What is Pediatric Sickle Cell Disease?
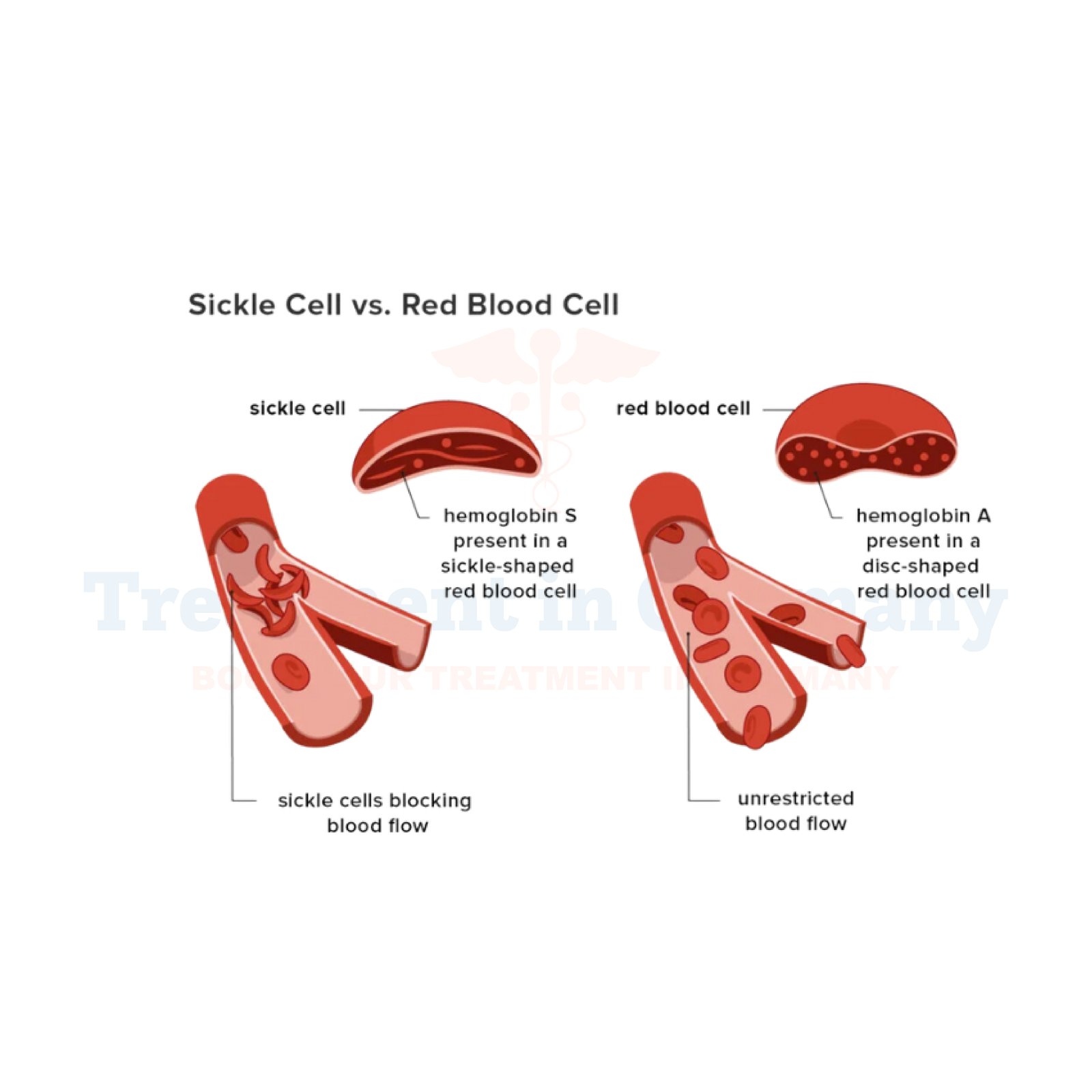
Pediatric Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is an inherited blood disorder characterized by abnormal hemoglobin, known as hemoglobin S.
This genetic condition causes red blood cells to become rigid and crescent-shaped (like a sickle), rather than round. These abnormal cells can stick together and block blood flow, leading to pain and potential organ damage.
SCD affects primarily people of African, Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, and Indian ancestry.
Side Effects of Pediatric Sickle Cell Disease
The symptoms and complications of Pediatric Sickle Cell Disease can vary widely. Common side effects include:
How is Pediatric Sickle Cell Disease Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves several tests, including:
Early diagnosis is crucial to initiate proper management and prevent complications.
Potential Treatment of Pediatric Sickle Cell Disease
While there is no universal cure for Pediatric Sickle Cell Disease, several treatments can manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
