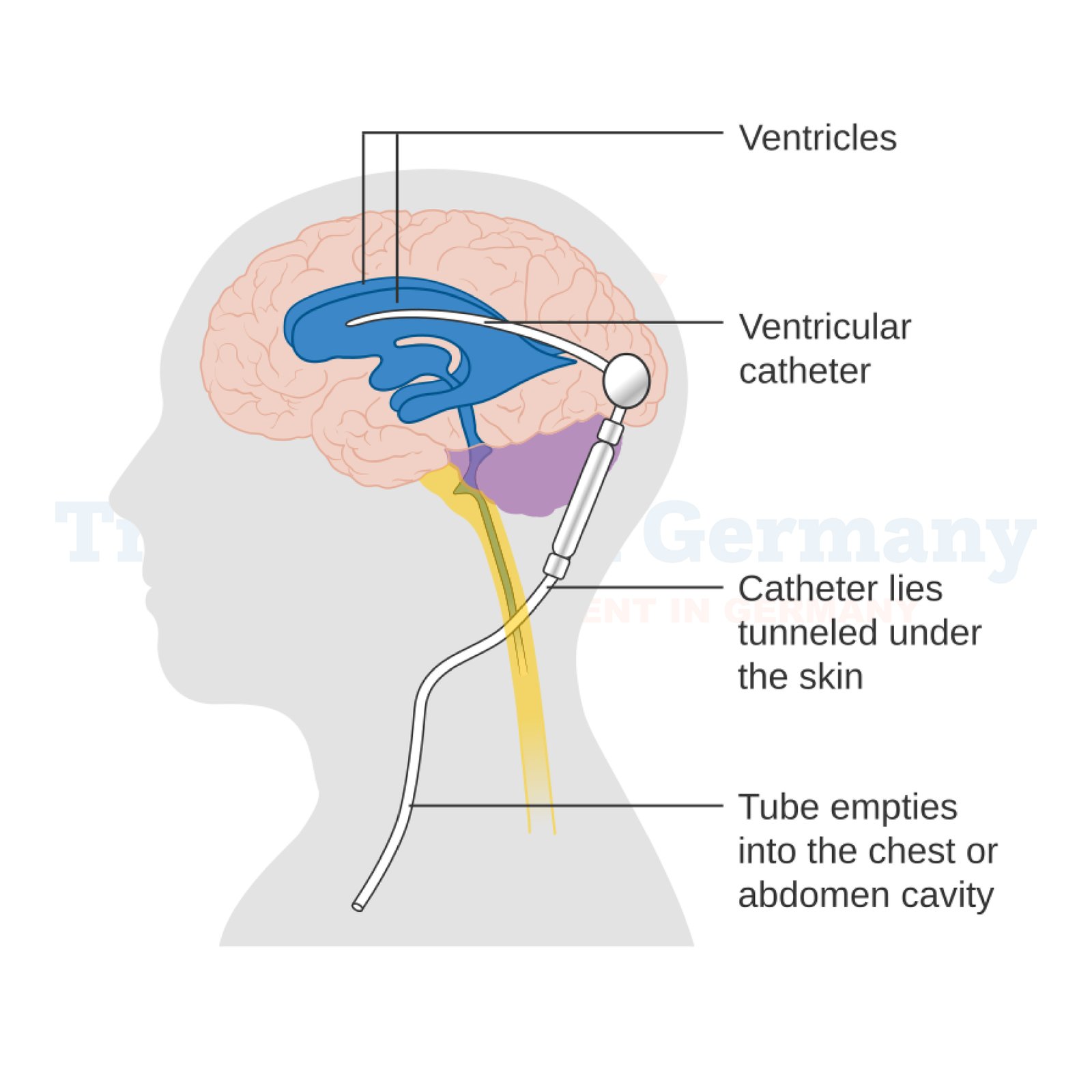
One of the most effective treatments for hydrocephalus is shunt placement surgery, and Germany is at the forefront of this life-changing procedure. A shunt is a thin, flexible tube surgically inserted to drain excess CSF from the brain to another part of the body, such as the abdomen. This relieves pressure and often alleviates debilitating symptoms like mobility issues and cognitive decline.
Surgical Procedures
Medicines and Therapies
While surgery is the primary treatment option, Germany also offers supplementary therapies to enhance recovery:
Why Choose Treatment in Germany for Hydrocephalus-Shunt Placement?
Germany stands out as a global leader in neurology and neurosurgery, offering unmatched benefits for hydrocephalus treatment:
Conclusion
Choosing treatment in Germany ensures that patients receive not only cutting-edge medical solutions but also compassionate and personalized care throughout their journey. With a focus on achieving the best possible outcomes, Germany's healthcare system equips patients with the tools and support they need to lead healthier, more fulfilling lives. By placing your trust in Germany's renowned medical expertise, you take a significant step toward improving your condition and regaining control over your future.
Effective hydrocephalus treatment can transform lives, providing relief from debilitating symptoms and a path toward improved health. Germany’s comprehensive care, advanced technology, and expertise ensure you’re in the best hands.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
