Intracerebral Hemorrhage Treatment in Germany
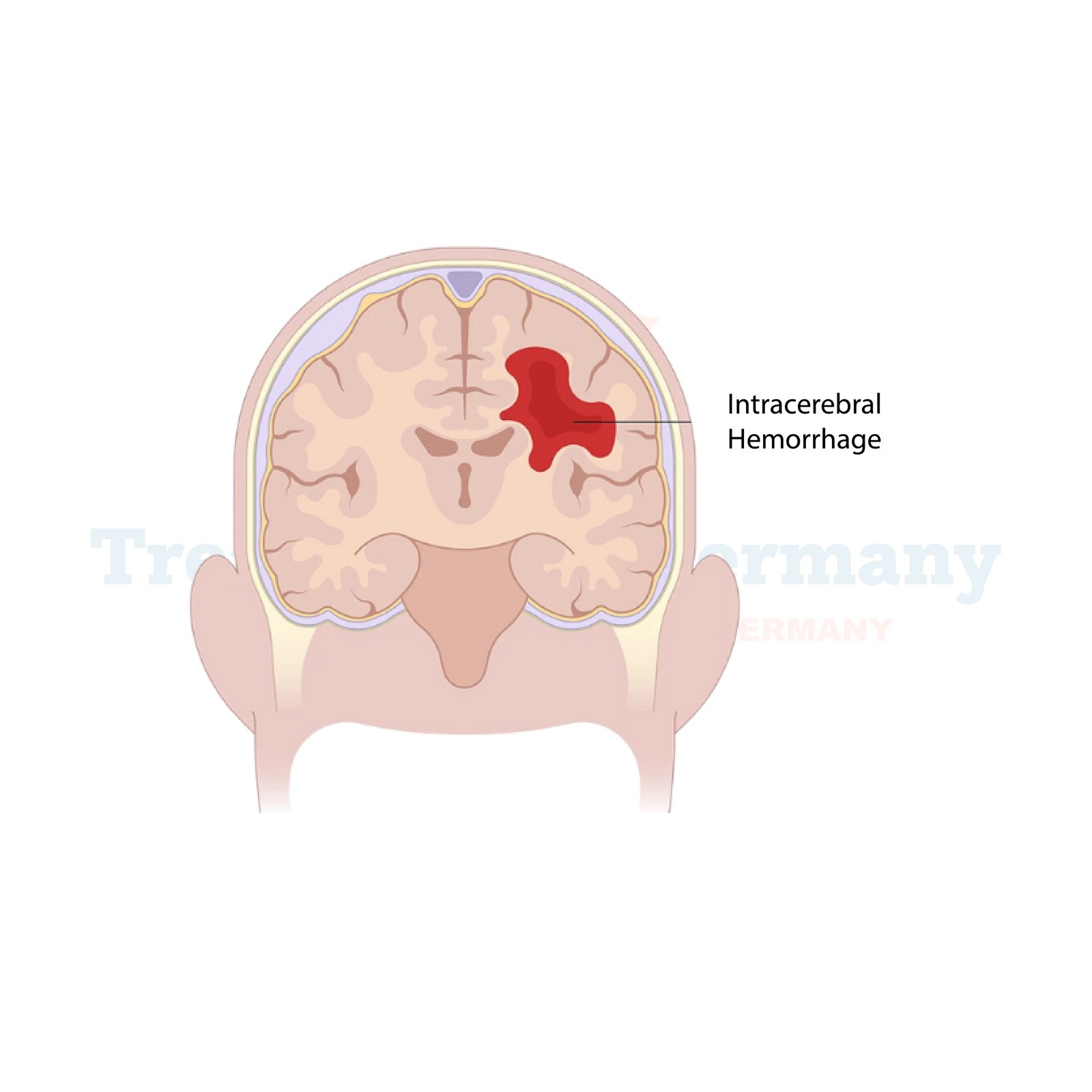
Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) is a severe medical condition involving bleeding directly into the brain tissue, causing significant neurological damage. It accounts for approximately 10-20% of all strokes and is considered a medical emergency requiring immediate intervention. Advanced treatment facilities in Germany provide state-of-the-art care, improving outcomes for patients with this life-threatening condition.
An intracerebral hemorrhage occurs when a blood vessel ruptures within the brain, leading to bleeding and increased pressure in the surrounding brain tissue. This can result in damage to brain cells and potentially life-threatening complications. The condition often requires a combination of surgical and medical treatments to stabilize the patient and manage long-term effects.
Causes of Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Several factors can lead to intracerebral hemorrhage, including:
- Hypertension: High blood pressure is the most common cause, weakening blood vessel walls over time.
- Trauma: Head injuries from accidents or falls can rupture blood vessels.
- Aneurysms and Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs): Structural abnormalities in blood vessels increase the risk of rupture.
- Blood Thinners: Medications such as warfarin or antiplatelet drugs can increase bleeding risk.
- Amyloid Angiopathy: A condition where amyloid protein deposits in blood vessels, causing fragility.
- Brain Tumors: Certain tumors can lead to bleeding into brain tissue.
- Coagulation Disorders: Conditions affecting blood clotting, such as hemophilia or liver disease.
Symptoms of Intracerebral Hemorrhage
The symptoms of ICH often develop suddenly and may include:
- Severe headache, often described as the "worst headache of my life."
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Sudden weakness or numbness, typically on one side of the body.
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech.
- Loss of balance or coordination.
- Vision problems.
- Altered consciousness or confusion.
- Seizures in some cases.
Diagnosis and Diagnostic Tools
Accurate and prompt diagnosis is crucial for effective management of intracerebral hemorrhage. Germany is equipped with advanced diagnostic tools to identify and assess the condition, including:
- CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: The fastest and most effective method to detect bleeding in the brain.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides detailed imaging to assess the extent of bleeding and brain tissue damage.
- Angiography: Identifies abnormalities such as aneurysms or AVMs.
- Blood Tests: Assess clotting factors, blood cell counts, and underlying medical conditions.
Treatment Options for Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Germany
Germany’s healthcare system offers a comprehensive approach to treating ICH, combining immediate medical care with advanced surgical and rehabilitation options.
Emergency Medical Care
- Stabilization: Controlling blood pressure and managing breathing to prevent further complications.
- Medications: Includes drugs to reduce swelling (osmotic agents), manage seizures, or reverse anticoagulation if the patient is on blood thinners.
Surgical Interventions
- Craniotomy: An open surgery to remove blood clots and relieve pressure on the brain.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: Germany is a pioneer in minimally invasive techniques to evacuate hematomas, reducing recovery time and complications.
- Endovascular Procedures: In cases of aneurysms or AVMs, embolization or coiling is performed to prevent further bleeding.
Rehabilitation and Long-Term Management
- Physical Therapy: Restores motor function and mobility.
- Occupational Therapy: Focuses on daily living activities and regaining independence.
- Speech Therapy: Addresses language and communication difficulties.
- Psychological Support: Helps patients and families cope with emotional challenges.
Innovative Therapies in Germany
Germany is at the forefront of medical research and offers innovative treatment options for intracerebral hemorrhage:
- Stem Cell Therapy: Investigated for its potential to regenerate damaged brain tissue and improve neurological recovery.
- Dendritic Cell Therapy: Although primarily used in cancer and autoimmune conditions, ongoing research explores its role in modulating inflammation in brain injuries.
- Advanced Neurosurgical Techniques: Cutting-edge robotic-assisted surgeries ensure precision and better outcomes.
- Neurorehabilitation Centers: Germany’s specialized centers offer holistic recovery programs tailored to each patient.
Why Choose Germany for Treatment of Intracerebral Hemorrhage?
Germany is a top destination for the treatment of life-threatening neurological conditions due to its:
- State-of-the-Art Hospitals: Equipped with advanced imaging and surgical technologies.
- Expert Neurologists and Neurosurgeons: Highly trained specialists with extensive experience.
- Multidisciplinary Teams: Providing personalized care plans for optimal outcomes.
- Focus on Innovation: Access to clinical trials and cutting-edge therapies.
- Comprehensive Rehabilitation Services: World-class facilities for long-term recovery.
Prevention and Risk Reduction
While not all cases of ICH can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk:
- Blood Pressure Control: Regular monitoring and medication to manage hypertension.
- Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking or excessive alcohol consumption.
- Managing Medical Conditions: Proper management of diabetes, high cholesterol, and other chronic conditions.
- Regular Check-ups: Screening for aneurysms or AVMs in high-risk individuals.
- Safety Measures: Wearing helmets during activities with a risk of head injury and fall-proofing homes for the elderly.
Conclusion
Intracerebral hemorrhage is a life-threatening condition requiring prompt and specialized care. Germany’s world-class healthcare system offers advanced diagnostic tools, cutting-edge treatment options, and comprehensive rehabilitation programs to ensure the best possible outcomes. Early diagnosis, effective management, and lifestyle modifications can help patients navigate the challenges of ICH and improve their quality of life.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
