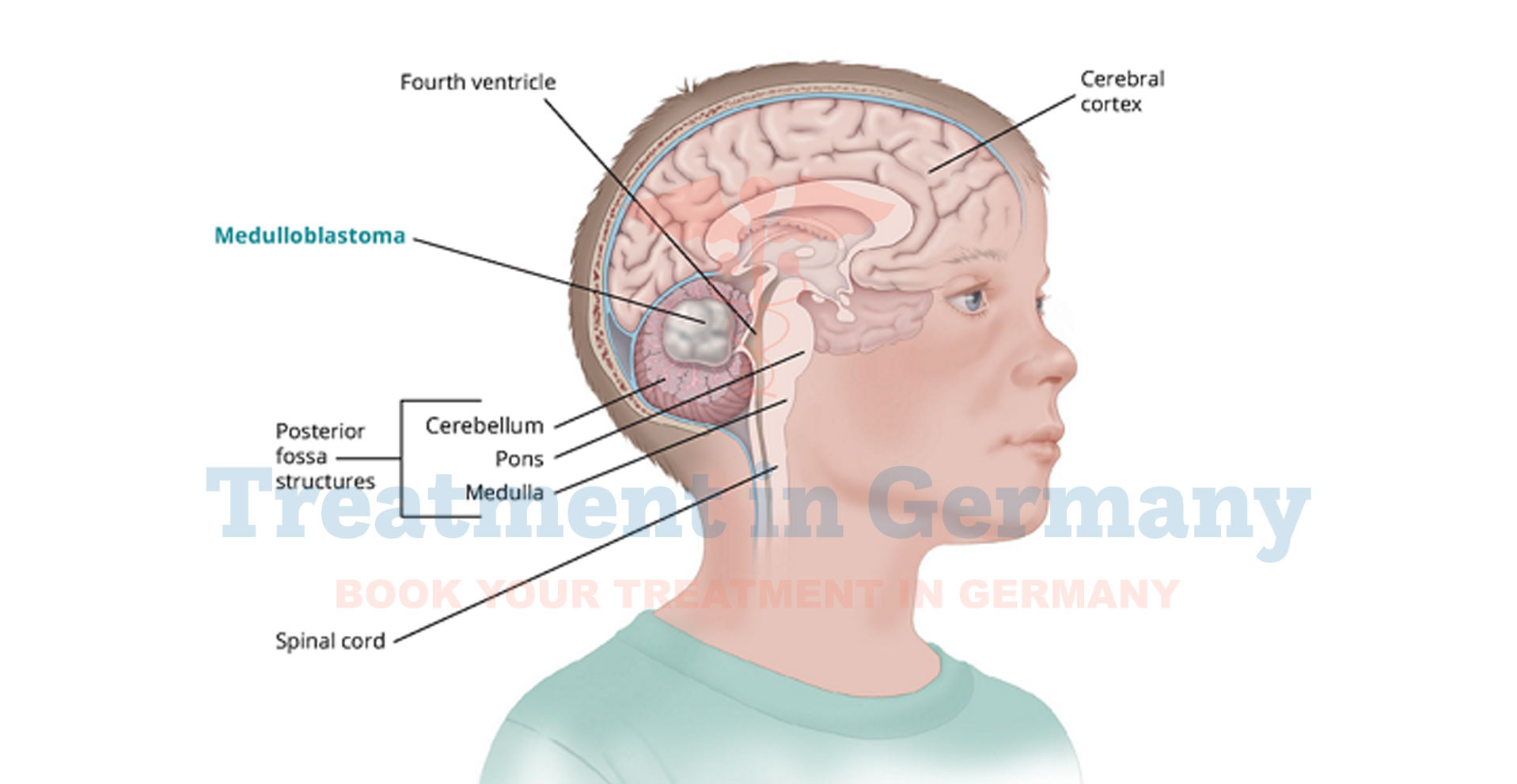
What is Medulloblastoma?
Medulloblastoma is a type of brain tumor that primarily affects children, though it can also occur in adults. It develops in the cerebellum, which is located at the lower back of the brain.
This tumor arises from abnormal growth of neural progenitor cells and is classified as a primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET). Medulloblastoma is considered a fast-growing tumor and requires prompt medical attention.
Side Effects of Medulloblastoma
The symptoms of Medulloblastoma can vary depending on the size and location of the tumor. Common signs may include severe headaches, nausea, vomiting (especially in the morning), problems with balance and coordination, difficulties with speech, vision problems, and changes in mood or behavior. These symptoms can significantly impact daily life and prompt individuals to seek medical advice.
How is Medulloblastoma Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Medulloblastoma typically involves a series of diagnostic tests and procedures:
Potential Treatment of Medulloblastoma
Treatment options for Medulloblastoma depend on several factors, including the age and overall health of the patient, as well as the tumor's size, location, and subtype. Common approaches may include:

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
