What is Innominate Artery Stenosis?
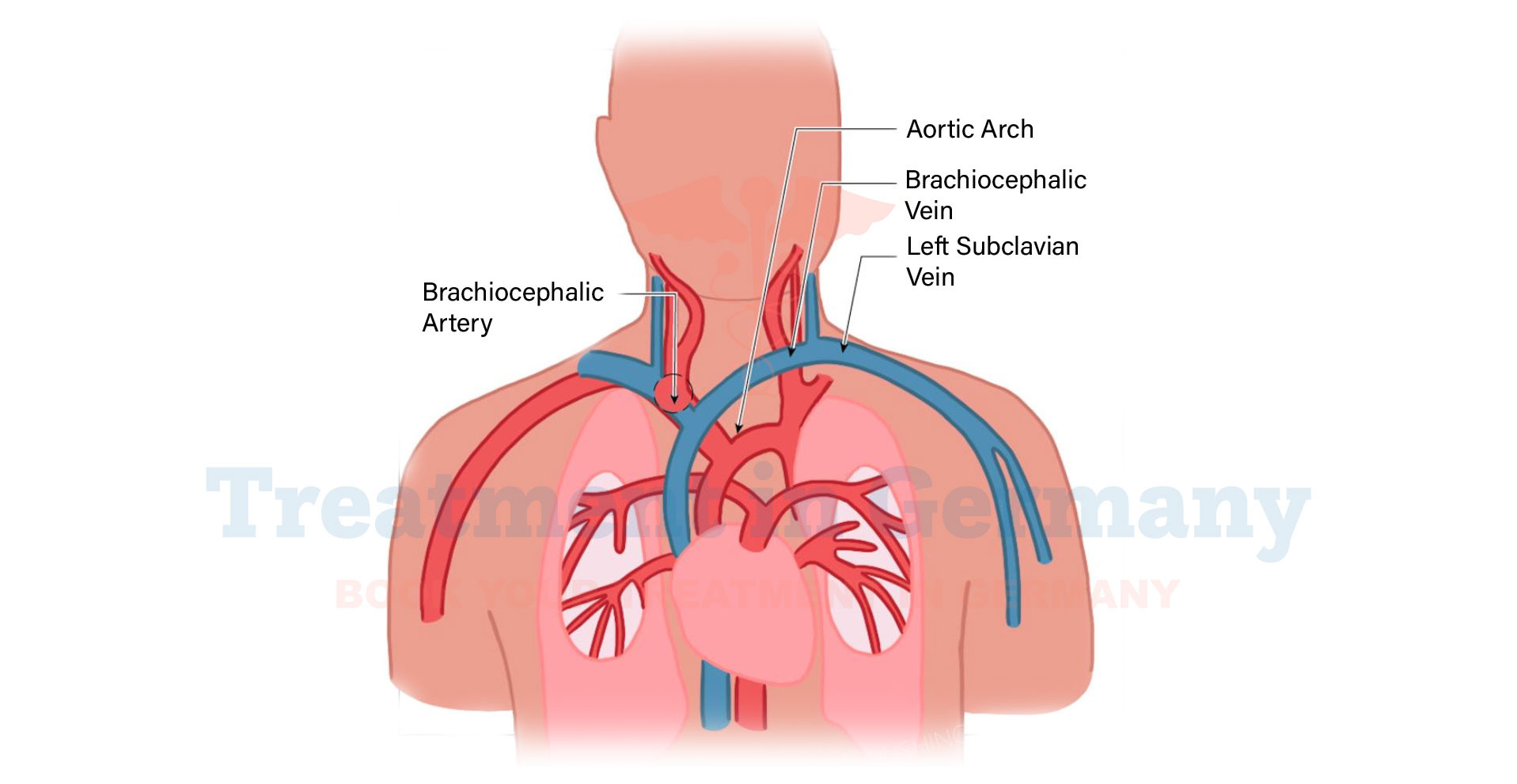
Innominate artery stenosis refers to a narrowing or blockage in the innominate artery, also known as the brachiocephalic artery.
This artery is crucial as it branches off the aortic arch and supplies blood to the right common carotid artery, right subclavian artery, and the right side of the head and neck.
Side Effects of Innominate Artery Stenosis
When the innominate artery becomes narrowed due to stenosis, it can lead to various health complications. Patients may experience symptoms such as:
If left untreated, severe cases of innominate artery stenosis can lead to stroke or heart attack.
How is Innominate Artery Stenosis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing innominate artery stenosis typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and imaging tests such as:
These diagnostic tests help healthcare providers accurately assess the extent and location of the stenosis.
Potential Treatment of Innominate Artery Stenosis
Treatment options for innominate artery stenosis depend on the severity of the condition and the patient's overall health. Possible treatments include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
