Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are rare cancers that originate in neuroendocrine cells that have characteristics of both nerve and hormone-producing cells. These tumors may occur in the GI (gastrointestinal) tract, lungs, pancreas, or another uncommon site such as the thyroid or adrenal glands.
The uniqueness of NETs from indolent benign tumors to aggressive metastatic cancers results in difficulty with treatment. Germany, which has always been synonymous with modern medicine, has also turned into a global hotspot for advances in NET diagnosis and therapy.
Neuroendocrine tumors originate from neuroendocrine cells that help regulate bodily functions by secreting hormones. Tumors are classified as either non-functional or functional (producing hormones).
Functional NETs will excessively release hormones, causing a wide variety of symptoms out of Neta rang for your body, while non-functional NETs may slowly grow without any symptom until they affect nearby organ systems.
Malignancy and Locations
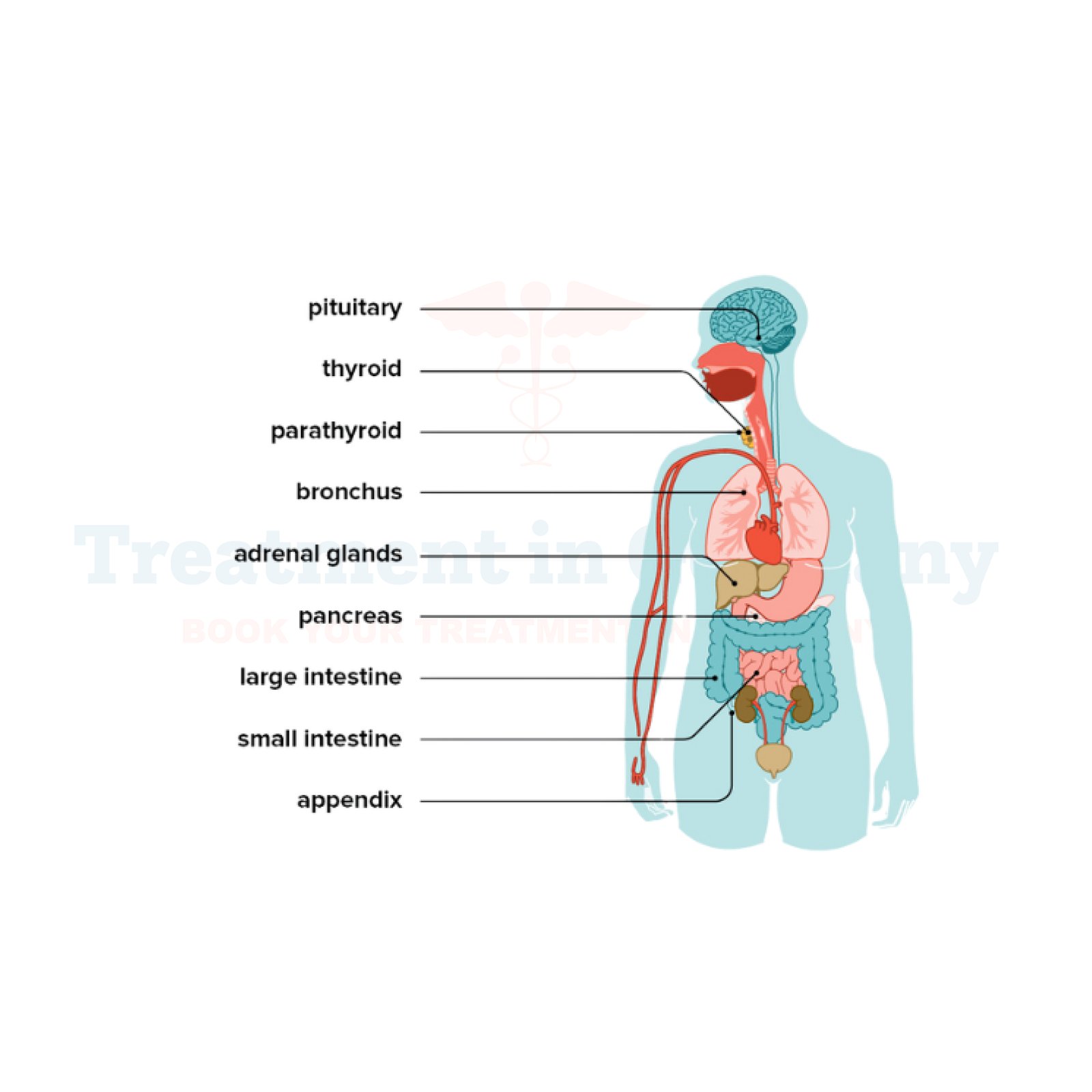
Although the majority of NETs are non-cancerous, some can be cancerous and metastasis to other regions in the body. NETs typically arise in these locations:
Types of Neuroendocrine Tumors
Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors
GI-NETs are most often found in the stomach, intestine, or appendix.
Lung Neuroendocrine Tumors
These are tumors that often originate in the lungs or windpipe and affect the respiratory system.
Neuroendocrine tumors of pancreas
Rare Neuroendocrine Tumor Sites
NETs can also affect:
Causes and Risk Factors
Genetic Mutations
When DNA mutations that affect neuroendocrine cells lead to increased production, NETs form. These abnormal cells grow to form tumors, which can invade neighboring organs and secrete more hormones.
Inherited Syndromes
Some genetic syndromes are also associated with an increased risk of NETs:
Symptoms and Complications
General Symptoms
The symptoms of NET are different depending on location and if the tumor is functional or non-functional.
Carcinoid Syndrome
A major complication of NETs, carcinoid syndrome, occurs when the tumors secrete high levels of hormones that lead to:
Untreated carcinoid syndrome may cause serious, even life-threatening, problems, including heart failure and massive swelling (edema).
Diagnostic Techniques
Treatment Options in Germany
Neuroendocrine tumors have some of the most advanced and innovative treatments available in Germany. Private hospitals provide specialists, modern laboratories, and advanced procedures used to tailor care.
Surgery
Removal of the tumor and surrounding tissues. For potentially curable NETs, especially when the tumor is localized, surgery is ideal.
Chemotherapy
Is using a medication that targets cancer cells that proliferate quickly. It is normally employed for the NETs that are progressed or metastatic in nature.
Targeted Therapy
Radiation Therapy
Innovative Therapies
Germany balances proven therapies with innovation, leading the way in experimental treatments such as PRRT and targeted drugs.
Managing Neuroendocrine Cancers
Coping Strategies
Affected people construct simple boundaries and plenty of relaxation to manipulate signs along with fatigue and diarrhea. A dietitian can provide guidance on how to keep patients strong throughout treatment.
Support Systems
Emotional Wellness Joining patient support groups and availing mental health services can be important for your emotional wellness. Many resources for NET patients and families in Germany.
Ongoing Monitoring
Its regular follow-up with imaging and biochemical tests can identify recurrences and monitor treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of neuroendocrine tumors in the gastrointestinal system?
The most common symptoms include stomach pain, diarrhea, and nausea.
How do neuroendocrine tumors of the lung get diagnosed?
A diagnosis is confirmed through imaging (CT scans and X-rays), in addition to biopsies.
How does peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) work?
PRRT is a targeted therapy that sends radiation directly to NET cells that excrete hormones.
Are neuroendocrine tumors curable?
Yes surgery can cure if the tumor is localized. In advanced cases, the focus shifts to symptom management and slowing tumor growth.
What complications are associated with carcinoid syndrome?
If not treated, the carcinoid syndrome can result in heart failure, extreme swelling, and increased hormone-associated symptoms.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
