What is Paranasal Sinus Cancer?
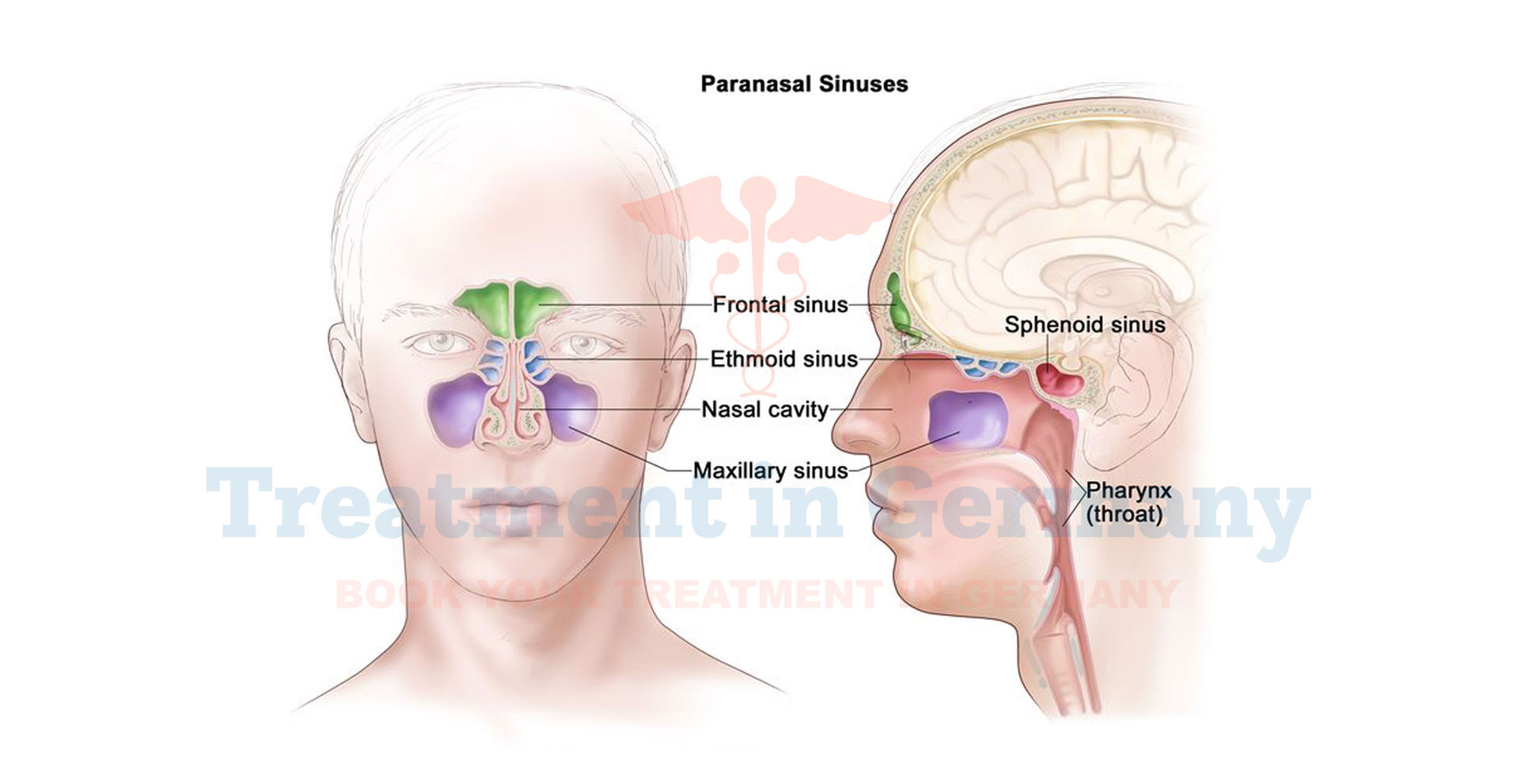
Paranasal sinus cancer refers to a rare type of cancer that develops in the paranasal sinuses, which are hollow spaces around the nose.
These sinuses are lined with cells that produce mucus, helping to moisten and filter the air we breathe. When cancerous cells form in these tissues, they can lead to the development of paranasal sinus cancer. This condition is relatively uncommon, accounting for less than 1% of all cancers.
Side Effects of Paranasal Sinus Cancer
The symptoms and side effects of paranasal sinus cancer can vary depending on the location and extent of the tumor. Common signs may include:
- Persistent nasal congestion or blockage
- Frequent nosebleeds
- Pain or pressure in the face, around the eyes, or in the ears
- Swelling or numbness in the face
- Vision problems
- Loosening of teeth or dentures
- Persistent sinus infections that do not respond to treatment
As the cancer progresses, patients may experience additional symptoms such as weight loss, fatigue, and difficulty breathing through the nose.
How is Paranasal Sinus Cancer Diagnosed?
Diagnosing paranasal sinus cancer typically involves several steps:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Your doctor will review your medical history and conduct a thorough physical examination, focusing on the head and neck area.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging studies such as CT scans, MRI scans, and PET scans are used to visualize the sinuses and determine the size and location of the tumor.
- Biopsy: A biopsy is performed to obtain a sample of tissue from the suspicious area. This sample is then examined under a microscope by a pathologist to determine if cancer cells are present.
- Staging: If cancer is confirmed, further tests may be done to determine the stage of the cancer and whether it has spread to other parts of the body.
Potential Treatment of Paranasal Sinus Cancer
Treatment for paranasal sinus cancer depends on factors such as the location and stage of the cancer, as well as the patient's overall health. Options may include:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor and surrounding tissues is often recommended, especially for early-stage cancers.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy radiation is used to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. It may be used alone or in combination with surgery.
- Chemotherapy: This treatment uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. It may be used when cancer has spread beyond the sinuses or to help shrink tumors before surgery or radiation.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs that target specific abnormalities within cancer cells may be used in some cases.
- Clinical Trials: Patients may also have the option to participate in clinical trials testing new treatments or combinations of treatments.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
