Understanding Macroglobulinemia (Waldenström's Macroglobulinemia)
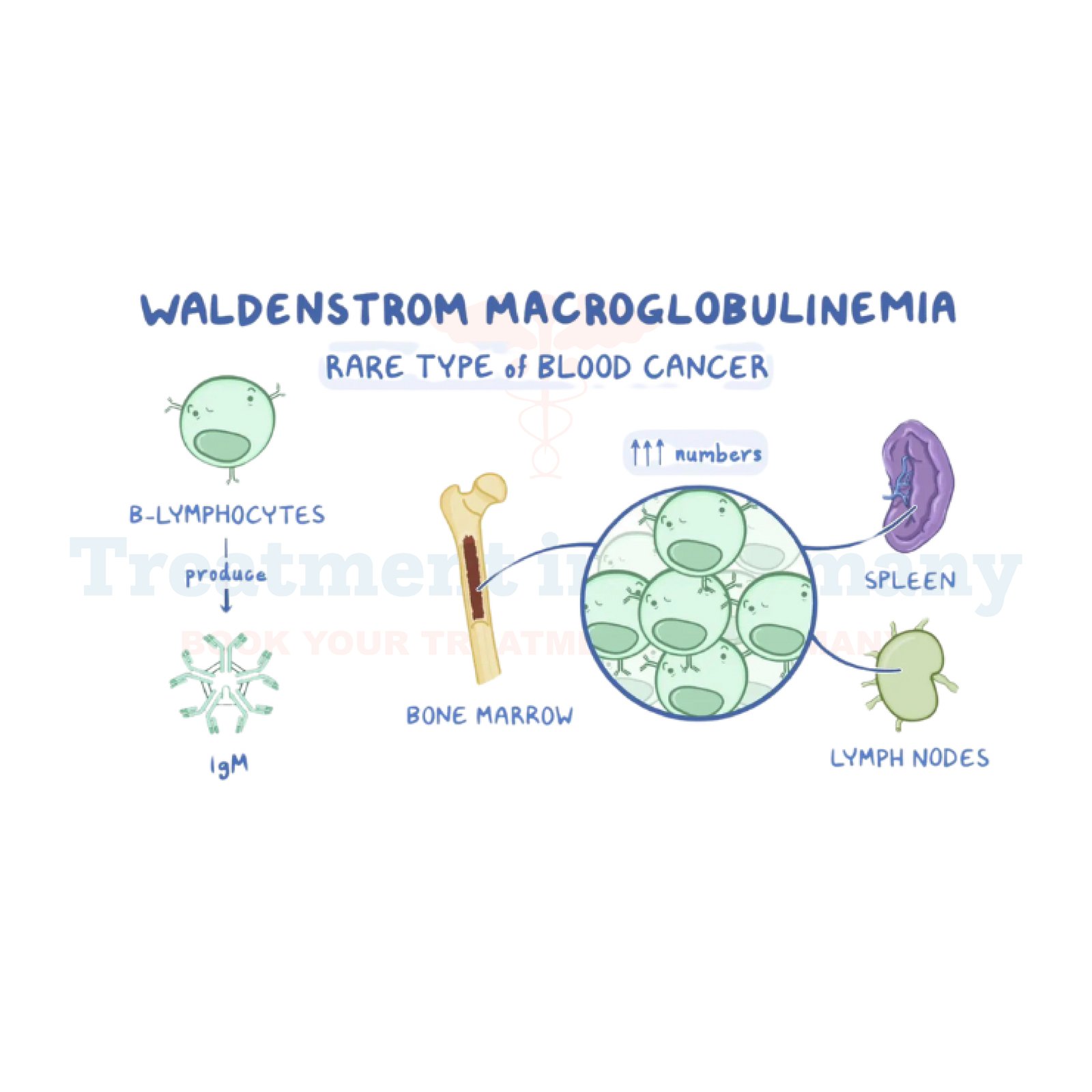
Macroglobulinemia, also known as Waldenström's Macroglobulinemia, is a rare type of blood cancer characterized by the abnormal growth of white blood cells called lymphoplasmacytic cells.
These cells produce an excess of a protein called immunoglobulin M (IgM), which can lead to thickening of the blood and impair normal blood flow.
Side Effects of Macroglobulinemia (Waldenström's Macroglobulinemia)
Patients with Macroglobulinemia may experience various symptoms, including fatigue, weakness, weight loss, easy bruising or bleeding, enlarged lymph nodes, and recurring infections.
Additionally,the thickening of the blood can increase the risk of blood clots, which may lead to serious complications such as stroke or heart attack.
Diagnosis of Macroglobulinemia (Waldenström's Macroglobulinemia)
Diagnosing Macroglobulinemia typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Blood tests can reveal elevated levels of IgM and other markers associated with the disease. Bone marrow biopsy may also be performed to examine the presence of abnormal cells. Imaging studies like CT scans or MRIs may help assess organ involvement.
Potential Treatments of Macroglobulinemia (Waldenström's Macroglobulinemia)
Treatment options for Macroglobulinemia aim to manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve quality of life. The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the patient's overall health, the extent of the disease, and individual preferences.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
