What is Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack)?
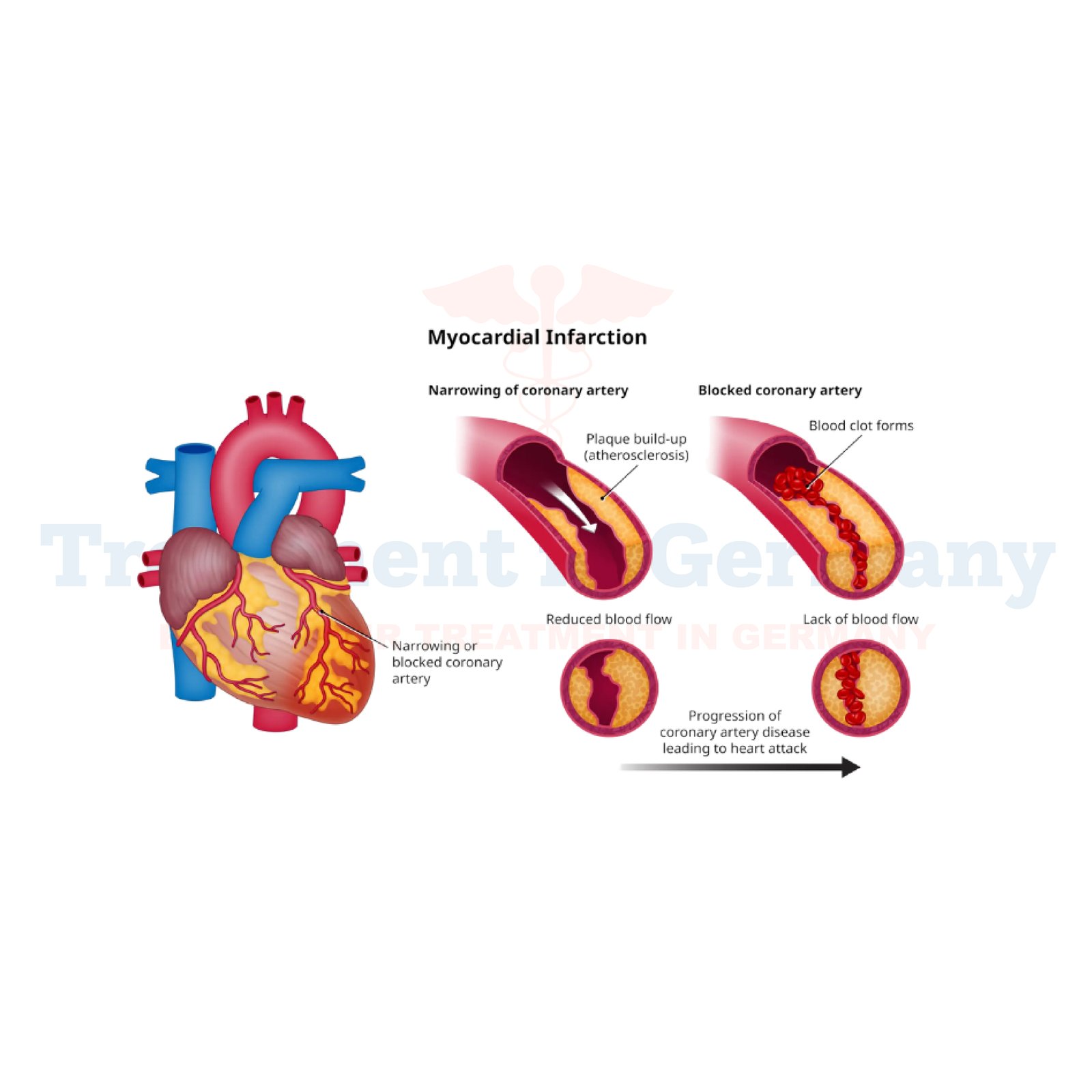
Myocardial infarction, commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked for a long enough time that part of the heart muscle is damaged or dies.
This blockage is usually caused by a buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle.
When the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the heart is reduced or blocked, the affected part of the heart muscle is deprived of oxygen and nutrients, leading to tissue damage.
Side effects of Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack):
The side effects of a myocardial infarction can vary depending on the severity of the attack and the extent of damage to the heart muscle. Common symptoms include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, lightheadedness, and sweating.
In some cases, a heart attack can cause complications such as heart failure, irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias), or even sudden cardiac arrest.
How is Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack) diagnosed?
Diagnosing a myocardial infarction typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Doctors may perform an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) to measure the electrical activity of the heart and identify any abnormalities indicative of a heart attack.
Blood tests, such as cardiac enzyme tests, can also help confirm the diagnosis by detecting certain proteins released into the bloodstream when the heart muscle is damaged.
Potential treatments of Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack):
Treatment for a myocardial infarction aims to restore blood flow to the affected part of the heart as quickly as possible to minimize damage and improve outcomes. Depending on the severity of the heart attack, treatment options may include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
