What is Lactose Intolerance:
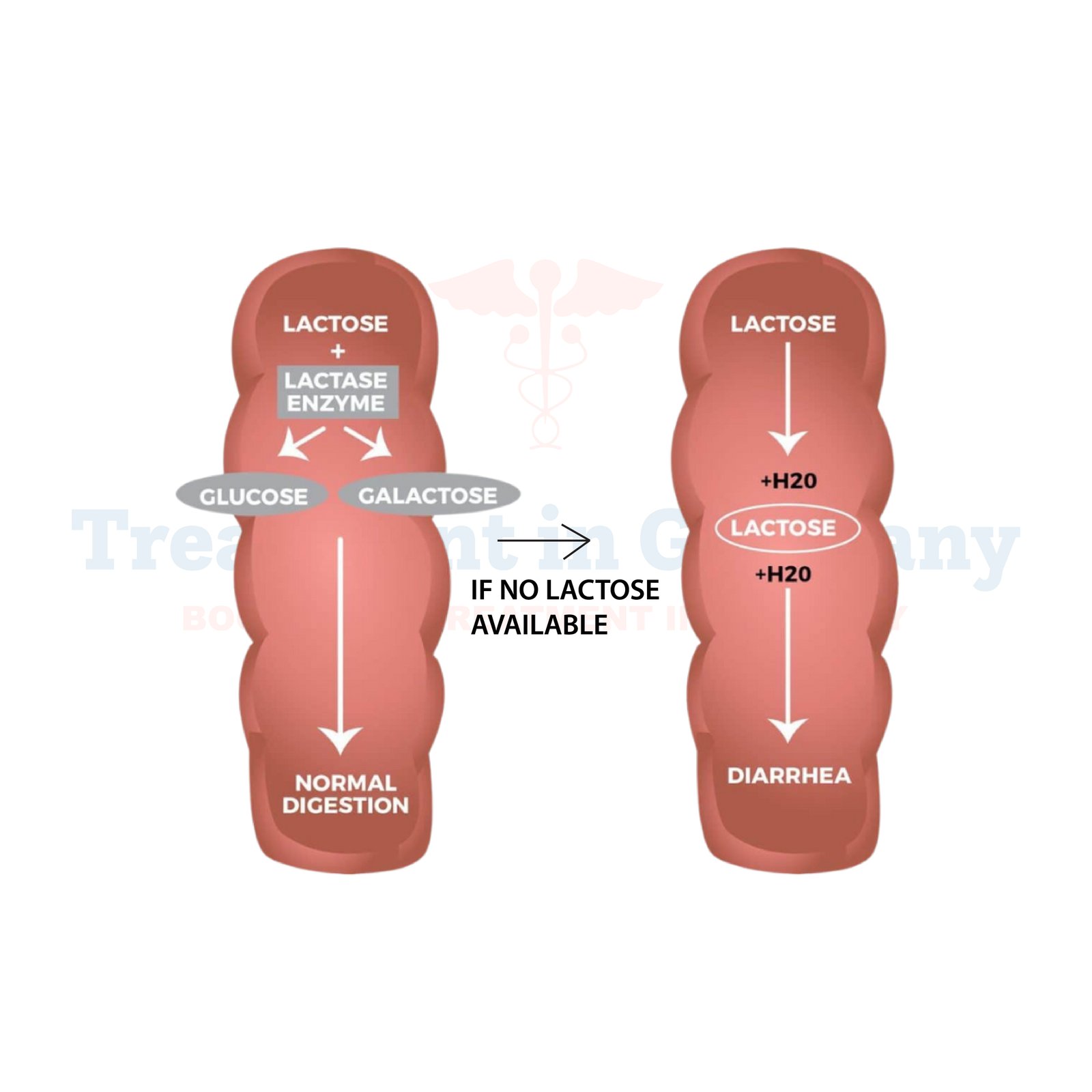
Lactose intolerance is a common digestive disorder characterized by the body's inability to digest lactose, a type of sugar found in milk and dairy products.
This occurs due to a deficiency of lactase, the enzyme responsible for breaking down lactose in the small intestine. Without enough lactase, lactose remains undigested and can cause various uncomfortable symptoms.
Side effects of Lactose Intolerance:
The symptoms of lactose intolerance can vary in severity from person to person but commonly include:
- Bloating: Excess gas production in the digestive system can lead to a feeling of fullness and discomfort.
- Abdominal Pain: Cramping or sharp pains in the abdominal area may occur, particularly after consuming lactose-containing foods.
- Diarrhea: Undigested lactose can draw water into the colon, resulting in loose stools and frequent bowel movements.
- Nausea: Some individuals may experience feelings of queasiness or an upset stomach after consuming lactose.
- Flatulence: Increased gas production in the intestines can lead to excessive flatulence, often accompanied by an unpleasant odor.
How is Lactose Intolerance diagnosed?:
In Germany, the Diagnosis of lactose intolerance typically involves a combination of medical history assessment, physical examination, and diagnostic tests.
Your healthcare provider may ask about your symptoms, dietary habits, and family history of lactose intolerance. Additionally, they may recommend one or more of the following tests:
- Lactose Tolerance Test: This test involves consuming a lactose-containing beverage and measuring blood glucose levels over several hours to determine how well your body digests lactose.
- Hydrogen Breath Test: After consuming a lactose solution, breath samples are collected at regular intervals to measure hydrogen levels, which increase when undigested lactose ferments in the colon.
- Stool Acidity Test: In infants and young children, a stool sample may be analyzed for acidity levels, which can indicate lactose malabsorption.
Potential treatments of Lactose Intolerance:
While there is no cure for lactose intolerance, several strategies can help manage symptoms effectively:
- Dietary Modifications: Avoiding or reducing consumption of lactose-containing foods and beverages, such as milk, cheese, and ice cream, can alleviate symptoms. Many lactose-free or lactose-reduced alternatives are available in Germany, including lactose-free milk and dairy-free products made from soy, almond, or coconut.
- Lactase Supplements: Over-the-counter lactase enzyme supplements can be taken before consuming lactose-containing foods to help digest lactose more effectively.
- Probiotics: Some studies suggest that certain probiotic strains may help improve lactose digestion and reduce symptoms of lactose intolerance by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
- Gradual Reintroduction: Some individuals may be able to gradually reintroduce small amounts of lactose-containing foods into their diet over time without experiencing significant symptoms.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
