Osteomyelitis Treatment in Germany
Osteomyelitis is a bone infection that can severely damage the bone if considered lightly. The infection may come from the bacteria and patients going through Osteomyelitis may feel extreme pain, swelling and redness at the infected area. Early diagnosis can save from further complications such as chronic infection, bone destruction or sepsis. This condition is most common in persons with weak immune systems, diabetes and recent surgeries or injuries.
Germany is famous for its advanced healthcare system and is always offering patients with innovative treatments for osteomyelitis. Hospitals in Germany are equipped with the latest equipment and technology, doctors, surgeons and specialists who use the latest technology to manage the condition. From antibiotic treatment, therapy, surgical interventions and physical therapy, treatment in Germany is always effective.
How Does Osteomyelitis Affect the Body?
Osteomyelitis is a dangerous condition that can cause long-term damage and affect a patient’s quality of life. It is a bone infection caused by bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and can spread throughout the bone and surrounded tissues if left untreated
Osteomyelitis typically occurs after an injury, surgery, or infection that reaches the bone through the bloodstream. The infection can affect any bone in the body, but it most commonly targets long bones, the spine, and the feet. Prompt diagnosis and intervention are crucial to prevent the infection from spreading and causing long-term damage.
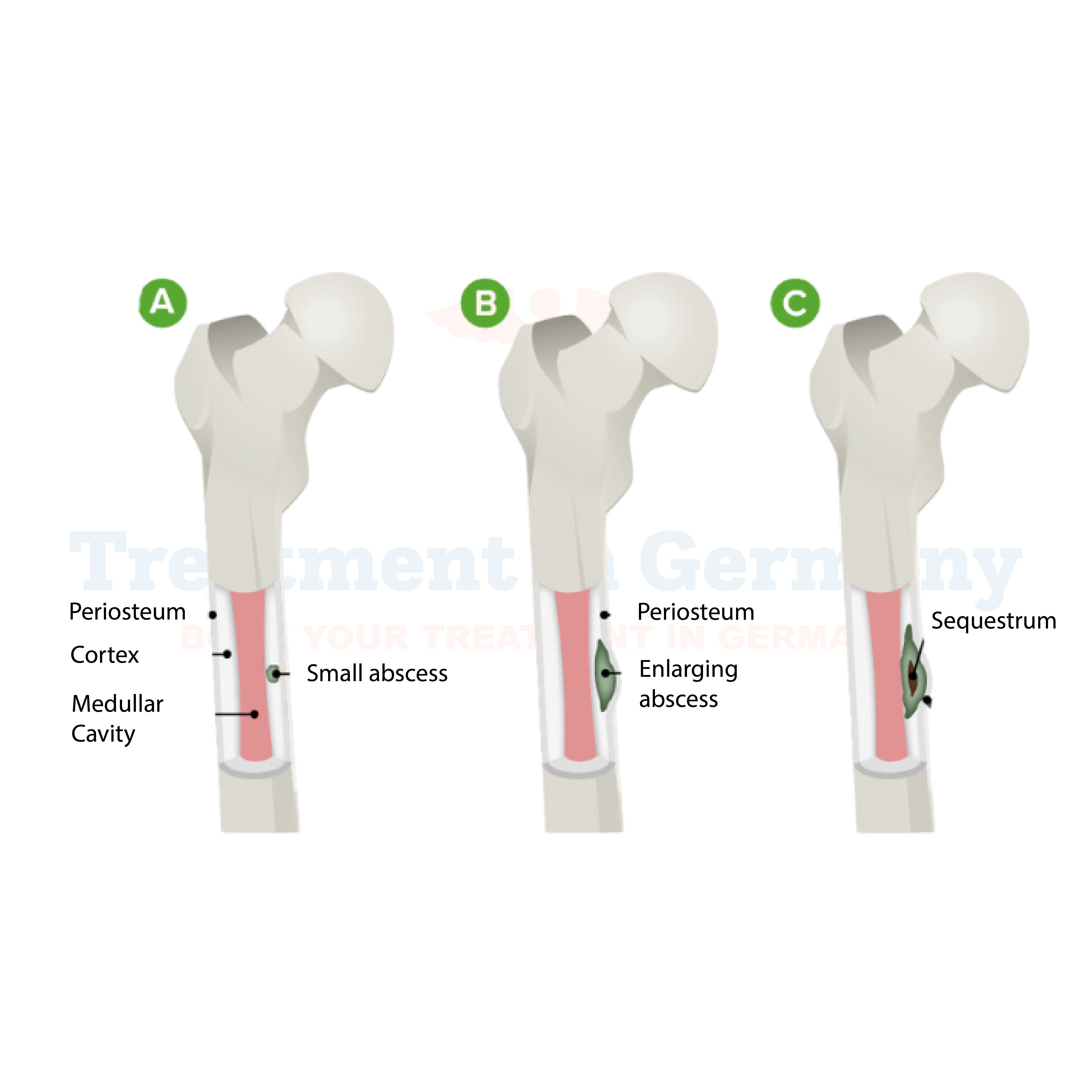
Types of Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis can be categorized into several types based on the source and duration of the infection:
- Acute Osteomyelitis: this type usually occurs right after injury or surgical procedure and shows rapid symptoms, such as fever, pain or redness, This type develops suddenly, usually following an injury or surgical procedure. Immediate treatment with antibiotics is needed, if not treated with antibiotics, surgery is required.
- Chronic Osteomyelitis: This type of infection occurs if Acute Osteomyelitis is left untreated and it lasts for several months or years. Chronic cases often require long-term antibiotic therapy and multiple surgeries to remove infected tissue.
- Hematogenous Osteomyelitis: This occurs when bacteria spread to the bone through the bloodstream. It targets the long bone and is common in children. So. Early diagnosis using blood tests and imaging scans is essential.
- Post-Traumatic Osteomyelitis: This type occurs when an open wound exposes the bone to bacteria after injury or surgery, Treatment typically includes antibiotics, surgery, and careful wound care.
- Vertebral Osteomyelitis: This rare form affects the spine and can lead to severe pain, neurological issues, or deformities. Treatment may involve antibiotics, surgery, and long-term physical therapy.
- Diabetic Osteomyelitis: This is common in people with diabetes, it usually effect feet or lower body, Diabetic patients, due to having poor circulation and immune system are at greater risk.
Risk Factors for Osteomyelitis
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing osteomyelitis, including:
- Diabetes: Poor immune system and blood circulation in diabetic patients make them more at risk.
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions such as HIV, cancer, and autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis) can affect the body's ability to fight infections.
- Recent Surgery or Injury: Any procedure or trauma that exposes the bone to an external wound leads to infection.
- Poor Circulation: Conditions like peripheral artery disease or vascular insufficiency can restrict the body’s ability to fight infection, increasing the risk of osteomyelitis.
- Intravenous Drug Use: Using needles or injecting drugs can introduce bacteria directly into the bloodstream, leading to osteomyelitis.
Symptoms of Osteomyelitis
The symptoms of osteomyelitis can vary depending on the location and severity of the infection. Common signs include:
- Pain at the Infection Site: This may be constant and worsen with movement.
- Swelling and Redness: Inflammation around the infected area may cause visible swelling, heat, and redness.
- Fever: Many patients experience fever as the body tries to fight the infection.
- Fatigue and Malaise: Patients may feel generally unwell due to the systemic effects of the infection.
- Drainage or Pus: In chronic cases, infected bone may drain pus or other fluids, signaling an ongoing infection.
Diagnosis and Diagnostic Tools
The diagnosis of osteomyelitis is based on a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Common diagnostic tools include:
- Blood Tests: Increased white blood cell counts and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels can indicate an infection.
- X-rays: It is used to detect bone damage or abscess formation, but cannot identify the early stage of infection.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI scans are imaging tools for diagnosing osteomyelitis, as it shows both the infection and any damage to the surrounding tissues.
- CT (Computed Tomography) Scans: It is used to assess bone damage and guide surgical planning.
- Bone Biopsy: A sample of infected bone tissue may be taken for culture to identify the exact pathogen causing the infection.
Treatment in Germany
Germany offers a range of innovative treatment options for osteomyelitis, utilizing the latest medical technology and expert care from doctors, surgeons, and specialists. Treatment typically includes:
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics target the specific bacteria causing the infection. In some cases, long-term oral antibiotics are prescribed.
- Surgical Intervention: Surgeons in Germany are skilled at removal of infected tissue and reconstructive surgery to restore bone function.
- Pain Relievers: Pain relievers are the main aspect of osteomyelitis treatment, with various pain relievers prescribed to reduce discomfort during recovery.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapists work with patients to help restore mobility and strength after the infection has been controlled.
Conclusion
Germany’s hospitals are equipped with state-of-the-art facilities and utilize innovative treatment methods to ensure the best outcomes for osteomyelitis patients. Specialized care, including the use of MRI and CT scans, ensures precise diagnosis and effective treatment planning.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
