What is Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis?
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic and progressive lung disease characterized by the thickening and stiffening of lung tissues.
The exact cause of IPF is unknown, hence the term "idiopathic." Over time, this condition leads to the formation of scar tissue (fibrosis) in the lungs, which hinders their ability to efficiently transport oxygen into the bloodstream.
Side Effects of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
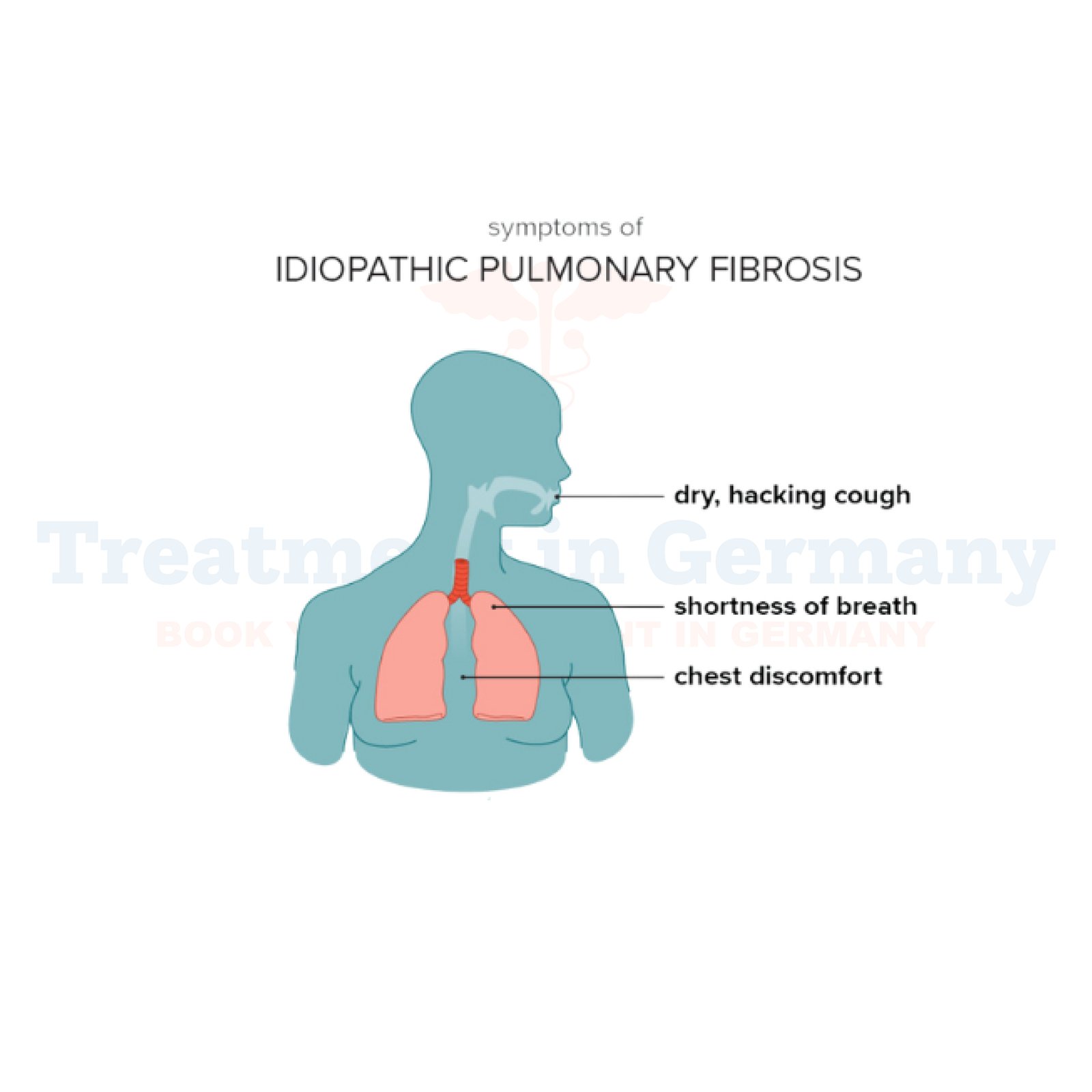
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis can significantly impact daily life and overall health. Common symptoms include persistent dry cough, shortness of breath (particularly during physical activity), fatigue, unexplained weight loss, and discomfort in the chest.
As the disease progresses, patients may experience increasing difficulty in performing routine activities and may require supplemental oxygen for breathing support.
How is Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis often involves a series of steps to rule out other potential causes of similar symptoms. Medical professionals typically begin with a thorough medical history and physical examination.
Diagnostic tests such as pulmonary function tests (PFTs), imaging studies (like high-resolution CT scans), and sometimes lung biopsies are performed to confirm the presence of IPF and assess its severity.
Potential Treatments for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
While there is currently no cure for IPF, various treatment approaches aim to manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve quality of life. Treatment plans may include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
