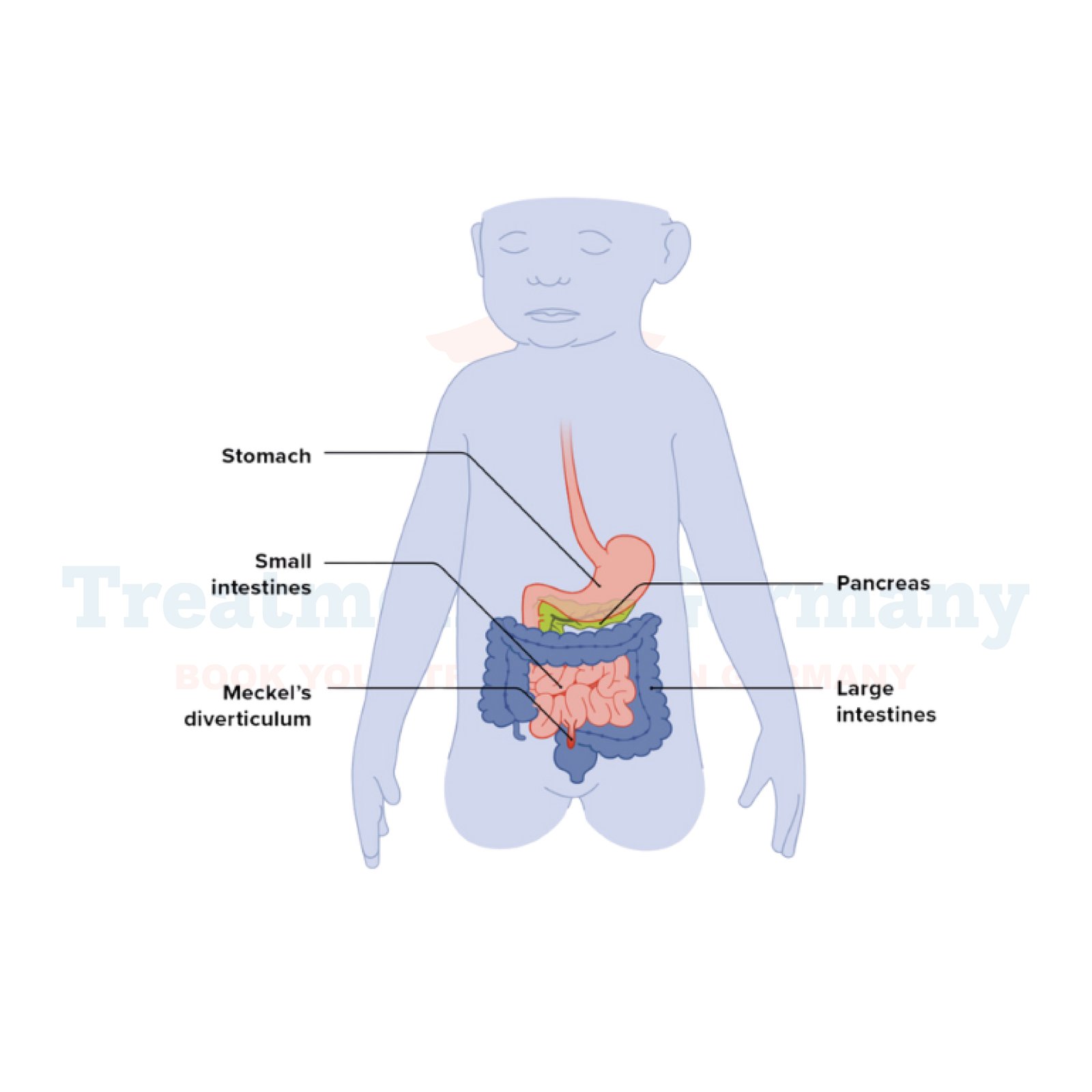
What is Meckel's Diverticulum?
Meckel's diverticulum is a congenital condition that involves a small pouch, called a diverticulum, forming in the wall of the small intestine.
This pouch is a remnant from fetal development, specifically from the embryonic yolk sac, and is found in about 2% of the general population.
It typically appears about 2 feet from the junction of the small and large intestines. Most people with Meckel's diverticulum have no symptoms and are unaware of its presence, but it can sometimes lead to various health issues.
Side Effects of Meckel's Diverticulum
While many individuals with Meckel's diverticulum remain asymptomatic, complications can arise, including:
- Gastrointestinal Bleeding: This can occur if the diverticulum contains gastric or pancreatic tissue that causes ulcers or bleeding.
- Intestinal Obstruction: The diverticulum may lead to blockage in the intestines.
- Diverticulitis: Inflammation of the diverticulum, which can mimic symptoms of appendicitis.
- Abdominal Pain: This can be acute and mimic other conditions, such as appendicitis or Crohn’s disease.
How is Meckel's Diverticulum Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Meckel's diverticulum typically involves several steps and diagnostic tools:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Your doctor will start with a detailed medical history and physical examination to assess symptoms and rule out other conditions.
- Imaging Tests: Techniques such as an abdominal ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI may be used to visualize the diverticulum and assess any related complications.
- Scintigraphy: A specific type of scan called a Meckel’s scan, using a radioactive tracer, can help identify ectopic gastric mucosa (stomach tissue) in the diverticulum.
Potential Treatment of Meckel's Diverticulum
Treatment options for Meckel's diverticulum depend on the presence and severity of symptoms:
- Conservative Management: If the diverticulum is asymptomatic and not causing any issues, no treatment may be necessary. Regular monitoring may be recommended.
- Surgical Intervention: For symptomatic cases or complications, surgery is often required. The procedure, typically performed laparoscopically, involves removing the diverticulum and addressing any related issues like bleeding or obstruction.
- Medications: In cases where the diverticulum causes inflammation or ulcers, medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms or treat underlying conditions.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
