What is Malignant Melanoma?
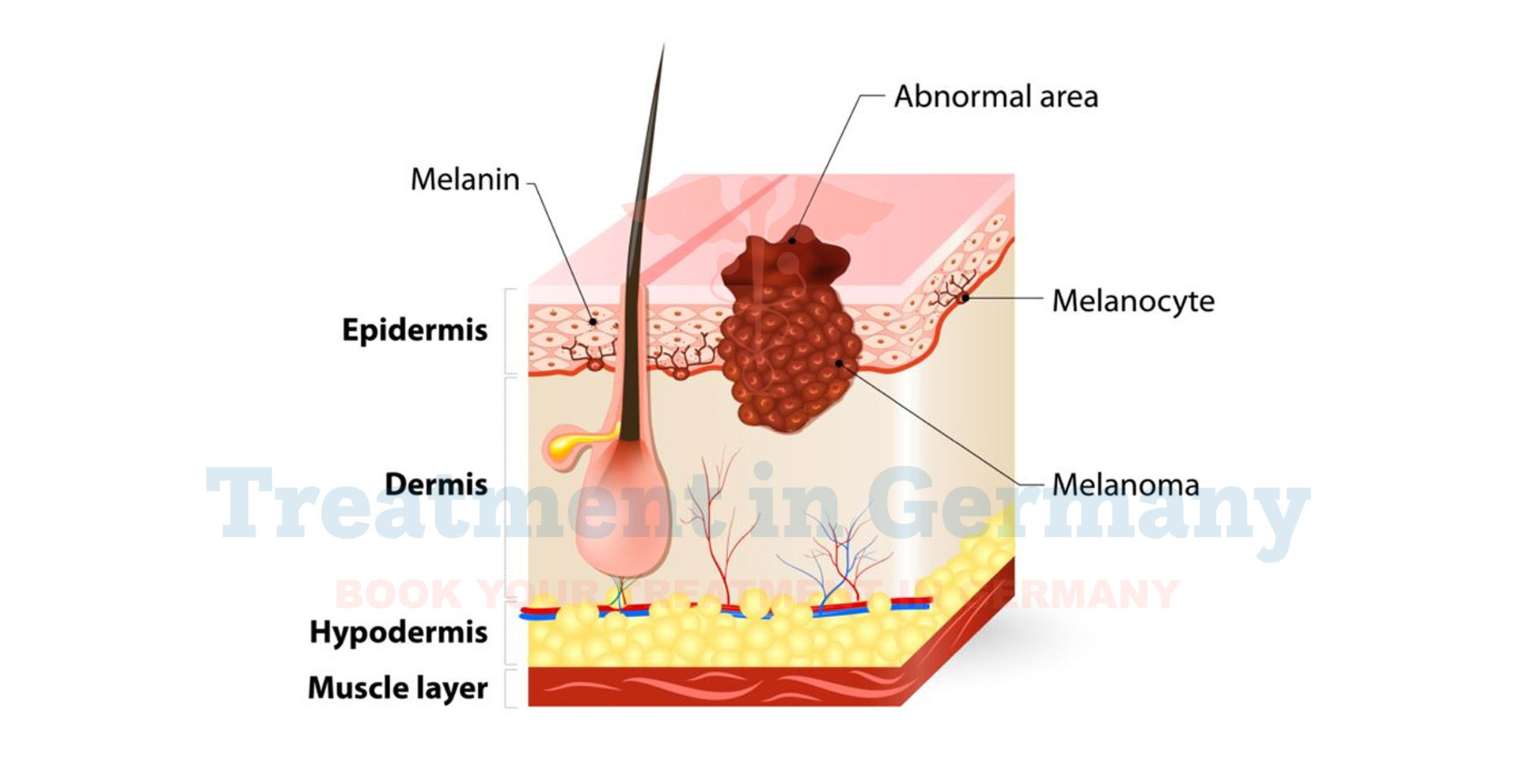
Malignant Melanoma, often referred to simply as melanoma, is a type of skin cancer that originates in melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its color.
When melanocytes begin to grow uncontrollably and invade nearby tissues, they form malignant tumors known as melanomas. These tumors can also spread to other parts of the body through the lymphatic system or bloodstream.
Side Effects of Malignant Melanoma
The potential side effects of malignant melanoma can vary depending on the stage and location of the cancer. Early-stage melanomas may not cause noticeable symptoms, but as the cancer progresses, patients may experience:
- Changes in skin pigmentation: Irregular or asymmetric growths or moles.
- Changes in size, shape, or color of existing moles: Moles that itch, bleed, or become painful.
- Spread to lymph nodes: Swelling or lumps in lymph nodes near the affected area.
- Advanced symptoms: Fatigue, unintended weight loss, and organ-specific symptoms if the cancer has spread.
How is Malignant Melanoma Diagnosed?
Diagnosing malignant melanoma typically involves several steps:
- Physical Examination: A dermatologist or healthcare provider examines the skin and any suspicious moles or growths.
- Biopsy: If a suspicious lesion is found, a biopsy is performed to remove a small sample of tissue for examination under a microscope. This helps confirm whether the lesion is cancerous and, if so, its specific type and characteristics.
- Imaging Tests: If melanoma is confirmed, further imaging tests such as CT scans, MRI scans, or PET scans may be conducted to determine if the cancer has spread to lymph nodes or other organs.
Potential Treatments of Malignant Melanoma
Treatment options for malignant melanoma depend on several factors including the stage of the cancer, its location, and the overall health of the patient. Common treatment modalities include:
- Surgery: The primary treatment for localized melanomas involves surgical removal of the tumor and a margin of healthy tissue around it.
- Chemotherapy: Medications used to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing.
- Immunotherapy: Drugs that help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs that target specific mutations in melanoma cells that help them grow.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy rays used to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
