What is Hypertension (Kidney-Related)?
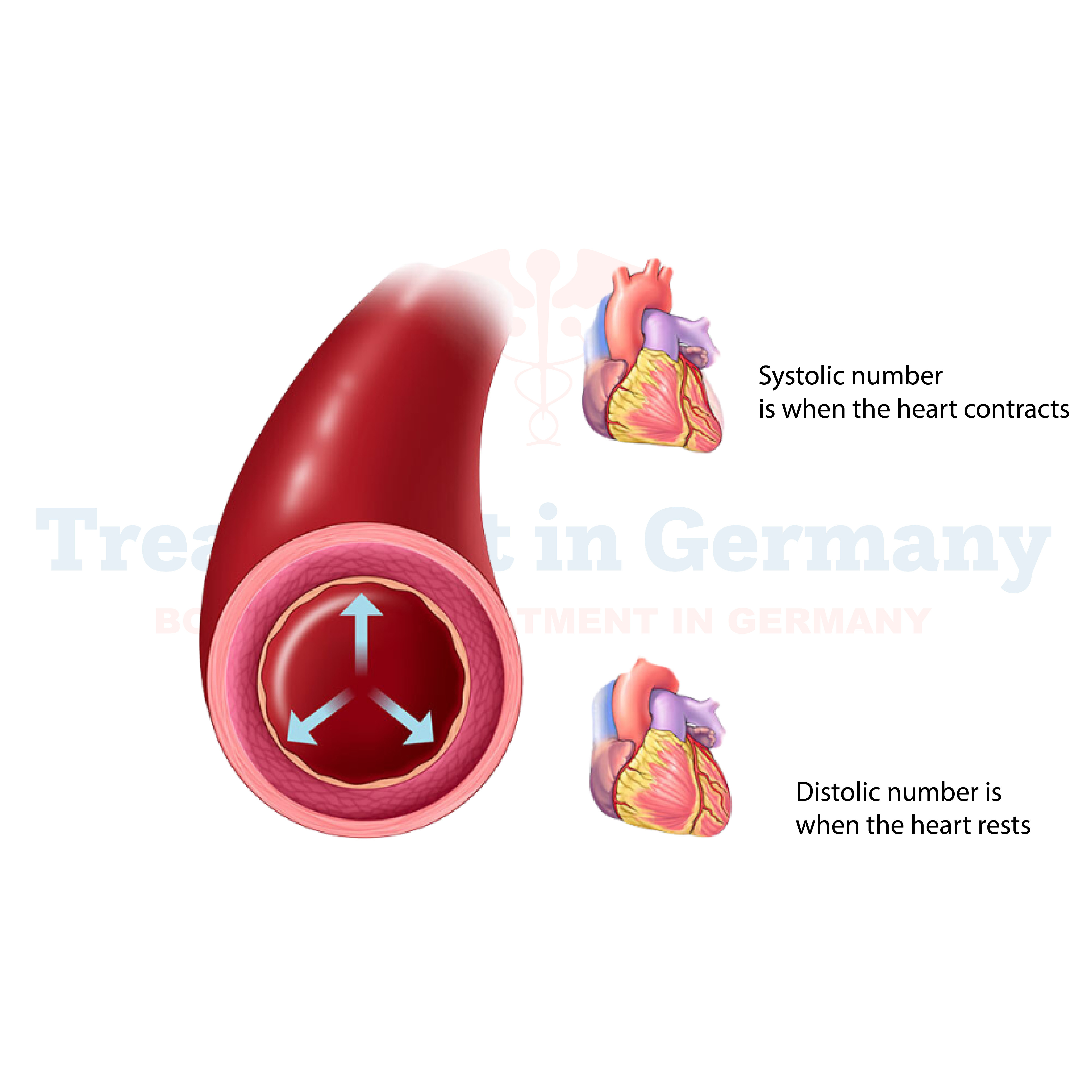
Hypertension, particularly when kidney-related, refers to elevated blood pressure that arises from underlying kidney issues. The kidneys play a crucial role in regulating blood pressure by managing fluid balance and producing hormones that influence blood pressure.
When kidneys are impaired, this delicate balance can be disrupted, leading to hypertension.
Side effects of Hypertension (Kidney-Related)
Hypertension, especially when associated with kidney problems, can have serious consequences on overall health. Some common side effects include:
- Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases: Hypertension strains the heart and blood vessels, increasing the risk of conditions like heart attacks, strokes, and heart failure.
- Kidney Damage: Chronic high blood pressure can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to kidney disease or even kidney failure over time.
- Vision Problems: Hypertension can cause damage to the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision impairment or even blindness if left untreated.
- Cognitive Decline: Long-term hypertension can impair cognitive function and increase the risk of dementia in older adults.
How is Hypertension (Kidney-Related) Diagnosed?
Diagnosing hypertension, especially when related to kidney issues, typically involves a series of tests and examinations. These may include:
- Blood Pressure Monitoring: Regular blood pressure measurements are essential to diagnose hypertension. High blood pressure readings over a period of time may indicate kidney-related hypertension.
- Kidney Function Tests: Blood and urine tests can assess how well the kidneys are functioning and detect any abnormalities that may be contributing to hypertension.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging studies such as ultrasounds or CT scans may be performed to evaluate the structure and function of the kidneys and detect any abnormalities that could be causing hypertension.
- Additional Tests: Depending on individual cases, additional tests such as electrocardiograms (ECGs) or echocardiograms may be recommended to assess heart function and identify any complications related to hypertension.
Potential Treatments of Hypertension (Kidney-Related)
Treatment for hypertension, especially when linked to kidney problems, aims to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of complications. Some potential treatments include:
- Medications: Various medications, including ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), diuretics, and calcium channel blockers, may be prescribed to help lower blood pressure and protect kidney function.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can play a significant role in managing hypertension. This may include maintaining a balanced diet low in sodium and saturated fats, regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol consumption, and quitting smoking.
- Kidney Disease Management: If hypertension has caused kidney damage or if kidney disease is contributing to high blood pressure, treatments to manage kidney disease, such as dialysis or kidney transplant, may be necessary.
- Regular Monitoring: Patients with hypertension, especially those with kidney-related issues, require regular monitoring of blood pressure and kidney function to ensure that treatment is effective and to identify any complications early on.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
