What is Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)?
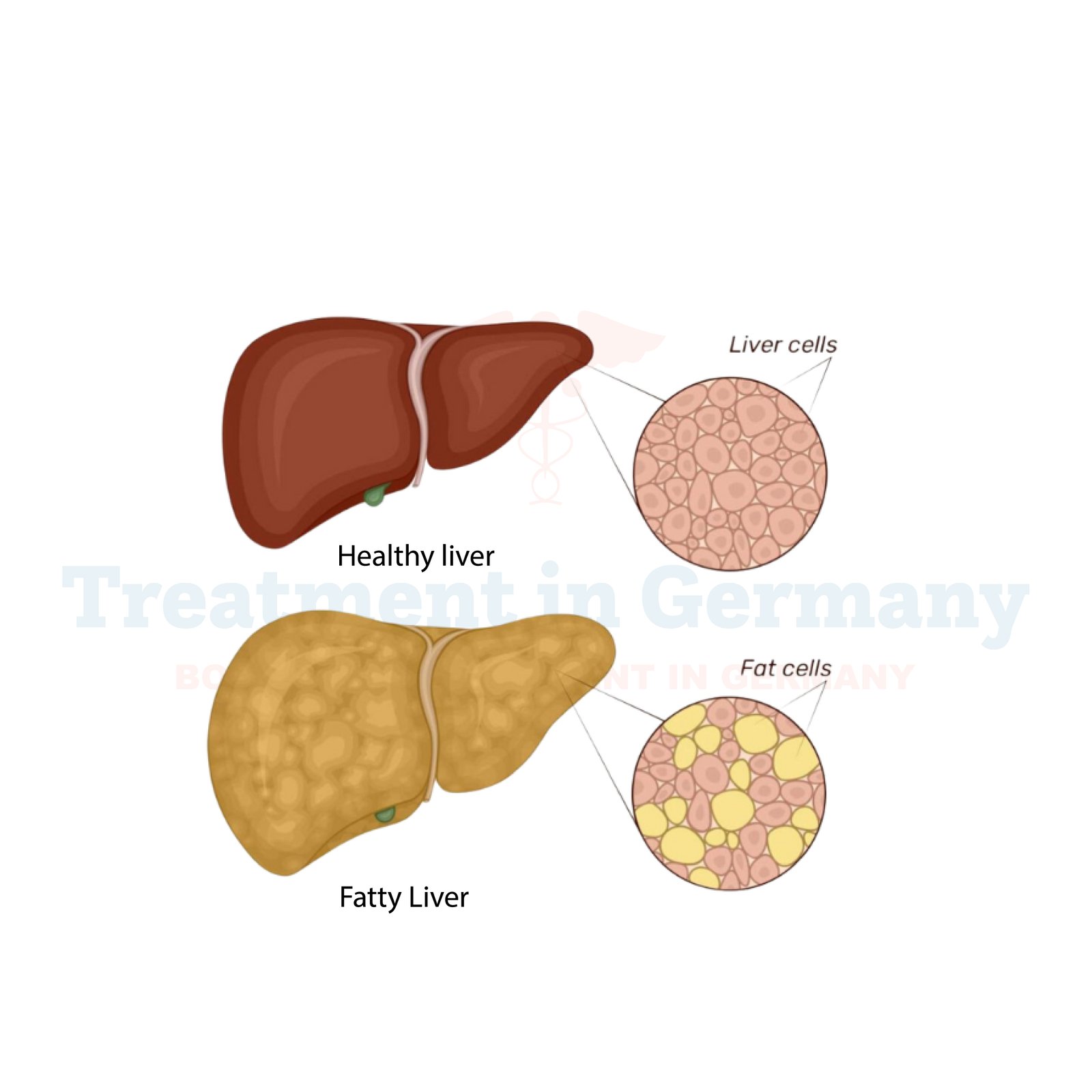
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a common liver condition where excess fat accumulates in the liver without the presence of significant alcohol consumption.
This buildup of fat can disrupt liver function and, if left untreated, may progress to more serious liver conditions such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis, or even liver cancer. NAFLD is often associated with metabolic syndrome, including obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
Side Effects of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease is often asymptomatic, meaning many people with the condition may not experience noticeable symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, it can cause a range of side effects:
- Fatigue and Weakness: A general feeling of tiredness and decreased energy levels.
- Abdominal Discomfort: Mild to moderate pain or discomfort in the upper right side of the abdomen.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Sudden or unintentional loss of weight.
- Elevated Liver Enzymes: Detected through blood tests, indicating inflammation or liver damage.
- Jaundice: In more severe cases, the skin and eyes may take on a yellowish tint, indicating liver dysfunction.
How is Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease involves several steps:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Your healthcare provider will review your medical history, including alcohol consumption, and conduct a physical examination.
- Blood Tests: Tests to check for elevated liver enzymes, which may suggest liver inflammation or damage.
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI may be used to visualize fat deposits in the liver.
- Liver Biopsy: In some cases, a liver biopsy may be performed to assess the extent of liver damage and determine whether inflammation or fibrosis (scarring) is present.
- FibroScan: A specialized ultrasound technique that measures liver stiffness, which can indicate fibrosis or cirrhosis.
Potential Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
The treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease focuses on managing the underlying causes and improving liver health:
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Diet: Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while reducing saturated fats and sugars.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps reduce liver fat and improve overall health.
- Weight Loss: Gradual weight loss through diet and exercise can significantly reduce liver fat and inflammation.
- Medications: While there are no specific drugs approved solely for NAFLD, medications may be prescribed to manage associated conditions such as diabetes, high cholesterol, or hypertension.
- Monitoring and Follow-Up: Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider to monitor liver function and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
- Avoiding Alcohol: Even though NAFLD is not caused by alcohol, abstaining from alcohol is recommended to prevent additional liver stress.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
