What is Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome?
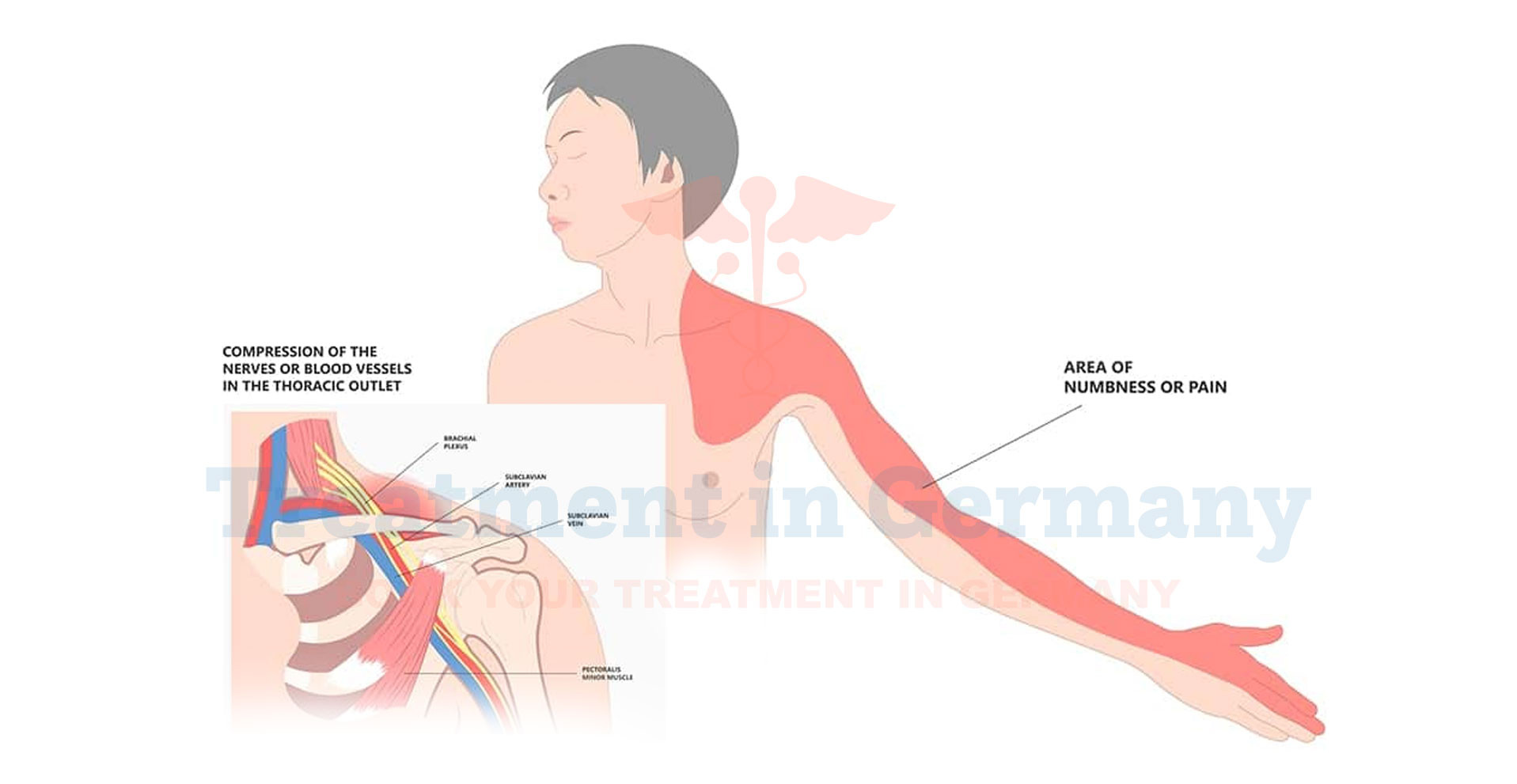
Neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome involves compression of the brachial plexus or its branches as they pass through the thoracic outlet. This compression can result from anatomical abnormalities (such as a cervical rib or an abnormal first rib), trauma, repetitive overhead activities, or poor posture.
Symptoms typically include pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the affected arm and hand.
Side Effects of Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
The symptoms of Neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome can significantly impact daily life. Patients may experience:
- Pain: Persistent pain in the shoulder, neck, and arm, worsened by certain activities or positions.
- Numbness and Tingling: Sensations of numbness, tingling ("pins and needles"), or a feeling of "falling asleep" in the fingers or hand.
- Weakness: Reduced strength and coordination in the affected arm and hand, affecting tasks like lifting objects or gripping.
- Muscle Atrophy: In severe cases, prolonged compression can lead to muscle wasting in the affected arm.
How is Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome involves a thorough clinical evaluation and may include:
- Medical History: Detailed discussion of symptoms and medical history, including any prior injuries or activities that may contribute to nerve compression.
- Physical Examination: Assessment of arm and shoulder strength, sensation, and reflexes to identify areas of weakness or sensory loss.
- Diagnostic Tests: These may include nerve conduction studies (EMG/NCS) to evaluate nerve function, imaging such as MRI or ultrasound to visualize the thoracic outlet and surrounding structures, and possibly vascular studies to rule out other conditions.
Potential Treatment of Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Treatment for Neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome depends on the severity of symptoms and may include:
- Conservative Measures: Initial treatment often involves physical therapy to improve posture, strengthen muscles, and relieve pressure on the nerves. Lifestyle modifications such as avoiding repetitive overhead activities may also be recommended.
- Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or other pain relievers may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation.
- Interventional Procedures: In cases where conservative measures do not provide sufficient relief, injections of corticosteroids or local anesthetics into the affected area can help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
- Surgical Intervention: For severe or persistent cases of NTOS, surgical options may be considered. These may include removing the first rib (first rib resection) to relieve pressure on the nerves and improve symptoms. Surgery is generally reserved for cases that do not respond to conservative treatments.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
