Optic neuritis is a challenging condition, but with the right care, you can improve outcomes and manage symptoms effectively. Germany is renowned for its advanced medical facilities and expertise in treating optic neuritis.
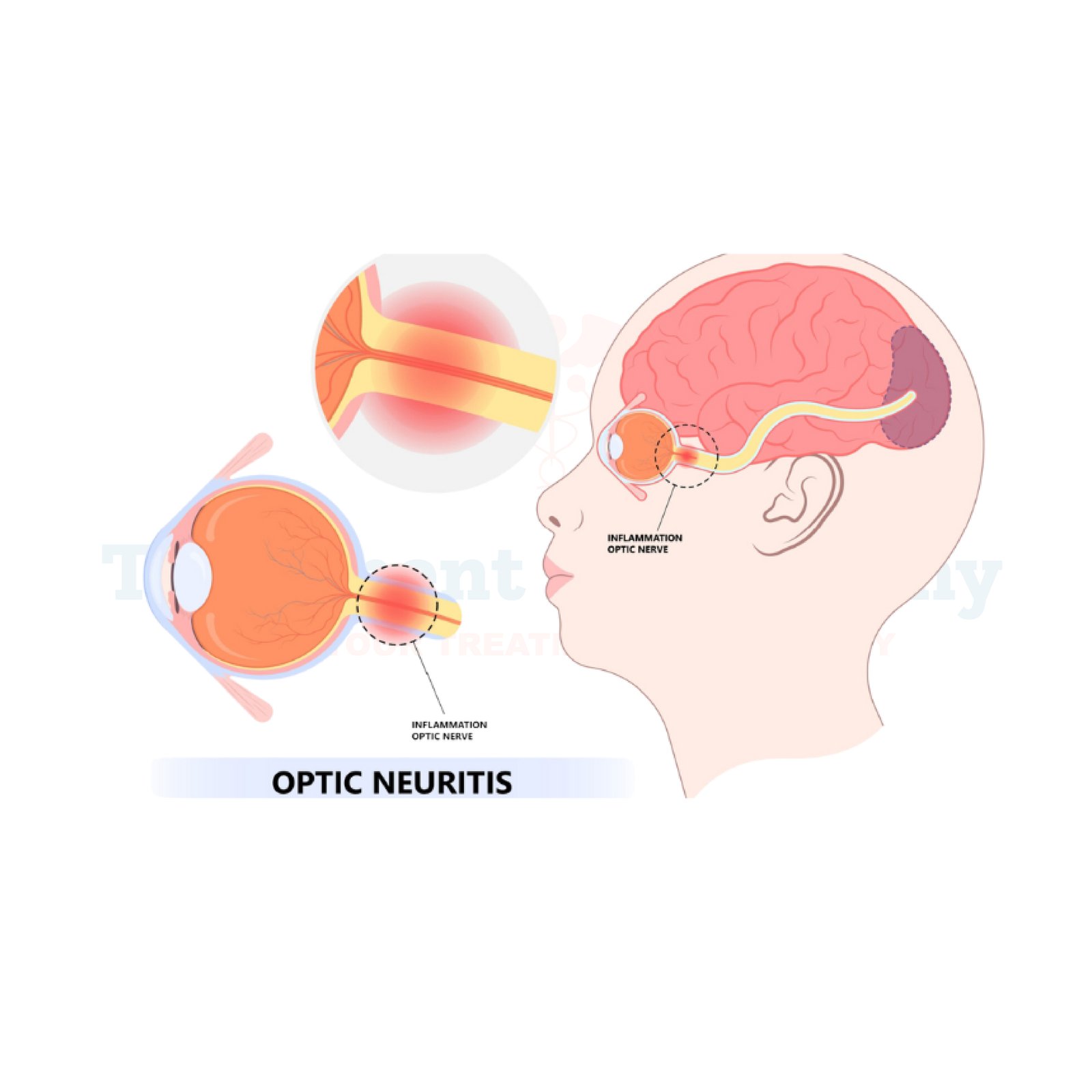
What is Optic Neuritis?
Optic neuritis occurs when inflammation damages the optic nerve, leading to temporary vision problems. It often requires medical attention to prevent further complications. Neuritis may cause temporary vision loss or blurriness in one eye. It is often associated with multiple sclerosis (MS) or other autoimmune diseases. However, with proper treatment, most patients regain near-normal vision.
Side Effects of Optic Neuritis
Optic neuritis may lead to a range of vision-related issues, it’s vital to seek a diagnosis and early treatment to mitigate long-term effects. Such as:
Causes of Optic Neuritis
Identifying the cause is critical for effective treatment. Optic neuritis is often triggered by underlying conditions or external factors, such as:
Symptoms of Optic Neuritis
Early detection can expedite recovery and reduce long-term complications. If you’re experiencing these symptoms, consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and care.
Diagnosis of Optic Neuritis
Proper and accurate diagnosis ensures the most effective treatment plan. Germany's highly advanced diagnostic technologies ensure precision in identifying optic neuritis.
Treatment for Optic Neuritis
With timely intervention, most patients recover nearly full vision. Germany’s healthcare system is globally recognized for offering cutting-edge optic neuritis treatments. Common treatments include:
Prevention and Management
While optic neuritis can't always be prevented, these strategies can help manage the condition and lower risks of recurrence.
Why Choose Germany for Optic Neuritis Treatment?
Opt for Germany’s trusted medical expertise to ensure the best possible care for optic neuritis. Germany is among the world’s top destinations for medical care, and here’s why:
Conclusion
When it comes to optic neuritis treatment, Germany stands out as a global leader, offering unparalleled expertise, cutting-edge technology, and compassionate patient care. By choosing Germany, you are investing in a recovery plan tailored specifically to your needs, supported by some of the finest medical professionals in the world. Don’t compromise on your vision and overall well-being—take the opportunity to access world-class treatment solutions and restore your quality of life today.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
