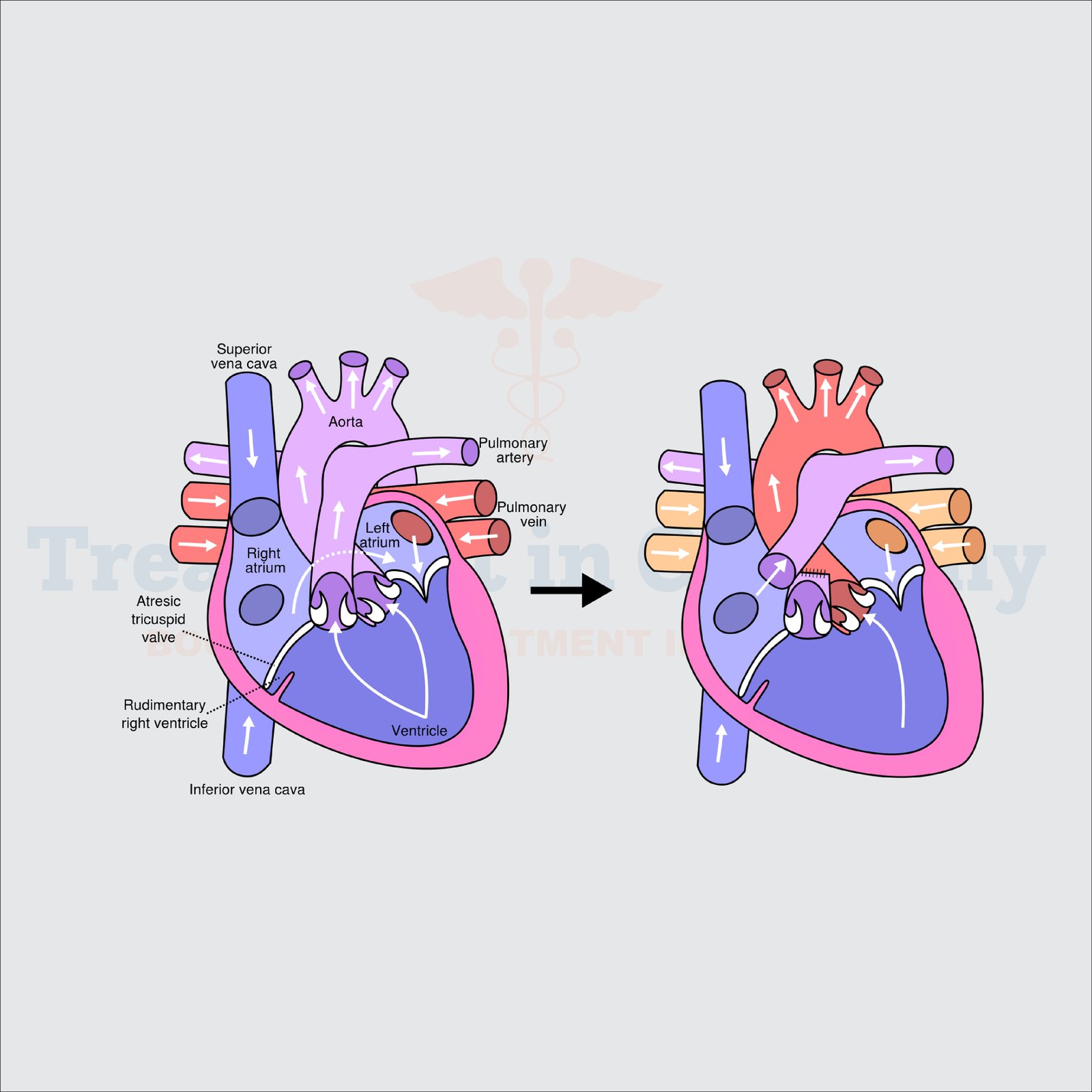
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) is a rare but serious congenital heart defect in which the left side of the heart is underdeveloped. This condition poses significant challenges for normal blood circulation, as the left ventricle, mitral valve, aortic valve, and aorta are either too small or improperly formed. Germany, renowned for its cutting-edge medical innovations, offers advanced treatment options for HLHS, ensuring better outcomes for affected individuals, particularly children.
HLHS is a congenital condition that develops during fetal growth. The underdevelopment of the left side of the heart makes it difficult for the heart to pump oxygenated blood to the body, leading to severe complications if untreated. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to managing this life-threatening condition.
While HLHS is generally categorized as a single condition, the severity and specific structural abnormalities can vary:
Risk Factors for Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
Although the exact causes of HLHS remain unknown, several factors may increase the risk of this condition:
Symptoms of Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
Symptoms of HLHS typically appear within the first few days of life and include:
Diagnosis and Diagnostic Tools
German hospitals are equipped with state-of-the-art technologies to ensure early and accurate diagnosis of HLHS:
Innovative Treatments for Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome in Germany
Germany is a leader in providing comprehensive and advanced treatment options for HLHS. Key therapies include:
Staged Surgical Interventions
Treatment often involves a series of surgeries to improve blood flow and heart function:
Heart Transplantation
For severe cases where surgeries are insufficient, a heart transplant may be the best option. Germany’s transplant centers offer world-class care with high success rates.
Stem Cell and Dendritic Cell Therapy
Emerging therapies like stem cell treatments and dendritic cell therapy aim to repair damaged heart tissue and improve overall heart function.
Hybrid Procedures
Combining surgical and catheter-based interventions, hybrid procedures are less invasive and reduce the risk of complications.
Medication Management
Complementary Therapies
Why Choose Treatment in Germany?
Germany’s healthcare system is globally recognized for its excellence in treating complex conditions like HLHS. Here’s why patients choose Germany:
Lifestyle Solutions
Effective management of HLHS often requires a multidisciplinary approach:
Conclusion
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome is a challenging condition, but advancements in medical science have significantly improved outcomes for affected individuals. Germany’s expertise in treating HLHS through innovative therapies, state-of-the-art facilities, and dedicated specialists makes it a leading destination for families seeking comprehensive care.
Choosing treatment in Germany ensures access to the best medical technologies, holistic care programs, and highly skilled professionals. If your child is diagnosed with HLHS, exploring treatment options in Germany could provide a new lease on life and a brighter future.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
