What is Hypersensitivity Vasculitis?
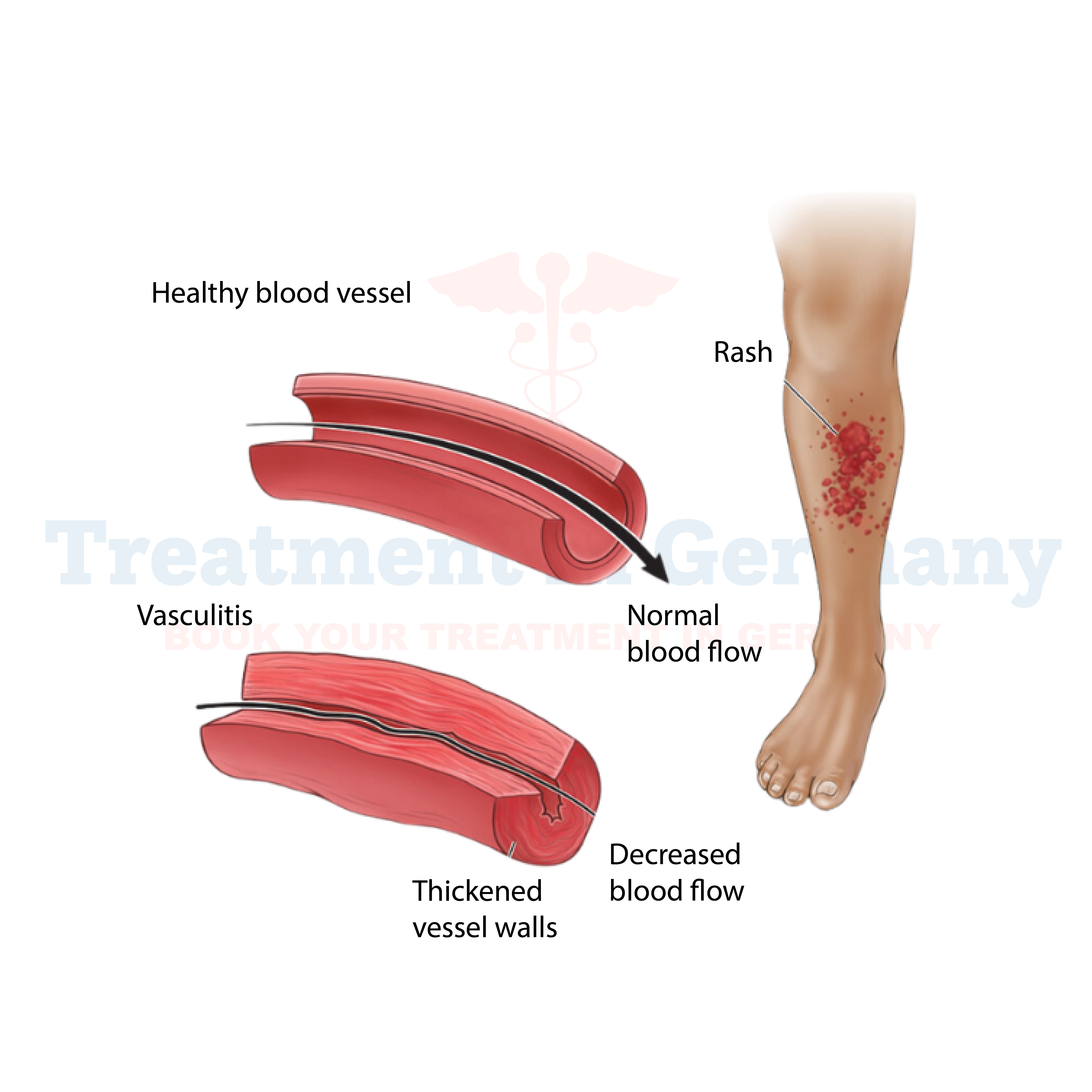
Hypersensitivity vasculitis, also known as leukocytoclastic vasculitis, is a condition where blood vessels become inflamed due to an immune reaction triggered by hypersensitivity to certain substances.
This inflammation primarily affects the small blood vessels in the skin, resulting in characteristic skin lesions that can range from small red dots (petechiae) to larger, palpable purpura (purple patches).
Side Effects of Hypersensitivity Vasculitis
The most common symptoms of hypersensitivity vasculitis include:
- Skin lesions such as rash, red spots, or purple patches
- Itching or burning sensation over affected skin areas
- Joint pain or swelling
- Fever
- Abdominal pain or gastrointestinal symptoms in severe cases
In rare instances, internal organs such as kidneys, lungs, or nerves may also be affected, leading to more serious complications.
How is Hypersensitivity Vasculitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of hypersensitivity vasculitis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, which may include:
- Skin Biopsy: A small sample of affected skin is taken and examined under a microscope to check for characteristic signs of vasculitis.
- Blood Tests: These may include tests to measure inflammation markers, assess organ function, and detect specific antibodies.
- Imaging Studies: Occasionally, imaging tests like ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI may be used to evaluate internal organs if there are signs of systemic involvement.
Potential Treatment of Hypersensitivity Vasculitis
Treatment of hypersensitivity vasculitis aims to relieve symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent complications. The approach may include:
- Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be used to relieve pain and inflammation. Corticosteroids are often prescribed to suppress the immune response and reduce inflammation in moderate to severe cases.
- Immunosuppressive Therapy: In cases where corticosteroids alone are insufficient, immunosuppressive medications such as methotrexate, azathioprine, or cyclophosphamide may be used.
- Treatment of Underlying Cause: Identifying and avoiding triggers that may have caused the hypersensitivity reaction is crucial. This may involve stopping certain medications or avoiding allergens or infections.
- Supportive Care: Symptomatic treatment such as pain relief, wound care for skin lesions, and management of associated conditions (e.g., kidney involvement) is also important.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
