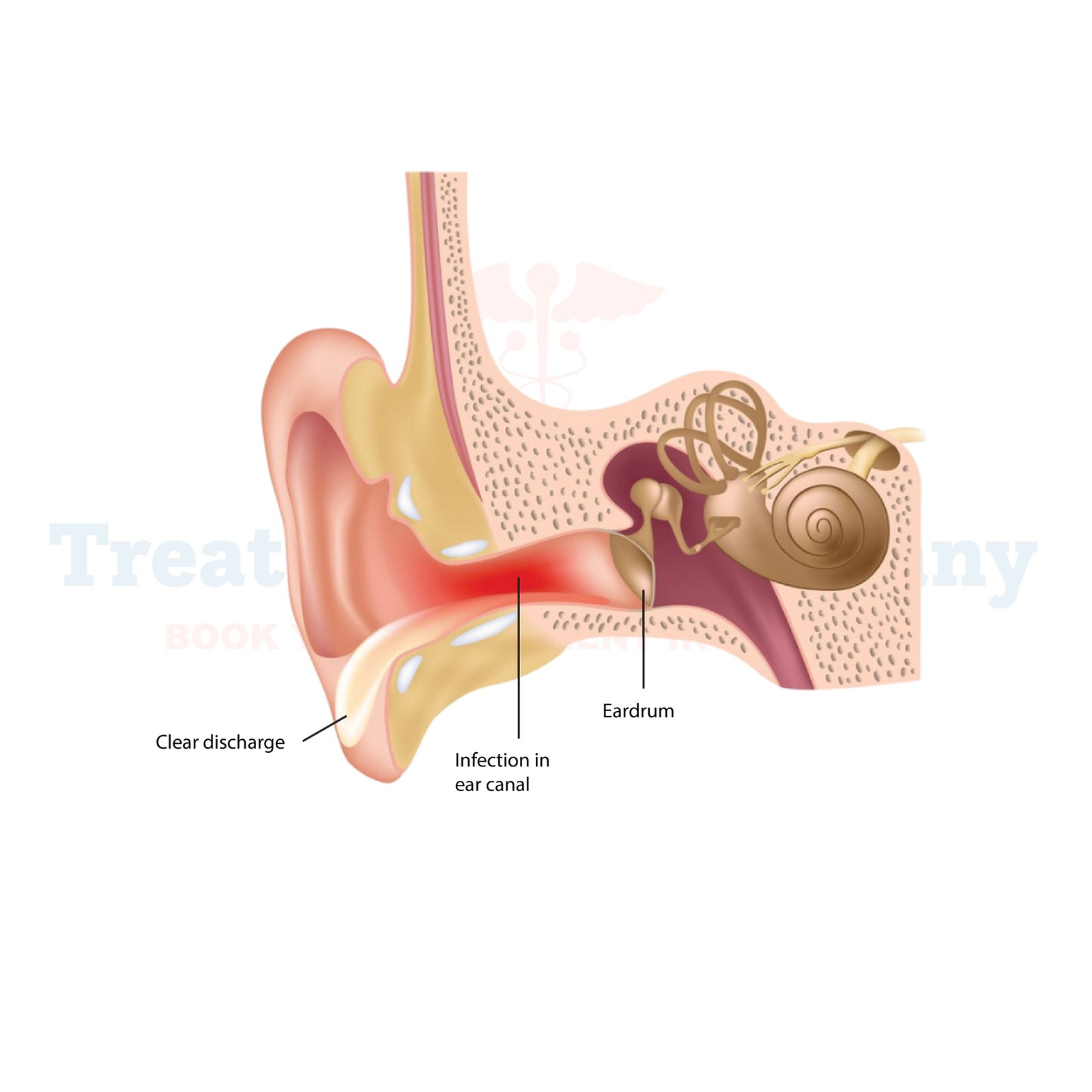
What is Otitis Externa (Swimmer's Ear):
Otitis externa, commonly known as Swimmer's Ear, is a painful condition affecting the outer ear canal. It typically occurs when water, bacteria, or fungi enter the ear canal, leading to inflammation and infection. Swimmer's Ear is often associated with activities involving water, such as swimming, hence its name. However, it can also develop from other causes like excessive moisture in the ear, scratches or abrasions in the ear canal, or allergic reactions to certain substances.
Side effects of Otitis Externa (Swimmer's Ear):
The symptoms of Swimmer's Ear can vary in severity but commonly include:
If left untreated, Swimmer's Ear can lead to complications such as a spread of the infection to surrounding tissues or a chronic infection that is difficult to treat.
How is Otitis Externa (Swimmer's Ear) diagnosed?:
To diagnose Swimmer's Ear, a healthcare professional will typically perform a physical examination of the ear canal using an otoscope, a tool that allows them to look inside the ear. They will check for signs of inflammation, redness, swelling, and any discharge. In some cases, a swab of the affected area may be taken to identify the specific bacteria or fungi causing the infection.
Potential treatments of Otitis Externa (Swimmer's Ear):
Treatment for Swimmer's Ear aims to relieve symptoms and eliminate the infection. Depending on the severity of the condition, treatment options may include:
1. Ear drops: Antibiotic or antifungal ear drops are commonly prescribed to treat the infection. These drops are usually applied directly into the ear canal several times a day for a week or more.
2. Pain medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate ear pain and discomfort.
3. Anti-inflammatory medication: In some cases, corticosteroid ear drops may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and swelling in the ear canal.
4. Keeping the ear dry: Patients are advised to keep the affected ear dry during treatment to prevent further irritation and infection. This may involve avoiding swimming or wearing a shower cap while bathing.
5. Avoiding ear manipulation: Patients should refrain from inserting objects such as cotton swabs or fingers into the ear canal, as this can worsen the condition or cause injury.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
