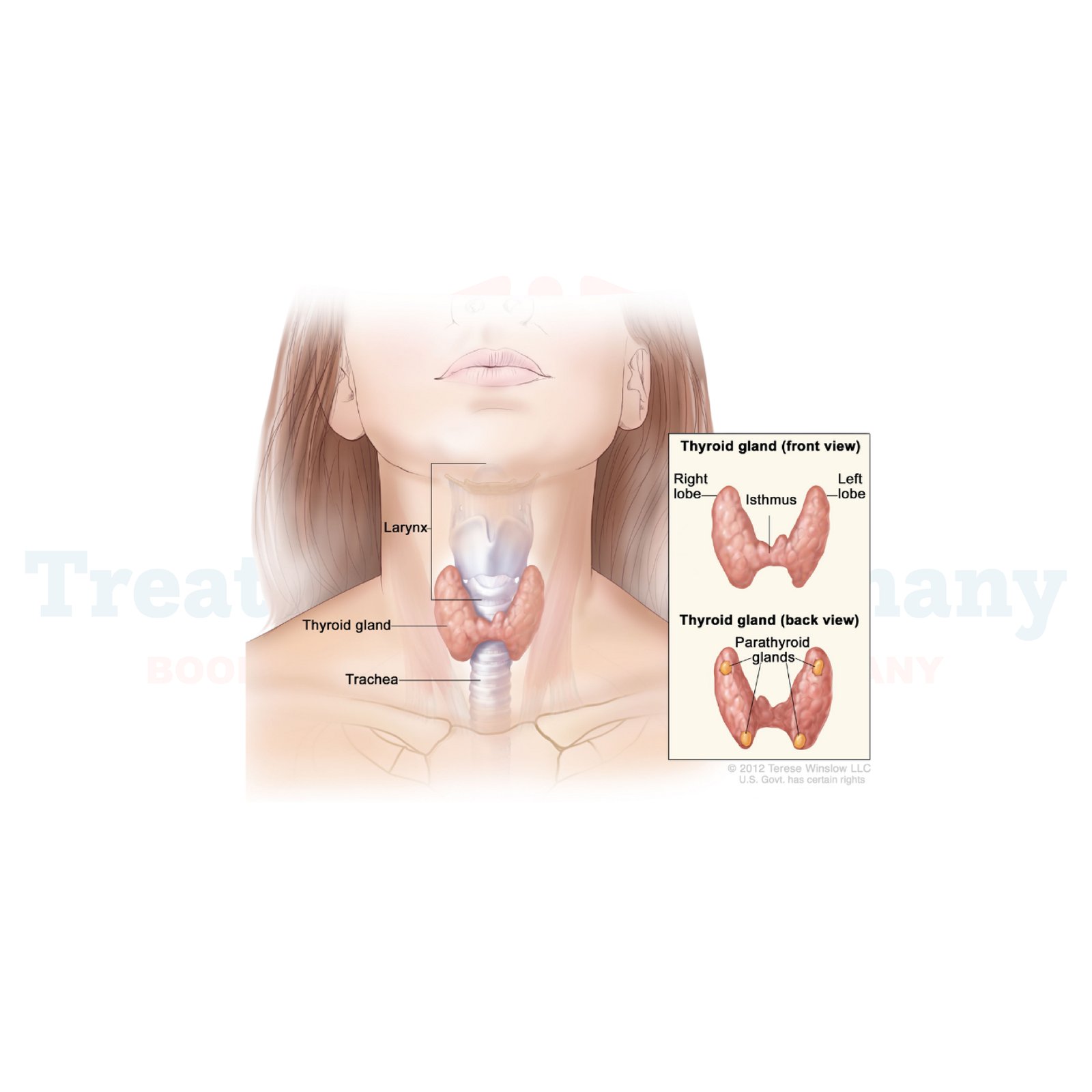
What is Parathyroid Cancer?
Parathyroid cancer is a rare yet serious condition that develops in the parathyroid glands, which are responsible for managing calcium levels in the body. While the disease progresses slowly, its management requires timely and specialized medical care. Surgery remains the most effective treatment, offering the best chance of cure or prolonging life even in cases where cancer has metastasized.
Early diagnosis and treatment are vital to managing hypercalcemia and improving long-term outcomes.
Understanding what may increase your risk of parathyroid cancer is crucial for early detection.
Symptoms of Parathyroid Cancer
While the symptoms may overlap with benign conditions like hyperparathyroidism, it’s important not to ignore them:
How is Parathyroid Cancer Diagnosed?
Germany is equipped with world-class diagnostic tools and medical expertise to confirm and evaluate parathyroid cancer. Common diagnostic methods include:
Parathyroid Cancer Treatment in Germany
Germany offers a comprehensive approach to parathyroid cancer treatment, utilizing a combination of traditional methods and cutting-edge advancements:
Surgery
Surgery is often the first and most critical step in treating parathyroid cancer:
Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapy
Dendritic Cell Therapy
Processes where dendritic cells are programmed to attack cancer cells, boosting the body’s natural defenses.
Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell transplants are emerging as options for those with advanced or metastatic parathyroid cancer. Assisting in tissue regrowth and recovery of critical body functions.
Why Choose Treatment in Germany?
Germany is known for its state-of-the-art facilities, expert oncologists, and personalized care:
World-Class Hospitals
Germany is home to some of the best healthcare facilities globally.
Specialized Expertise
Leading surgeons and oncologists with decades of focused experience in parathyroid cancer treatment.
Cutting-Edge Innovation
Access the latest advancements in surgical techniques and therapies.
Comprehensive Patient Care
Multidisciplinary teams that combine medical, emotional, and psychological support.
Conclusion
Effective and comprehensive treatment for parathyroid cancer is not just a possibility; it’s within reach. Germany is celebrated for its advanced healthcare system, offering cutting-edge treatment options tailored to your unique medical needs. Whether you are seeking surgery, targeted therapy, or innovative treatments like dendritic cell therapy, Germany’s leading cancer experts are here to guide you every step of the way. Begin your healing process with confidence and expertise by your side.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
