What is Interstitial Cystitis (Painful Bladder Syndrome)?
Interstitial Cystitis (IC), also known as Painful Bladder Syndrome (PBS), is a chronic condition characterized by persistent bladder pain, discomfort, and pressure. Unlike typical urinary tract infections, IC is not caused by bacteria but rather involves inflammation and irritation of the bladder wall.
Symptoms may vary from person to person but commonly include frequent urination, a strong urge to urinate, and pain in the pelvic area. The exact cause of IC is still unclear, but it may involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors.
Side Effects of Interstitial Cystitis (Painful Bladder Syndrome)
The symptoms and side effects of Interstitial Cystitis can significantly impact daily life and overall well-being. Common side effects include:
- Pelvic Pain: Persistent pain or discomfort in the pelvic region, which may vary in intensity.
- Frequent Urination: An urgent need to urinate often, sometimes as frequently as every 15 minutes.
- Painful Urination: Discomfort or pain during urination.
- Sexual Dysfunction: Pain during sexual intercourse or discomfort in the genital area.
- Sleep Disturbances: Frequent nighttime urination can disrupt sleep, leading to fatigue.
These symptoms can affect mental health, contributing to stress, anxiety, and depression due to the chronic nature of the condition and its impact on daily activities.
How is Interstitial Cystitis (Painful Bladder Syndrome) Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Interstitial Cystitis involves a comprehensive approach, as no single test can confirm the condition. The diagnostic process typically includes:
- Medical History and Symptom Review: Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, their duration, and their impact on your life.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination, including a pelvic exam, may be conducted to assess tenderness and other related issues.
- Urinalysis and Urine Culture: These tests rule out urinary tract infections and other potential causes of symptoms.
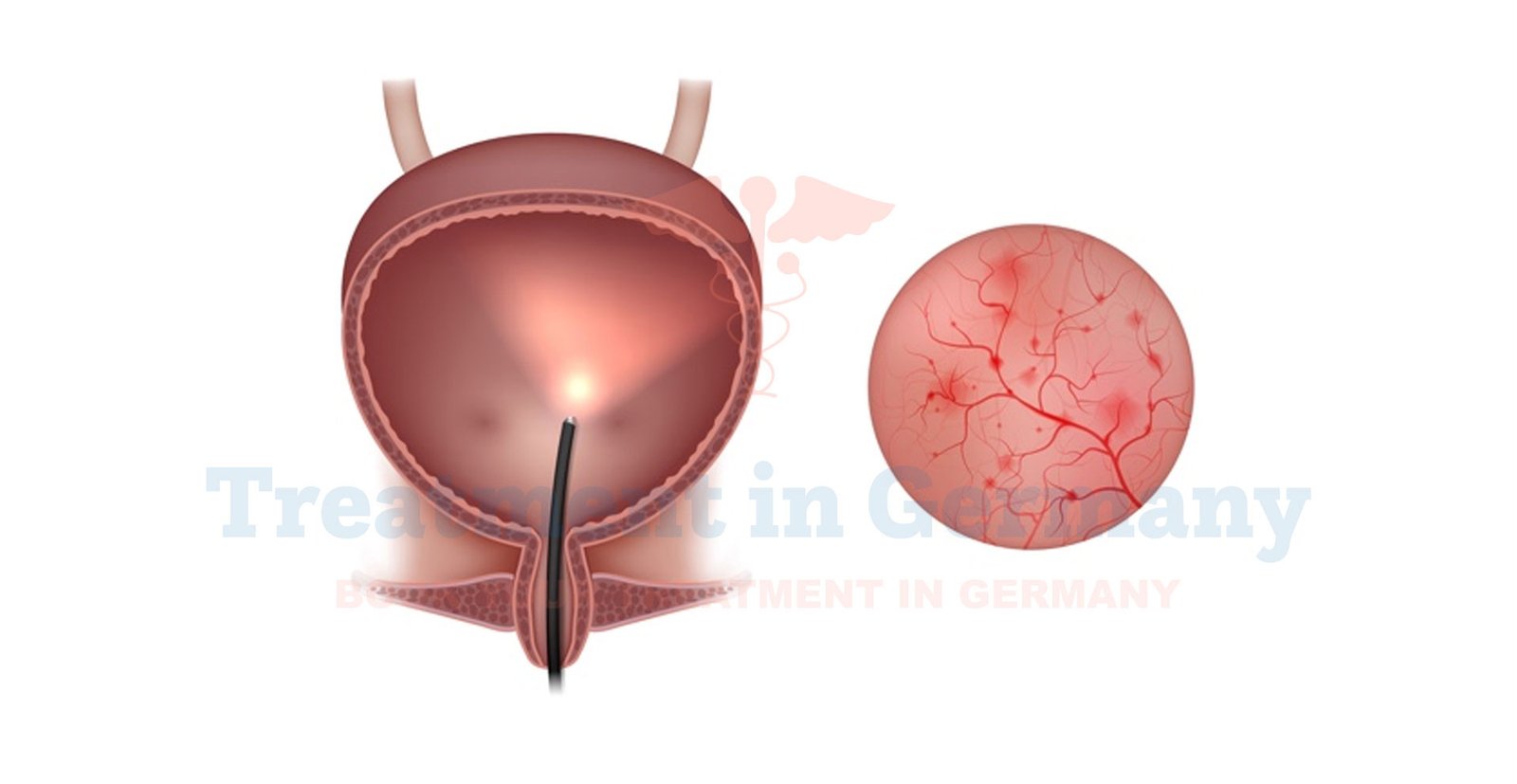
- Cystoscopy: A procedure where a thin, flexible tube with a camera (cystoscope) is inserted into the bladder to inspect the bladder lining and check for abnormalities.
- Bladder Biopsy: In some cases, a small sample of bladder tissue may be taken during cystoscopy to rule out other conditions.
Potential Treatment of Interstitial Cystitis (Painful Bladder Syndrome)
Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis is aimed at relieving symptoms and improving quality of life. Approaches vary depending on the severity of symptoms and individual response. Common treatment options include:
- Medications: Pain relievers, antihistamines, and tricyclic antidepressants can help manage symptoms. Bladder instillations, where medication is directly applied to the bladder, may also be used.
- Physical Therapy: Pelvic floor physical therapy can help alleviate pain and improve bladder function.
- Dietary Changes: Identifying and avoiding foods and beverages that may irritate the bladder, such as caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods, can be beneficial.
- Bladder Training: Techniques to gradually increase the time between urinations and reduce urgency.
- Surgical Options: In severe cases, surgical interventions such as bladder augmentation or, rarely, bladder removal, might be considered.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
