What is Hypoglycemia:
Hypoglycemia occurs when the body's blood sugar levels drop below the normal range, typically below 70 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). This can happen for various reasons, including excessive insulin production, inadequate food intake, excessive physical activity, or certain medications.
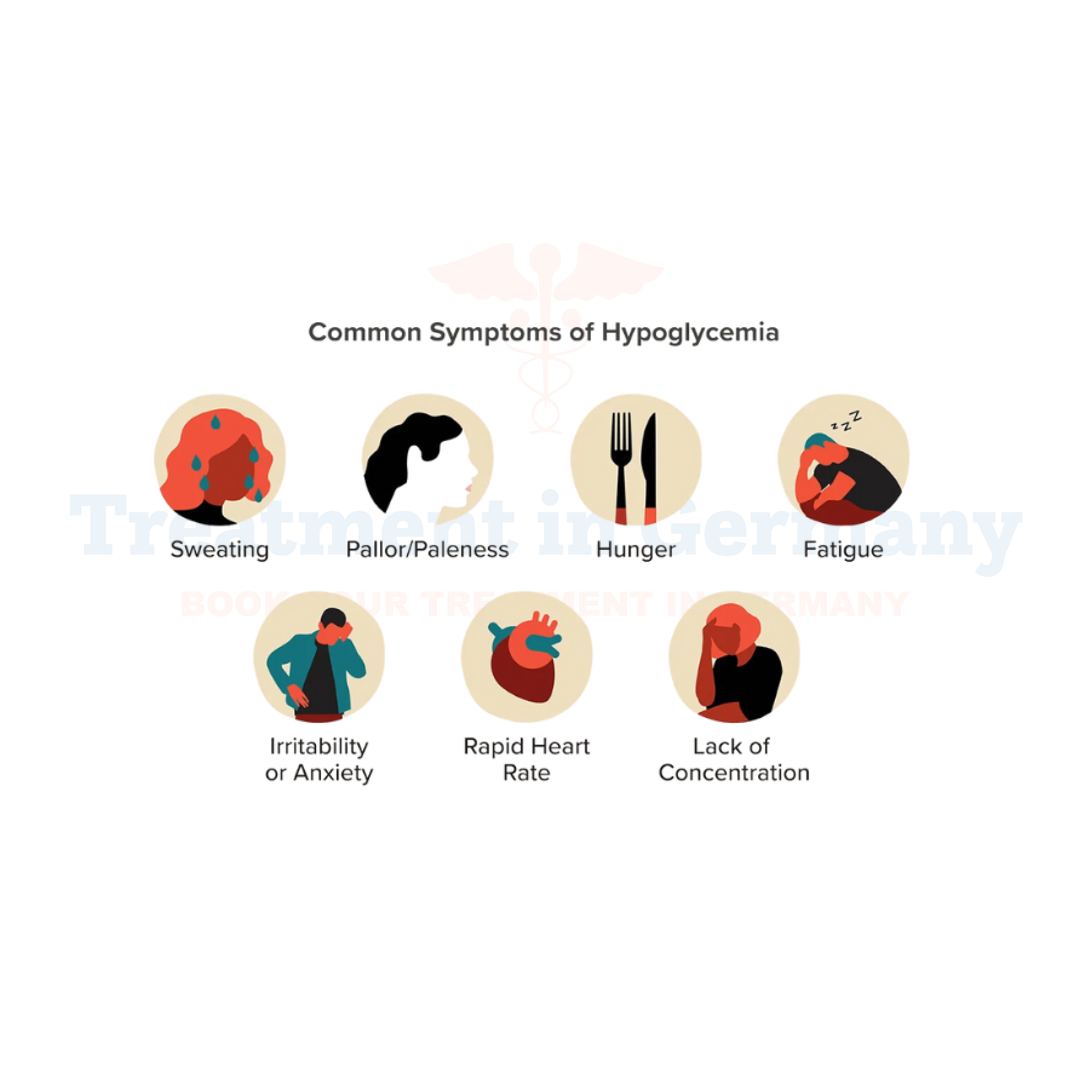
Side effects of Hypoglycemia:
The symptoms of hypoglycemia can vary depending on the severity and individual response. Common side effects may include:
How is Hypoglycemia diagnosed:
Diagnosing Hypoglycemia typically involves a combination of symptoms assessment, blood sugar testing, and identifying potential underlying causes.
Your healthcare provider may conduct a physical examination, review your medical history, and perform blood tests, including fasting blood sugar tests and glucose tolerance tests, to confirm hypoglycemia.
Potential treatments of Hypoglycemia:
Treatment strategies for hypoglycemia aim to restore blood sugar levels to normal and prevent future episodes. Depending on the severity and underlying cause of hypoglycemia, treatment options may include:
1. Dietary adjustments: Following a balanced diet rich in complex carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats can help stabilize blood sugar levels.
2. Medications: In some cases, your doctor may prescribe medications such as glucagon or diazoxide to manage hypoglycemia.
3. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): CGM devices can track your blood sugar levels in real-time, allowing for better management and prevention of hypoglycemic episodes.
4. Lifestyle modifications: Regular exercise, adequate sleep, stress management techniques, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption can help prevent hypoglycemia.
5. Diabetes management: For individuals with diabetes, closely monitoring blood sugar levels, adjusting insulin or other diabetes medications as needed, and working with a healthcare team to develop a personalized treatment plan is essential in managing hypoglycemia.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
