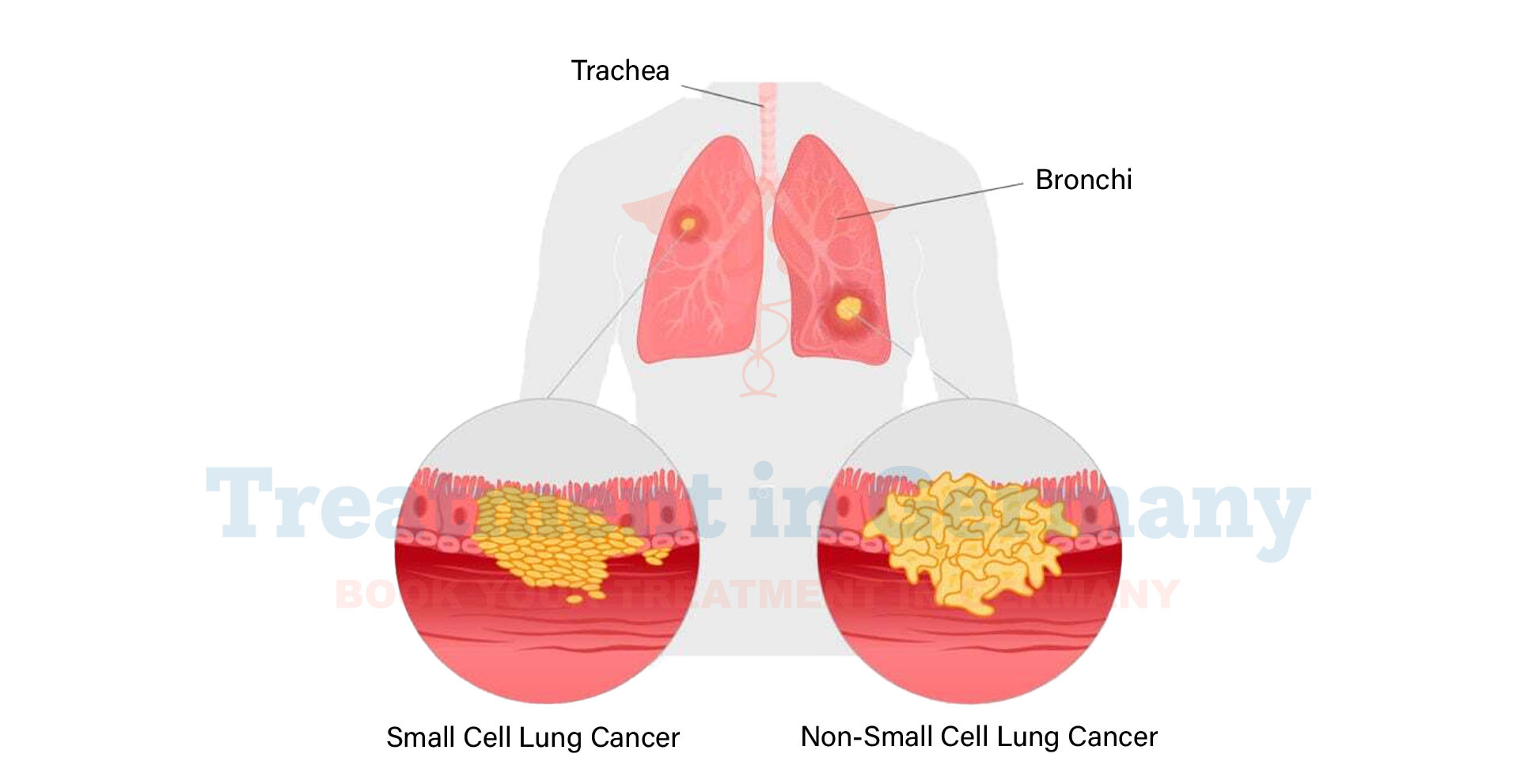
What is Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell and Small Cell)?
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the lungs. There are two main types: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC):
- NSCLC is the most common type, accounting for about 85% of all lung cancers.
- It usually grows and spreads more slowly than small cell lung cancer.
- There are different subtypes of NSCLC, such as adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC):
- SCLC accounts for about 10-15% of all lung cancers.
- It tends to grow more quickly and is more likely to spread to other parts of the body early on.
Side Effects of Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell and Small Cell)
The side effects of lung cancer can vary depending on the type of cancer, its stage, and the treatment being used. Common side effects may include:
- Fatigue: Feeling tired and lacking energy.
- Coughing: Persistent or worsening cough, sometimes with blood.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity.
- Chest Pain: Pain or discomfort in the chest area.
- Weight Loss: Unintentional weight loss.
- Hoarseness: Changes in the voice.
- Bone Pain: Pain in the bones, if the cancer has spread.
How is Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell and Small Cell) Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of lung cancer usually involves several steps:
- Imaging Tests: Such as chest X-rays, CT scans, or PET scans to detect any abnormalities in the lungs.
- Biopsy: A sample of tissue is taken from the lung to determine if cancer cells are present and to identify the type of lung cancer (NSCLC or SCLC).
- Staging: Determining the extent of the cancer (whether it has spread and to what parts of the body) helps guide treatment decisions.
Potential Treatment of Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell and Small Cell)
Treatment options for lung cancer depend on several factors including the type of lung cancer, its stage, and the overall health of the patient. Common treatments include:
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC):
- Surgery: If the cancer is in an early stage and confined to the lung.
- Radiation Therapy: Uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs that kill cancer cells or stop them from growing.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs that target specific abnormalities in cancer cells.
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC):
- Chemotherapy: Main treatment for SCLC, often combined with radiation therapy.
- Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation (PCI): Radiation therapy to the brain to prevent or delay spread of cancer to the brain.
- Immunotherapy: Drugs that help the body's immune system recognize and attack cancer cells.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
