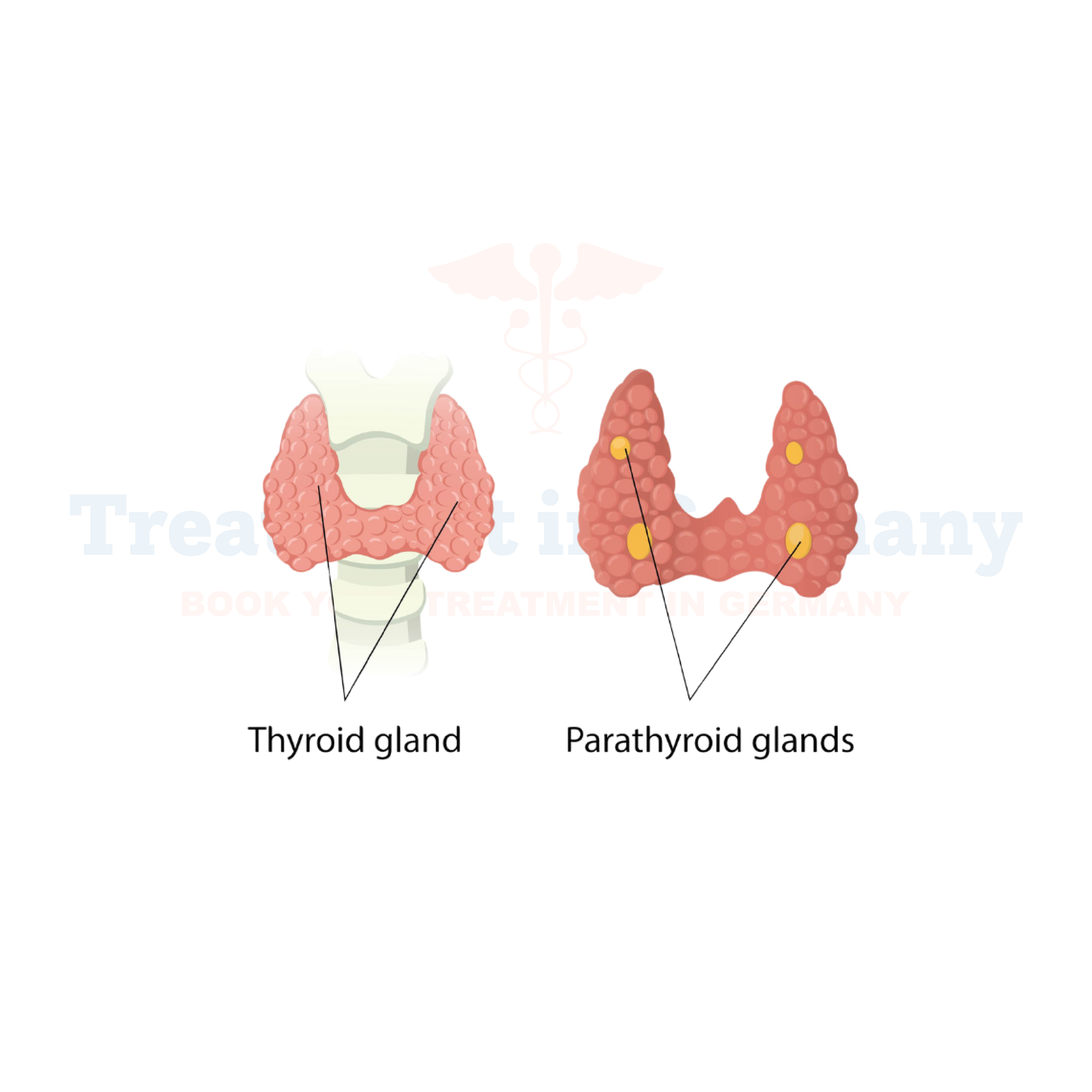
What is Hyperparathyroidism?
Hyperparathyroidism is a condition characterized by overactivity of the parathyroid glands, which are small glands located in the neck. These glands play a crucial role in regulating calcium levels in the body. When they produce too much parathyroid hormone (PTH), it leads to elevated levels of calcium in the blood, disrupting the balance of minerals in the body.
Side effects of Hyperparathyroidism:
Hyperparathyroidism can cause a range of symptoms, including:
How is Hyperparathyroidism diagnosed?
Diagnosing Hyperparathyroidism typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Common diagnostic tests include:
1. Blood Tests: Measuring calcium and PTH levels in the blood can help identify abnormalities associated with hyperparathyroidism.
2. Imaging Studies: Imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scans, or nuclear medicine scans may be used to locate abnormal parathyroid glands.
3. Bone Density Scan: A bone density scan (DEXA scan) may be performed to assess bone health and detect any signs of osteoporosis.
Potential Treatments of Hyperparathyroidism:
he treatment approach for hyperparathyroidism depends on the severity of the condition and its underlying cause. Common treatment options include:
1. Observation: In some cases, especially if the symptoms are mild or if the condition is asymptomatic, a watch-and-wait approach may be recommended, with regular monitoring of calcium levels.
2. Medication: Certain medications, such as calcimimetics, may be prescribed to help lower calcium levels and reduce the activity of the parathyroid glands.
3. Surgery: Surgical removal of the overactive parathyroid gland(s), known as parathyroidectomy, is often recommended for patients with symptomatic hyperparathyroidism or complications such as kidney stones or osteoporosis.
4. Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, maintaining adequate hydration, and following a balanced diet low in calcium and high in fiber can help manage hyperparathyroidism and reduce the risk of complications.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
