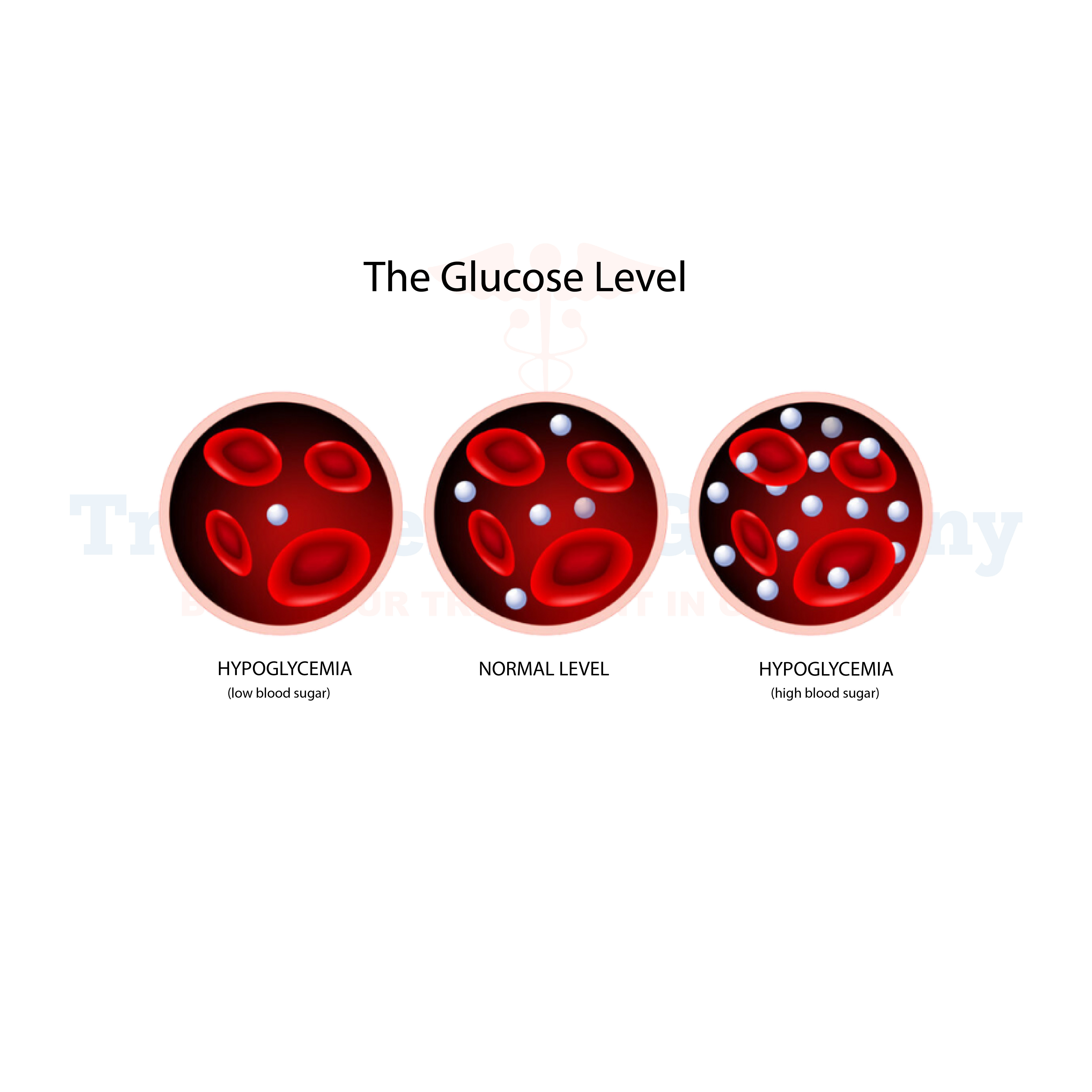
What is Hyperglycemia:
Hyperglycemia is a medical condition characterized by high levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. In individuals with diabetes, hyperglycemia occurs when the body either doesn't produce enough insulin or can't effectively use the insulin it produces.
Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels by allowing glucose to enter cells, where it's used for energy.
Side effects of Hyperglycemia:
If left untreated, hyperglycemia can lead to various complications, including:
How is Hyperglycemia diagnosed?:
Hyperglycemia is typically diagnosed through blood tests that measure the levels of glucose in the blood. These tests may include:
1. Fasting blood sugar test: This test measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast.
2. Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT): In this test, blood sugar levels are measured before and after consuming a sugary drink.
3. Hemoglobin A1c test: This test provides an average of blood sugar levels over the past two to three months.
Potential treatments of Hyperglycemia:
The treatment of hyperglycemia depends on its underlying cause and severity. For individuals with diabetes, treatments may include:
1. Insulin therapy: Insulin injections or insulin pumps may be prescribed to help lower blood sugar levels.
2. Oral medications: Medications such as metformin, sulfonylureas, and DPP-4 inhibitors may be prescribed to improve insulin sensitivity or stimulate insulin production.
3. Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and monitoring blood sugar levels can help manage hyperglycemia.
4. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): CGM devices can provide real-time information about blood sugar levels, allowing for better management and control of hyperglycemia.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
