Discover advanced treatment and care options in Germany to prevent fractures and restore bone health.
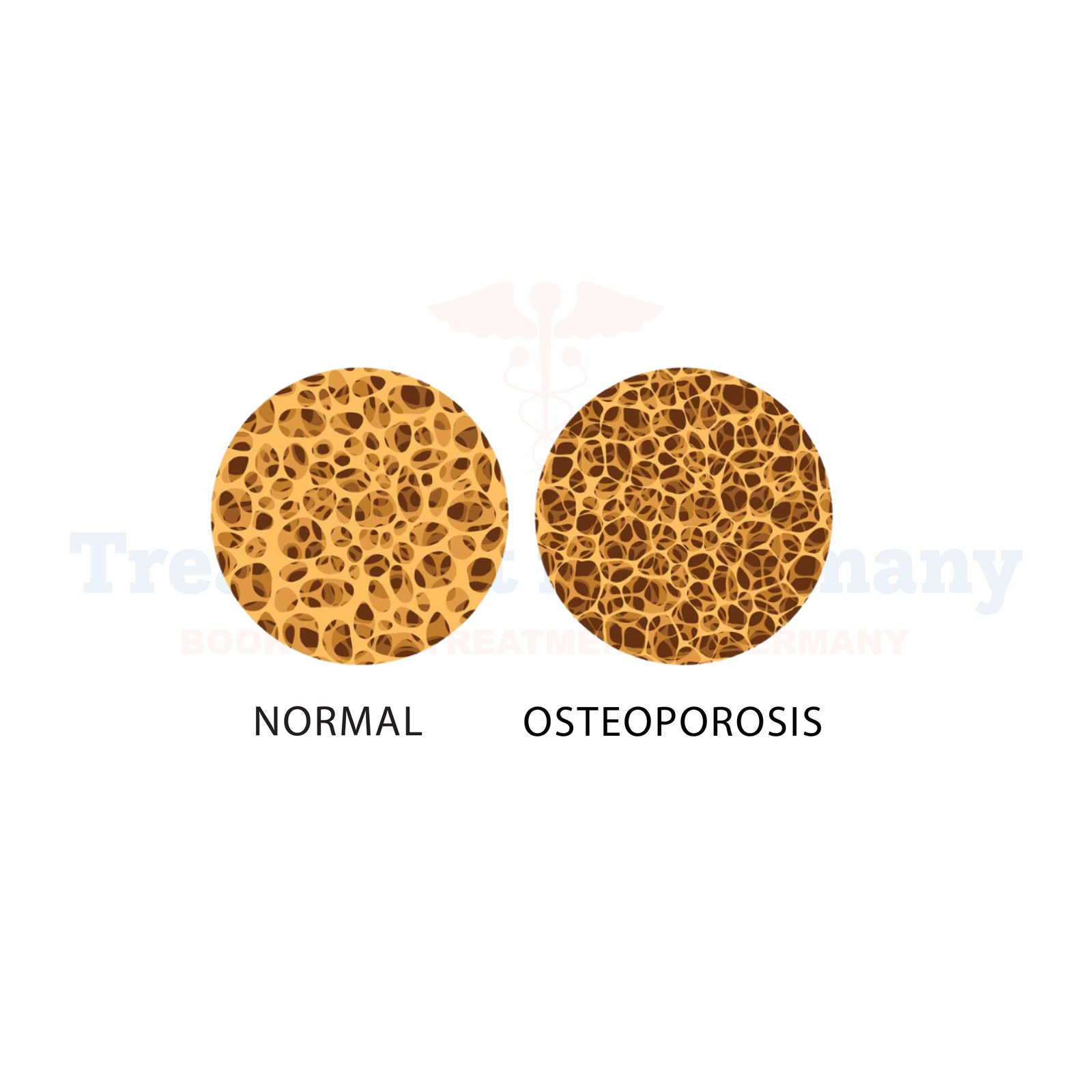
Osteoporosis is a medical condition that leads to the loss of bone density. Osteoporosis silently weakens your bones, making fractures more likely. Over time, your bones become fragile and more susceptible to fractures, even from minor injuries or falls. Often called the “silent disease,” osteoporosis progresses without obvious symptoms until a fracture occurs.
Side Effects of Osteoporosis
While often symptomless, some warning signs include. Potential symptoms suffered by osteoporosis patients can be:
Causes of Osteoporosis
The exact cause for osteoporosis does not remain same in all patients, but osteoporosis can be led by:
Diagnosis of Osteoporosis
Doctors rely on thorough assessments, including:
Osteoporosis Treatment in Germany
Effectively managing osteoporosis often involves a combination of approaches, including:
Prevention and Management
Take proactive steps to protect your bones by focusing on prevention and managing risk factors like:
Why Choose Treatment in Germany?
Germany is a global leader in medical advancements, offering exceptional osteoporosis care.
Conclusion
Don’t wait for osteoporosis to slow you down. Explore globally recognized treatment options in Germany that can help prevent complications and improve your quality of life. Choosing Germany for osteoporosis treatment means accessing cutting-edge medical care, personalized treatment plans, and a commitment to improving patient outcomes. With world-class facilities, expert specialists, and innovative approaches, you can take control of your bone health and regain a better quality of life. Start your journey to stronger bones today.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
