Germany is considered a suitable place for advanced treatment of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which is a complex group of blood cancers acting on the lymphatic system. German institutes are also known for their innovative approach and comprehensive care in disease treatment. These centers offer state of the art therapies targeting the root cause of the disease and deliver high-quality life support to patients.
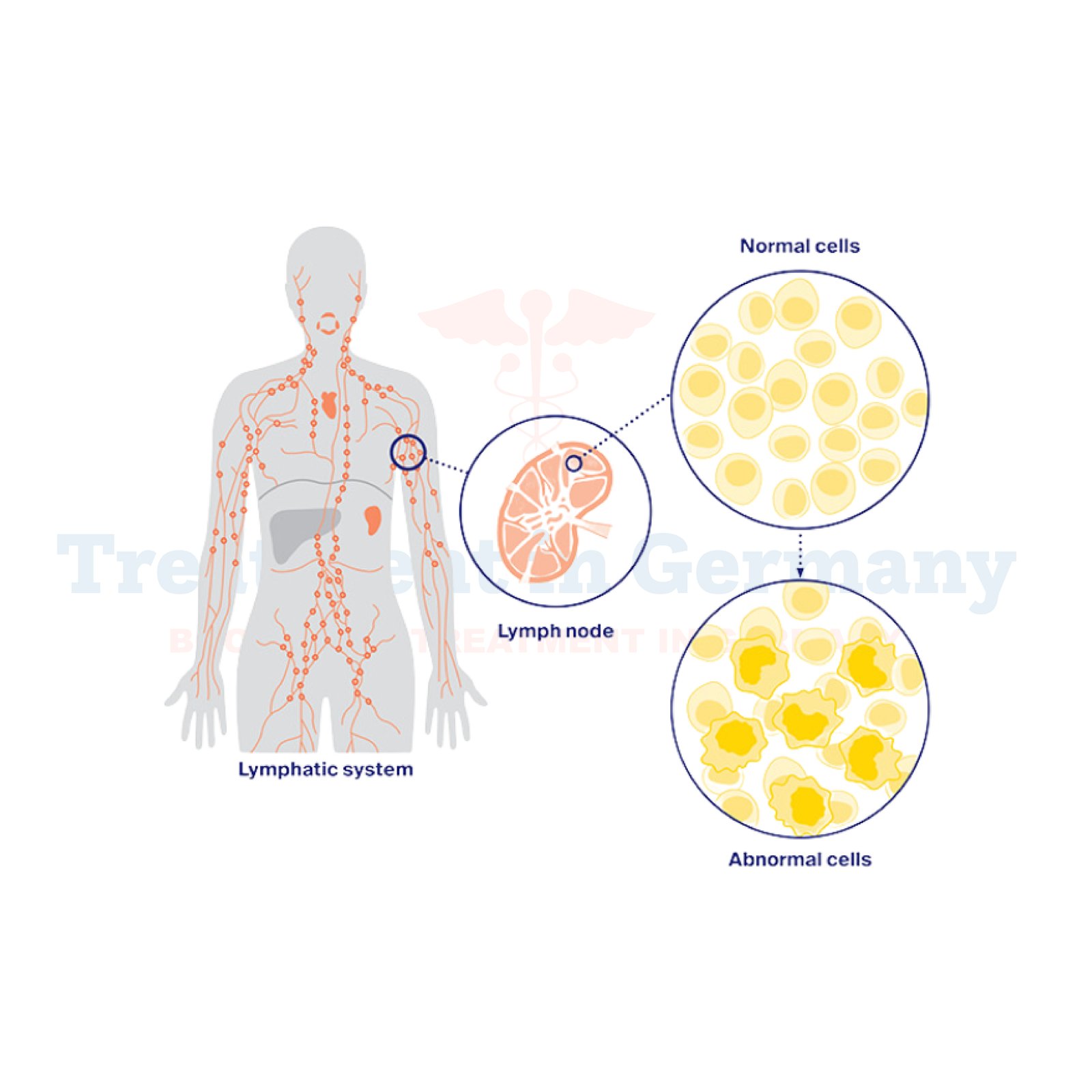
A deadly cancer that develops in the body's lymphatic tissues a vital component of the immune system is known as non-Hodgkin lymphoma. It derives from dysfunctional lymphocytes.
Lymphocytes are a family of white blood cells made up of B cells, T cells, and NK cells that normally fight infections and produce antibodies. In non-Hodgkin lymphoma, they transform, multiply uncontrollably, and eventually develop tumors.
This type of lymphoma is differentiated by the lymphocyte affected and may influence any of the organs, including lymph nodes, spleen, liver, or even the thymus in some patients.
General Signs and Testing Methods
Primary Sign Indicators
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma has been known to manifest in a wide variation, depending on the location and the type of the tumor. A few of the common signs include:
Diagnostic Methods in Germany
Germany applies high-class diagnostic techniques for accurate staging and classification, both of which can guide proper treatment. Some of the techniques include:
Types of Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas Treated in Germany
Only German oncology centers offer separate types of non-Hodgkin lymphomas depending on their characteristics and treatment needs.
Aggressive Lymphomas
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma (DLBCL)
DLBCL is the most common aggressive lymphoma, aggressive in growth, but often presents with anatomic distribution nodal. Systemic chemotherapy and CAR-T cell therapy are the main treatments offered in Germany to achieve remission.
Mantle Cell Lymphoma
This B-cell lymphoma can be seen in the circulation, spleen, or lymph nodes and usually affects adult men over 60. Aggressive though it is, a favorable response to targeted therapy therapies administered at cancer clinics in Germany is often witnessed.
Burkitt Lymphoma
This is a very rapidly growing type of lymphoma but has a good response to high-dose chemotherapy; thus, it is widely used in Germany. Its cure rate is also very high.
Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma (PTCL)
It affects mature T cells and NK cells, targeting the organs including the spleen and the skin. According to German oncologists, the primary therapy would be the integration of immunotherapy, monoclonal antibody therapy, and traditional chemotherapy.
Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALCL)
It is an infrequent and aggressive disease, which initially affects the lymph nodes and subsequently extends to other parts of the body. In Germany, this type of lymphoma is treated using therapies that target the CD30 protein, which is located on the surface of cancerous cells.
Follicular Lymphoma
This slow-growing type of lymphoma is the second most common in Europe. Most German patients receive active surveillance as the first approach, with radiotherapy or chemotherapy used for more advanced diseases.
CLL/SLL
CLL and SLL share many characteristics and affect the blood or lymph nodes. The treatments by the German may include immunotherapy and targeted therapy in patients with symptoms.
Marginal Zone Lymphoma
This lymphoma may infiltrate the spleen, lymph nodes, and organs outside of the lymphatic system. German hospitals commonly use treatments that vary depending on the specific subtype, including MALT lymphoma, which sometimes involves the stomach and is linked to infections caused by Helicobacter pylori.
Waldenström Macroglobulinemia
This is one of the rarest forms of lymphoma, affecting the B cells that are supposed to produce antibodies. Anemia and tiredness are common symptoms. Targeted therapies in Germany target the abnormal IgM antibodies produced by this disease.
Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma
This disease affects the skin, including forms like Mycosis Fungoides and Sézary Syndrome. In Germany, treatment methods available might include topical therapies, radiation, and sometimes stem cell transplantation.
Treatment Methods Available in Germany
German health care is patient-centered, blending traditional methods of treatment with modern treatments to produce comprehensive care plans.
Watchful Waiting/Active Surveillance
For the indolent forms, like follicular lymphoma, German medical oncologists may adopt a period of active surveillance or "watchful waiting," depending on the slow-growing nature or minimal expression of the cancer. This strategy usually enables the patients to defer therapy until necessary.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy, however, remains the mainstay treatment for many aggressive lymphomas. This affects the cancer cells systemically and is adjusted in the form of side effect management such as nausea and fatigue in German clinics, where new, innovative drug combinations are used for maximum efficacy.
Targeted Therapy and Monoclonal Antibody Therapy
Targeted therapies, including monoclonal antibody therapy, try to determine and kill cancerous cells without destroying normal cells. Monoclonal antibodies, for example, Rituximab or Obinutuzumab, only bind to B cells whose malignancy is commonly found in non-Hodgkin's lymphomas.
Immunotherapy
It helps stimulate the immune system to identify and fight lymphoma. One of the most revolutionary therapies is CAR-T cell therapy, which was developed in Germany, and it makes T cells taken from a patient genetically engineered so that they can recognize and kill lymphoma cells. It has produced fairly promising results, mainly for aggressive cases like DLBCL.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy involves beaming high-energy rays at the targeted area. This destroys the cancerous cells in a localized area. The radiology departments in Germany concentrate on the precision of radiation techniques as much as possible to reduce damage to normal tissues close to the tumor. Radiation therapy is often the only treatment required for indolent lymphomas or is used in conjunction with chemotherapy.
Stem Cell Transplantation
Severe chemotherapy frequently destroys blood-forming cells. Supportive care with stem-cell transplants is therefore necessary to replace these cells.
Palliative and Supportive Care in Germany
German healthcare pays more attention to palliative care than curative ones, especially when dealing with advanced diseases. Palliative care relates to the relief of pain, stress, and other side effects, thus ensuring the overall support of the patient's comfort and quality of life.
Risk Management and Relapse Prevention
Treatments in Germany, on the other hand, cannot guarantee remission. Relapse is always a possibility. The German centers monitor patients with follow-up visits, blood tests, and imaging studies. Lifestyle change advice, including stress moderation, among others, may also be given. Such lifestyles may likely lead to relapse.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma treated in Germany?
Most subtypes of lymphomas are treated in Germany, which includes aggressive ones like DLBCL and indolent forms like follicular lymphoma.
CAR-T cell therapy: Is it well established for the patient with non-Hodgkin lymphoma in Germany?
Yes, CAR-T is universal for aggressive lymphomas. It is a strong treatment for those patients who do not respond to the disease.
What is active surveillance? Can it be found in considerable practice in Germany?
It is a protocol whereby patients follow their track without definite treatment, the majority being due to the disease having slow progression.
Active surveillance is also termed watchful waiting. This is characterized by close monitoring of indolent lymphomas without immediate treatment, which is a common approach in Germany to avoid unnecessary intervention.
Are there options for patients with a need for palliative care?
The healthcare system emphasizes palliative care to improve quality of life. The approach focuses mainly on the management of symptoms and the provision of emotional support.
How are treatments tailored for specific types of non-Hodgkin lymphomas?
German clinics employ various diagnostic techniques, such as immunophenotyping and imaging, in order to adapt the proper treatment for each patient according to specific subtypes of lymphomas and their stage.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
