What is Pediatric Scoliosis?
Pediatric scoliosis refers to an abnormal sideways curvature of the spine that typically develops in children and adolescents.
This condition can range from mild to severe and may affect the overall alignment of the spine, potentially causing it to twist or rotate.
Side Effects of Pediatric Scoliosis
The effects of pediatric scoliosis can vary depending on the severity and progression of the curvature. Common side effects may include:
How is Pediatric Scoliosis Diagnosed?
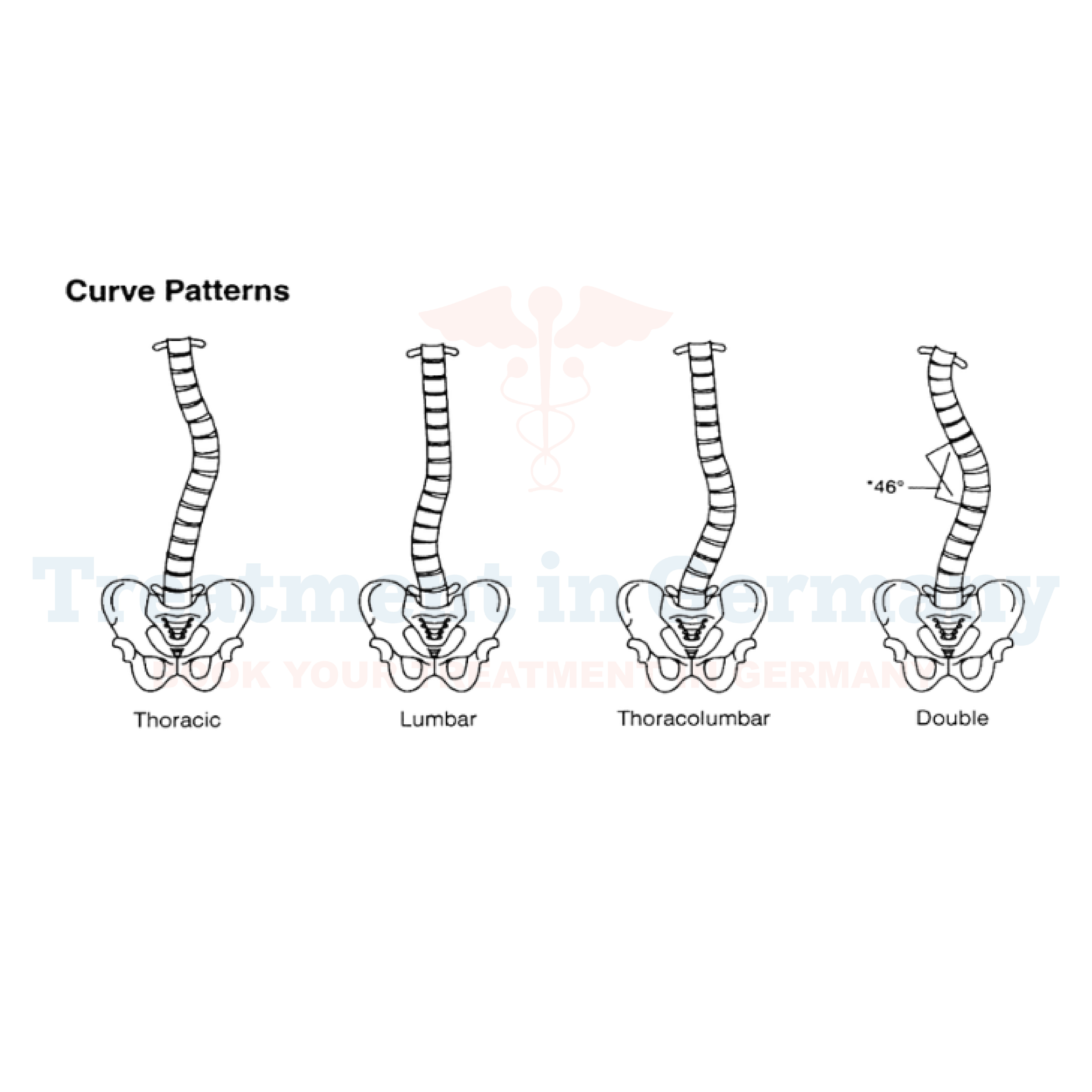
Diagnosing pediatric scoliosis typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and imaging studies such as X-rays.
During the physical exam, the doctor will assess the child's spine for signs of curvature, asymmetry, or abnormal alignment. X-rays provide detailed images that help measure the degree of curvature and determine the specific type of scoliosis present.
Potential Treatments for Pediatric Scoliosis
Treatment options for pediatric scoliosis depend on several factors including the age of the child, the degree of curvature, and the potential for progression. Common approaches include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
