Myocarditis is a serious condition characterized by inflammation of the heart muscle (myocardium). This inflammation can weaken the heart, impair its ability to pump blood, and lead to arrhythmias, heart failure, or sudden cardiac death in severe cases. While myocarditis can affect anyone, prompt diagnosis and effective treatment are essential for minimizing complications. Germany has emerged as a leader in providing state-of-the-art treatments and care for myocarditis patients, offering access to the latest diagnostic tools and therapies.
Myocarditis occurs when the heart muscle becomes inflamed, often due to infections, autoimmune reactions, or other triggers. The condition can vary in severity, ranging from mild cases that resolve on their own to severe forms requiring advanced medical interventions.
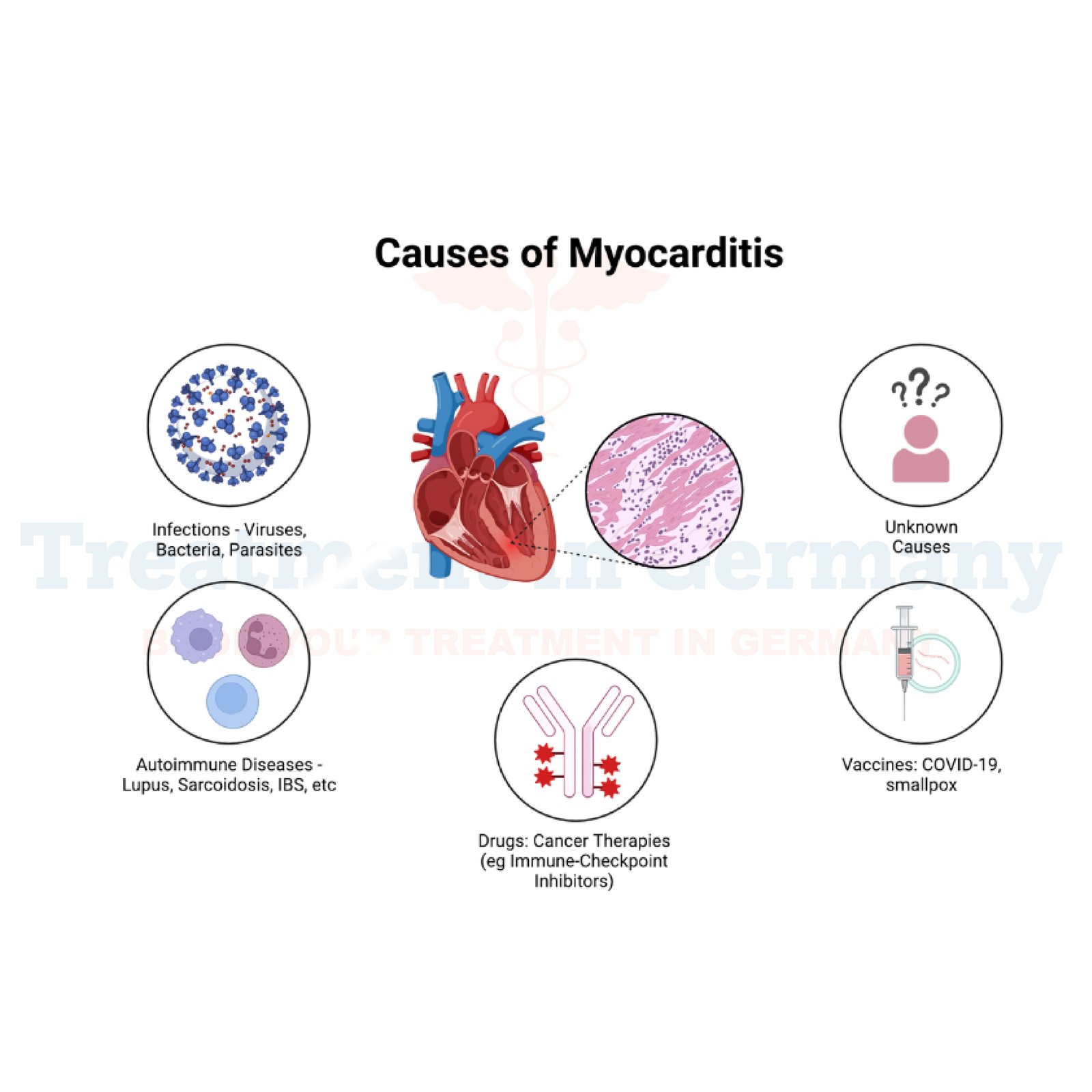
Causes of Myocarditis
The primary causes of myocarditis include:
Symptoms of Myocarditis
Symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the inflammation and the underlying cause. Common signs include:
Risk Factors for Myocarditis
Several factors can increase the risk of developing myocarditis:
Diagnosis of Myocarditis
Germany offers advanced diagnostic technologies to detect myocarditis accurately and efficiently. Diagnostic tools include:
Blood Tests
Detect markers of inflammation and infection.
Identify elevated levels of cardiac enzymes indicating heart damage.
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Measures the electrical activity of the heart.
Detects irregular heart rhythms and other abnormalities.
Echocardiography (ECHO)
Uses ultrasound waves to create images of the heart.
Assesses heart size, function, and any structural damage.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Offers detailed images of the heart.
Detects inflammation, scarring, and other abnormalities.
Endomyocardial Biopsy
A small sample of heart tissue is taken and analyzed to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Myocarditis in Germany
Germany is renowned for its comprehensive care and advanced treatment strategies for myocarditis. Treatment plans are personalized based on the severity of the condition, the underlying cause, and the patient’s overall health.
Medications
Physical Therapy and Lifestyle Changes
Supervised physical activity helps restore cardiac function.
Diet modifications reduce strain on the heart and support recovery.
Dendritic Cell Therapy
A groundbreaking approach to modulate the immune system.
Targets and reduces the immune response causing heart inflammation.
Stem Cell Therapy
Encourages regeneration of damaged heart muscle tissue.
Ongoing research in Germany makes this an emerging treatment option.
Implantable Devices
Pacemakers or Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators (ICDs): Regulate heart rhythm and prevent life-threatening arrhythmias.
Mechanical Circulatory Support
Ventricular Assist Devices (VADs): Help maintain heart function in severe cases.
Heart Transplantation
A last-resort option for patients with severe, irreversible damage.
Solutions to Prevent Myocarditis
While myocarditis cannot always be prevented, adopting the following measures can significantly reduce the risk:
Why Choose Germany for Myocarditis Treatment?
Germany is a global leader in healthcare, offering exceptional medical care and innovative treatment options for myocarditis. Reasons to seek treatment in Germany include:
Conclusion
Myocarditis is a complex condition requiring prompt and effective management to prevent complications. Germany’s healthcare system is at the forefront of diagnosing and treating myocarditis, offering patients access to world-class facilities, advanced therapies, and highly skilled specialists. By combining innovative treatments, preventive measures, and comprehensive care, Germany provides hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for myocarditis patients
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
