What is Osteoarthritis (related to obesity)?
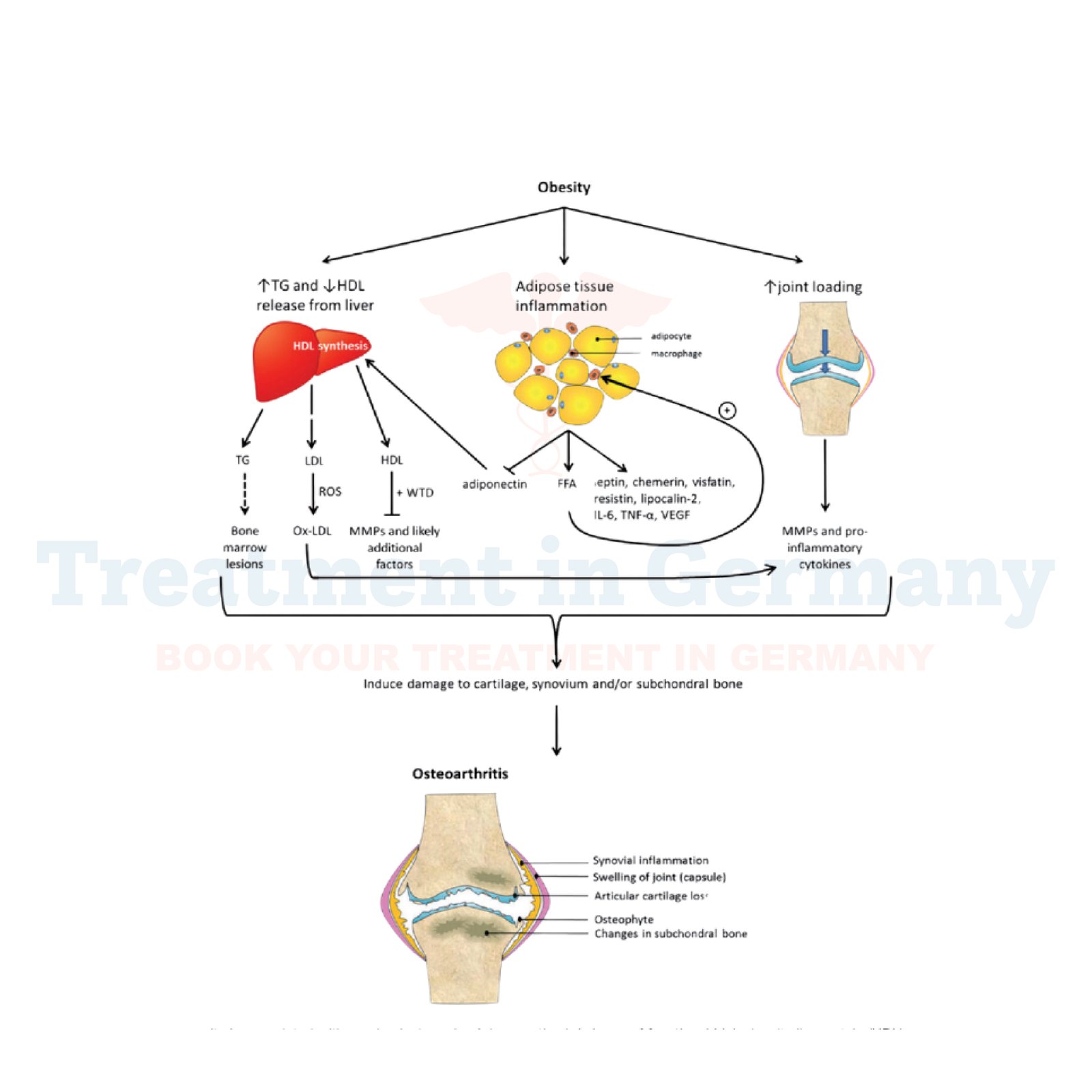
Osteoarthritis (OA) related to obesity is a degenerative joint disease that occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of your bones wears down over time. Obesity significantly increases the risk of developing OA, especially in weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, and spine. The excess weight puts additional stress on these joints, accelerating the breakdown of cartilage and leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
Side effects of Osteoarthritis (related to obesity)
The side effects of OA related to obesity can be debilitating. Patients often experience:
- Pain: Persistent joint pain that worsens with movement.
- Stiffness: Difficulty moving the affected joints, particularly after periods of rest.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Limited ability to fully move the joint.
- Decreased Quality of Life: Impaired ability to perform daily activities such as walking, climbing stairs, or even standing for extended periods.
How is Osteoarthritis (related to obesity) diagnosed?
Diagnosing OA related to obesity typically involves:
- Physical Examination: The doctor assesses joint function, swelling, and tenderness.
- Medical History: Discussion of symptoms, previous injuries, and lifestyle factors like weight and activity level.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays can reveal joint damage, such as narrowing of the joint space and bone spurs.
- Blood Tests: Exclude other forms of arthritis that may have similar symptoms.
Potential treatment of Osteoarthritis (related to obesity)
Effective management of OA related to obesity focuses on:
- Weight Management: Losing weight can reduce stress on joints, slow disease progression, and alleviate symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening exercises and stretching improve joint stability and flexibility.
- Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, and injections (e.g., corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid) can manage pain and inflammation.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adaptations to activities and the environment to reduce joint strain.
- Surgical Options: In severe cases, joint replacement surgery may be necessary to restore function.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
