What is Osteogenesis Imperfecta?
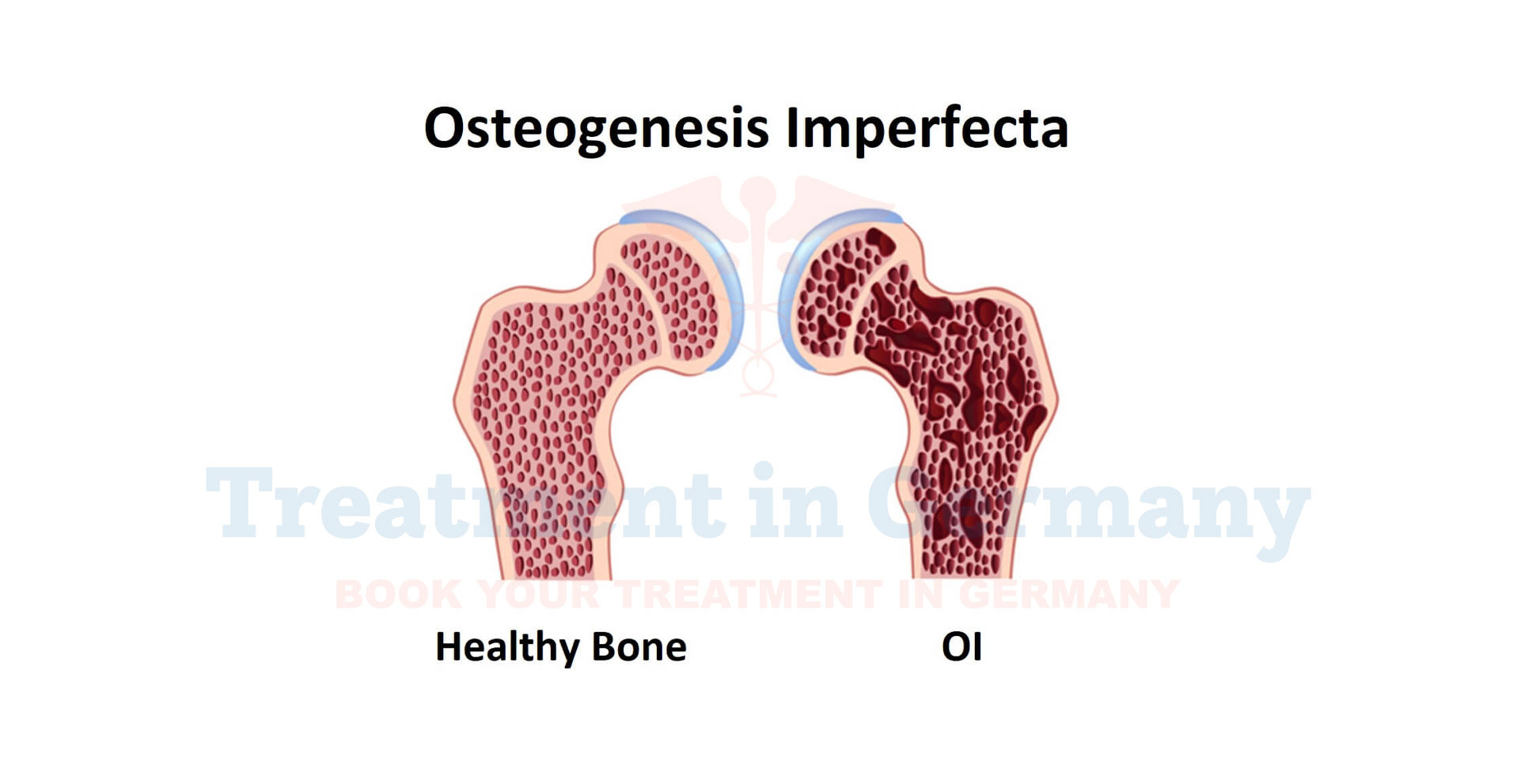
Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI), often referred to as brittle bone disease, is a genetic disorder characterized by fragile bones that break easily.
This condition is caused by a defect in the genes responsible for producing collagen, a key protein in bone structure.
As a result, individuals with OI have bones that are prone to fractures from minor trauma or even without apparent cause.
Side Effects of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Apart from the primary symptom of frequent fractures, OI can lead to various other complications:
- Bone deformities: Due to repeated fractures and improper healing, bones can become misshapen.
- Short stature: Some types of OI can cause short stature due to skeletal abnormalities.
- Joint laxity: Loose joints can be a common feature, contributing to mobility challenges.
- Respiratory problems: In severe cases, chest deformities can affect lung function.
- Hearing loss: Some forms of OI can affect the bones in the middle ear, leading to hearing impairment.
How is Osteogenesis Imperfecta Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Osteogenesis Imperfecta typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and genetic testing:
- Physical examination: Doctors look for signs such as blue sclera (the whites of the eyes), brittle teeth, and skeletal deformities.
- Imaging: X-rays and bone density scans can reveal fractures and bone density abnormalities.
- Genetic testing: DNA analysis can identify mutations in the genes associated with collagen production, confirming the diagnosis and sometimes indicating the specific type of OI.
Potential Treatment of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
While there is no cure for Osteogenesis Imperfecta, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing fractures:
- Medications: Bisphosphonates are often prescribed to increase bone density and reduce fracture risk.
- Physical therapy: Exercises can improve muscle strength and bone alignment, enhancing mobility and reducing the risk of fractures.
- Surgical interventions: Rodding surgery may be considered to stabilize bones and prevent fractures in severe cases.
- Mobility aids: Using braces, splints, or wheelchairs can help protect bones and improve mobility.
- Genetic counseling: This helps families understand the genetic basis of OI and make informed decisions about family planning.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
