What is Menorrhagia:
Menorrhagia refers to abnormally heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding. It's a common condition that can significantly impact a woman's quality of life, causing physical discomfort, emotional distress, and sometimes even interference with daily activities.
While some women may experience heavier periods occasionally, menorrhagia involves consistently heavy bleeding that may require medical intervention.
Side effects of Menorrhagia:
The effects of menorrhagia can extend beyond the inconvenience of heavy bleeding. Some common side effects include:
- Anemia: Excessive blood loss during menstruation can lead to anemia, characterized by fatigue, weakness, and pale skin.
- Physical discomfort: Menstrual cramps may become more intense with heavy bleeding, causing abdominal pain and discomfort.
- Emotional impact: Coping with the challenges of menorrhagia can take a toll on mental health, leading to stress, anxiety, and mood swings.
- Interference with daily life: Managing heavy bleeding may require frequent bathroom trips, limiting participation in activities, and impacting work or school attendance.
How is Menorrhagia diagnosed?
If you suspect you have menorrhagia, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. The diagnostic process may include:
- Medical history: Your doctor will inquire about your menstrual patterns, symptoms, and any underlying health conditions.
- Physical examination: A pelvic exam may be performed to assess the reproductive organs for any abnormalities.
- Blood tests: These tests can help determine if you have anemia or other underlying conditions contributing to menorrhagia.
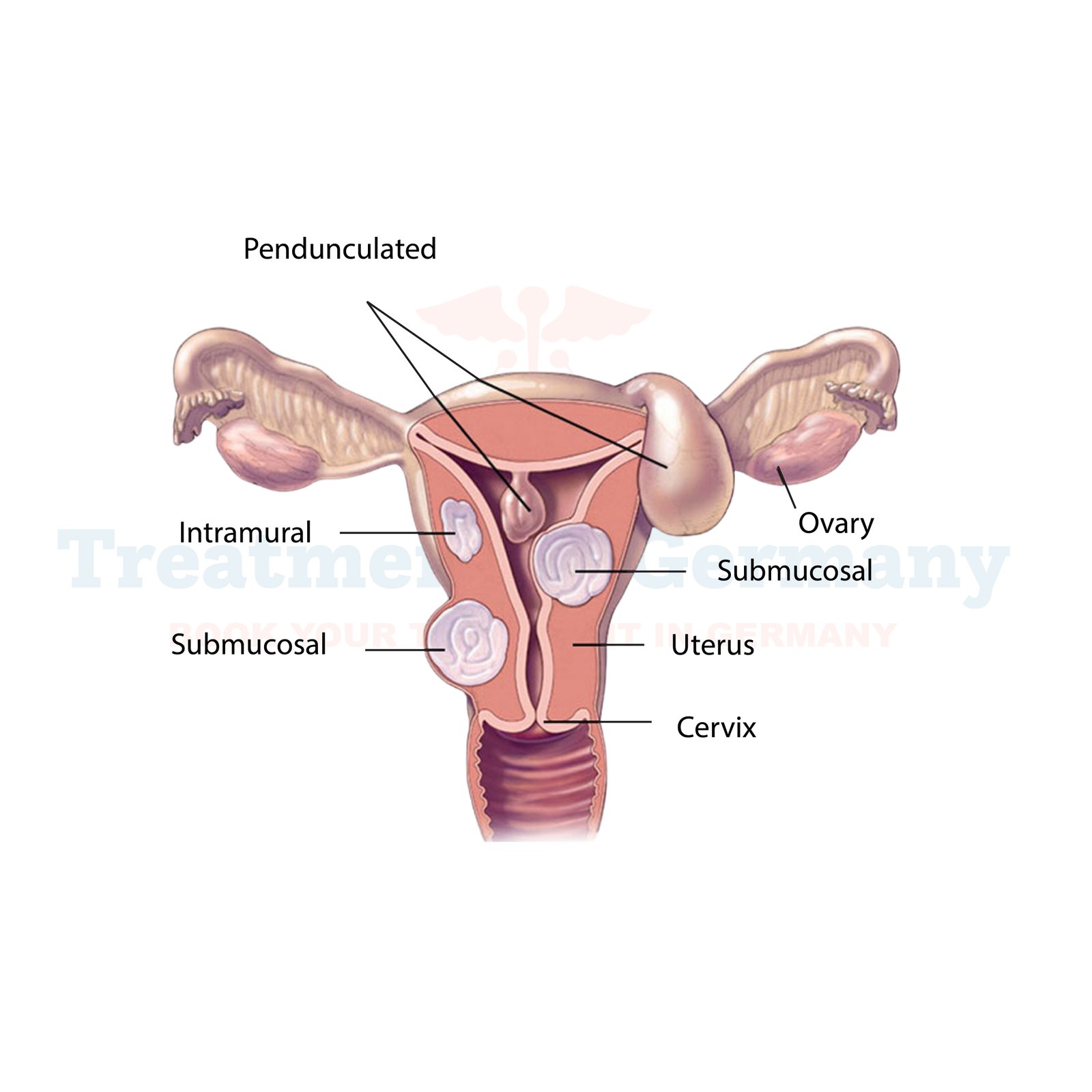
- Imaging tests: In some cases, ultrasound or other imaging tests may be ordered to evaluate the uterus and surrounding structures.
Potential treatments of Menorrhagia:
Treatment options for menorrhagia vary depending on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and individual preferences. Some common treatments include:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help reduce menstrual bleeding and alleviate cramps. Hormonal medications such as birth control pills, hormonal IUDs, or Hormone Therapy may also be prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles and reduce bleeding.
- Non-hormonal therapies: Tranexamic acid, a medication that promotes blood clotting, may be prescribed to help control heavy bleeding.
- Surgical interventions: If conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical options such as endometrial ablation or hysterectomy may be considered to remove or reduce the lining of the uterus.
- Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in iron, and stress management techniques, can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
