What is Juvenile Arthritis?
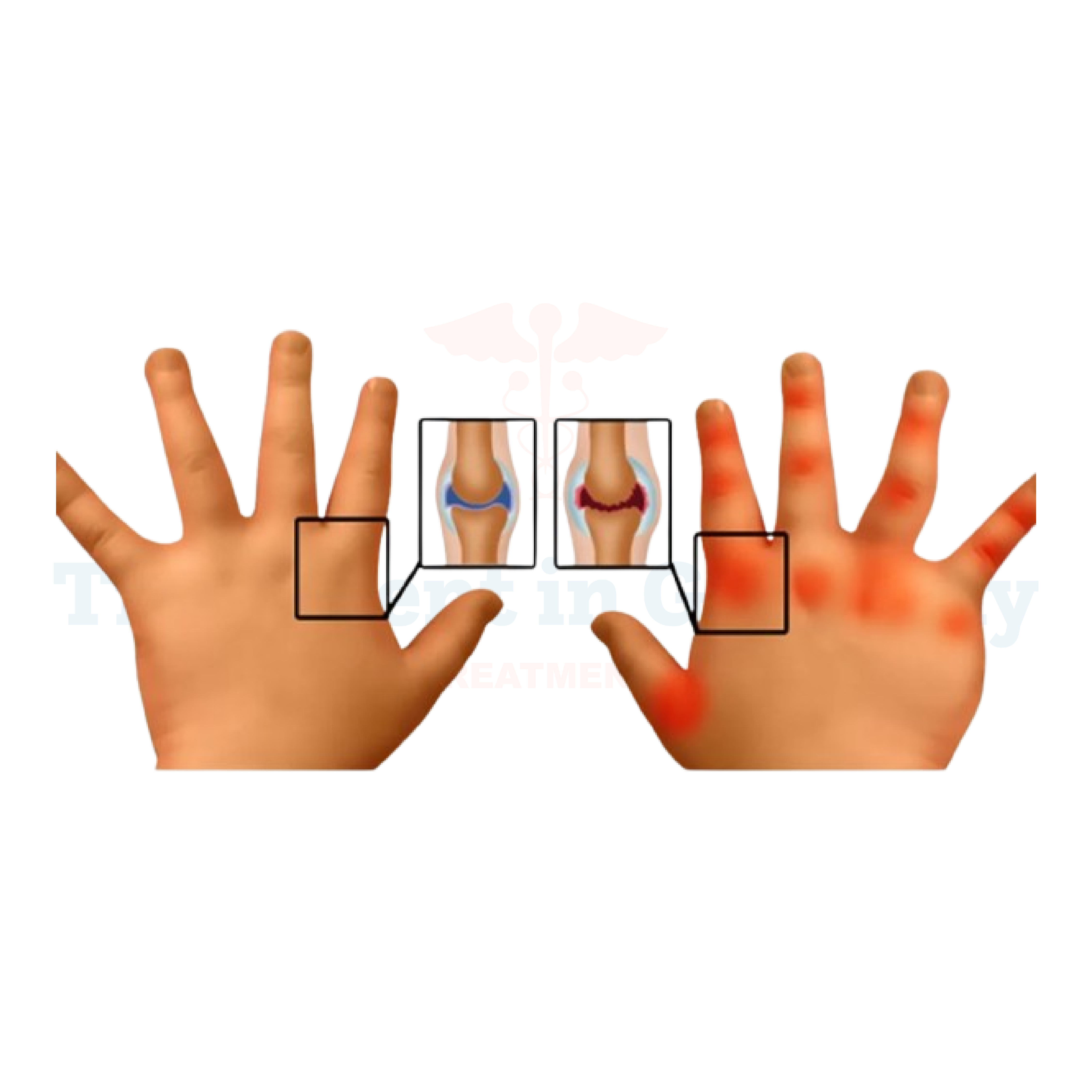
Juvenile Arthritis (JA), also known as pediatric rheumatic disease, refers to a group of autoimmune and inflammatory conditions that can develop in children under the age of 16.
This condition causes joint inflammation, stiffness, and pain, which can significantly impact a child's daily life and mobility. It is important to note that JA is not a single disease but encompasses several types, each with its own distinct features.
Side Effects of Juvenile Arthritis
The symptoms of Juvenile Arthritis extend beyond joint pain and stiffness. Children affected by JA may experience fatigue, fever, rash, and difficulties with growth and development.
In some cases, JA can also affect the eyes, skin, and internal organs, leading to complications if not properly managed.
How is Juvenile Arthritis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Juvenile Arthritis involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional, typically a pediatric rheumatologist.
The process may include a detailed medical history, physical examination, blood tests, imaging studies (such as X-rays or MRI), and possibly joint fluid analysis. Early diagnosis is crucial to prevent long-term joint damage and to manage symptoms effectively.
Potential Treatment of Juvenile Arthritis
Treatment for Juvenile Arthritis aims to relieve symptoms, prevent joint damage, and improve quality of life. Depending on the type and severity of JA, treatment strategies may include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
