What is Osteosarcoma?
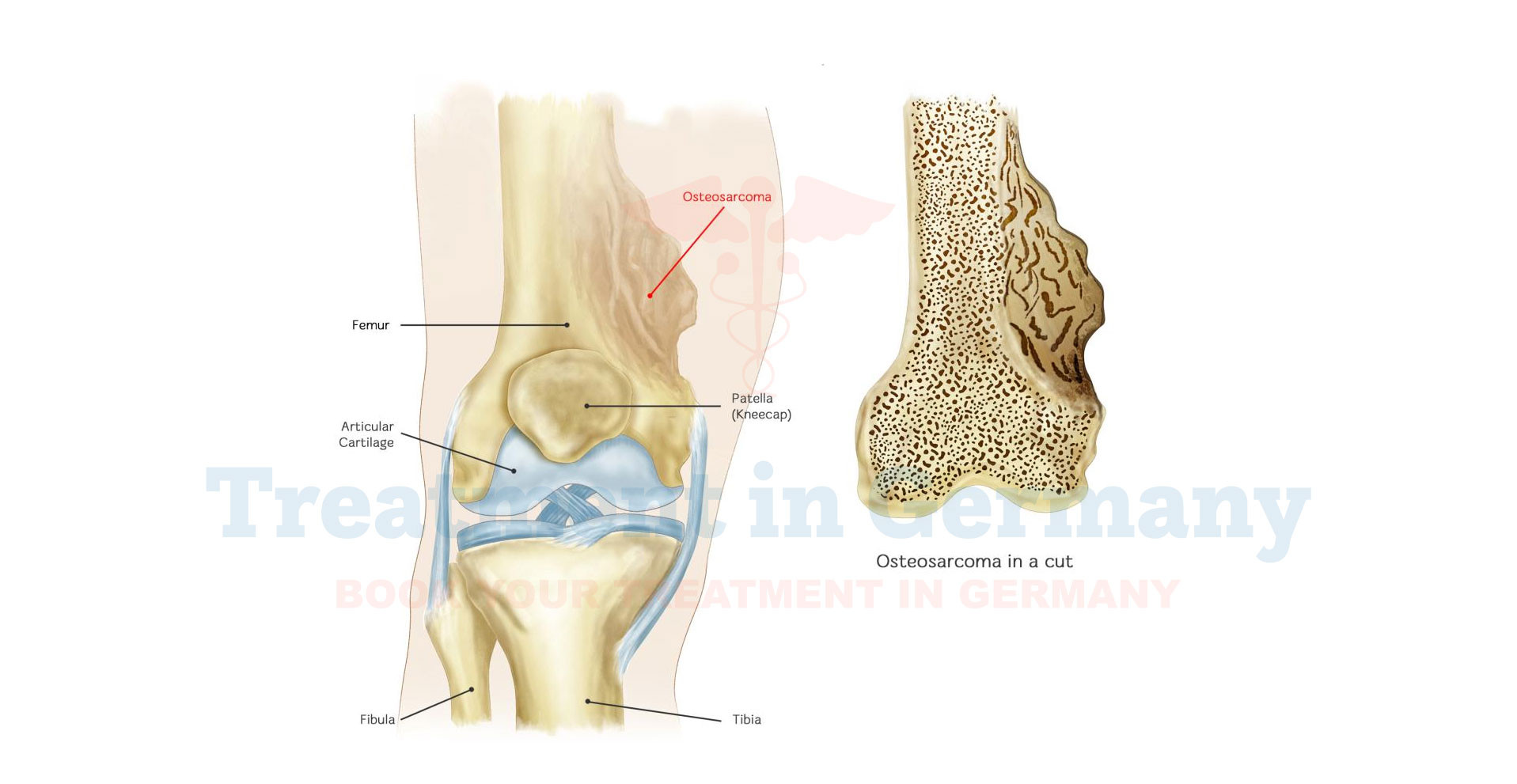
Osteosarcoma is a rare but aggressive type of cancer that originates in the bone. It primarily affects adolescents and young adults, though it can occur at any age.
This malignancy arises from osteoblasts, the cells responsible for bone formation, leading to the development of tumors in the bones.
The most commonly affected areas are the long bones, such as those in the arms and legs, though it can also occur in other bones and, in rare cases, outside the bones.
Side Effects of Osteosarcoma
Osteosarcoma can lead to a range of symptoms and side effects, including:
- Pain and Swelling: One of the most common symptoms is localized pain and swelling in the affected bone, which may worsen over time.
- Limited Range of Motion: If the tumor is near a joint, it can impair movement and flexibility.
- Fractures: The affected bone may become weakened, leading to fractures with minimal trauma.
- Fatigue and Weight Loss: As with many cancers, general fatigue, weight loss, and a feeling of being unwell can occur.
- Other Systemic Symptoms: Advanced cases may cause systemic symptoms such as fever and night sweats.
How is Osteosarcoma Diagnosed?
Diagnosing osteosarcoma typically involves a combination of the following procedures:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Your doctor will assess your symptoms, medical history, and perform a physical exam to identify any unusual findings.
Imaging Tests:
- X-rays: Often the first step to visualize any abnormalities in the bone structure.
- MRI Scans: Provide detailed images of the tumor and its extent in surrounding tissues.
- CT Scans: Help in assessing the spread of cancer to other areas, such as the lungs.
- Bone Scintigraphy: This scan can reveal any other potential areas of bone involvement.
- Biopsy: A crucial step for definitive diagnosis, involving the removal of a sample of the tumor for microscopic examination to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
- Blood Tests: Though not diagnostic on their own, blood tests can help evaluate overall health and support the diagnosis.
Potential Treatment of Osteosarcoma
Treatment for osteosarcoma typically involves a multidisciplinary approach tailored to the individual’s condition. Options include:
- Surgery: Often the primary treatment, aiming to remove the tumor and a margin of healthy tissue around it. In some cases, limb-sparing surgery is possible, while amputation may be necessary depending on the tumor's location and size.
- Chemotherapy: Used to target and destroy cancer cells that may have spread beyond the primary tumor. This treatment is often administered before surgery (neoadjuvant chemotherapy) to shrink the tumor and after surgery (adjuvant chemotherapy) to eliminate any remaining cancer cells.
- Radiation Therapy: While less common for osteosarcoma, it may be used in cases where surgery is not feasible or to target specific areas where cancer has spread.
- Clinical Trials: Participation in clinical trials may provide access to innovative treatments and therapies not yet widely available.
.👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
