What is Jejunal Diverticulosis?
Jejunal diverticulosis is a condition characterized by the presence of diverticula—small, bulging pouches—forming in the jejunum, which is a part of the small intestine.
These pouches develop through weak spots in the intestinal wall and can vary in size. While the exact cause of diverticulosis isn’t always clear, it’s thought to be related to increased pressure within the intestines, often exacerbated by factors such as diet and aging.
Side Effects of Jejunal Diverticulosis
Many people with jejunal diverticulosis may not experience any symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they can include:
- Abdominal Pain: Discomfort or pain in the upper abdomen, which may be intermittent or constant.
- Bloating: A feeling of fullness or swelling in the abdomen.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Digestive issues that may accompany the condition.
- Changes in Bowel Movements: Alterations in stool frequency or consistency can sometimes occur.
In more severe cases, complications such as diverticulitis (inflammation of the diverticula), bleeding, or intestinal obstruction can arise, leading to additional symptoms like severe abdominal pain, fever, or rectal bleeding.
How is Jejunal Diverticulosis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing jejunal diverticulosis typically involves a combination of the following methods:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Your doctor will review your symptoms and medical history and perform a physical exam to assess your condition.
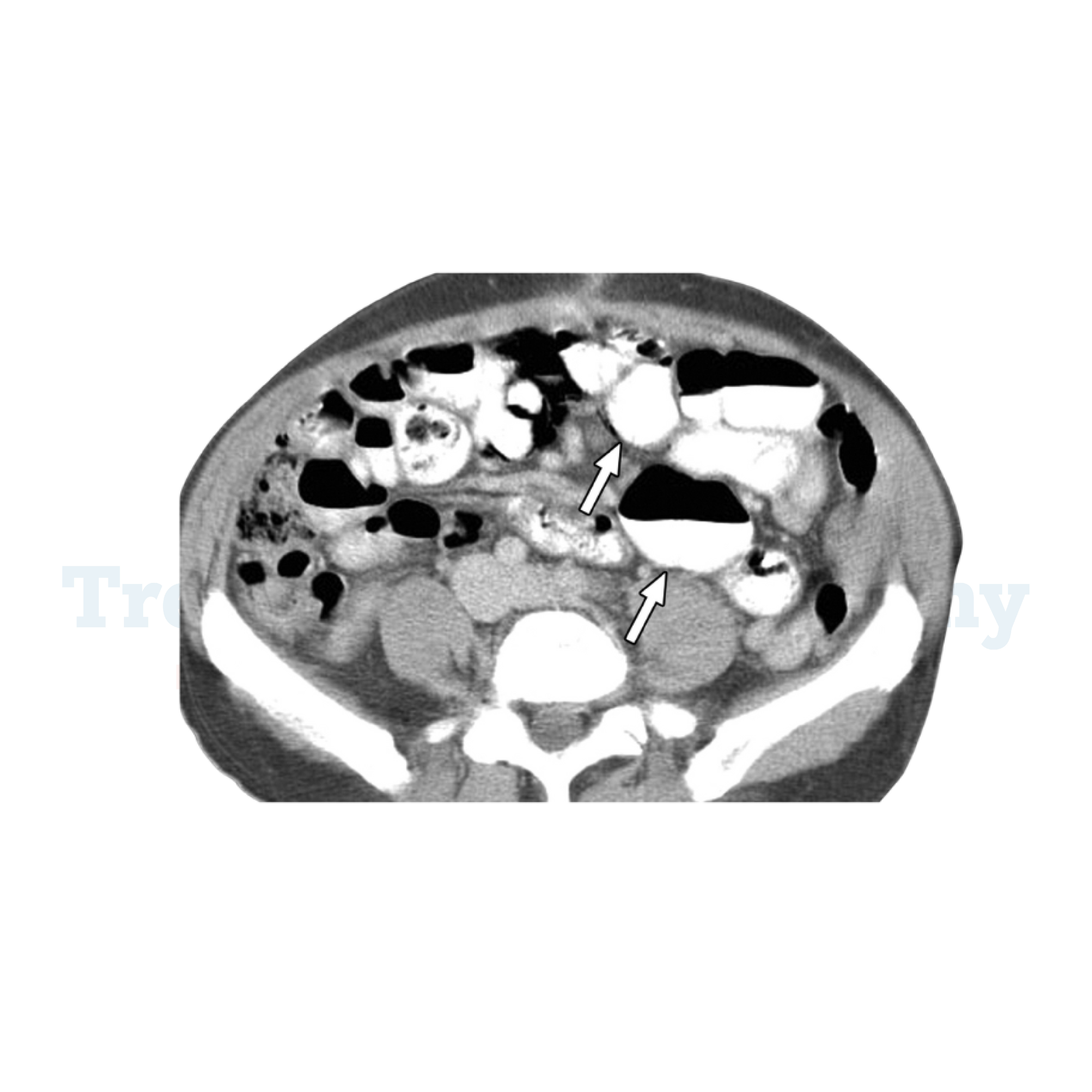
- Imaging Studies: To visualize the diverticula, imaging tests such as a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis are commonly used. These scans can help identify the presence and extent of diverticula.
- Endoscopy: In some cases, an endoscopic procedure may be performed to directly view the inside of the small intestine and confirm the diagnosis.
Potential Treatment of Jejunal Diverticulosis
The treatment approach for jejunal diverticulosis largely depends on the presence and severity of symptoms:
- Dietary Changes: If you are asymptomatic, dietary adjustments may be recommended. A high-fiber diet can help reduce the risk of complications by easing bowel movements and reducing pressure within the intestines.
- Medications: For those with symptoms, medications may be prescribed to manage pain and address any digestive issues. In cases of diverticulitis, antibiotics may be necessary.
- Surgical Intervention: If complications such as severe diverticulitis, bleeding, or obstruction occur, surgery may be required. The procedure typically involves removing the affected portion of the jejunum.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
