What is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)?
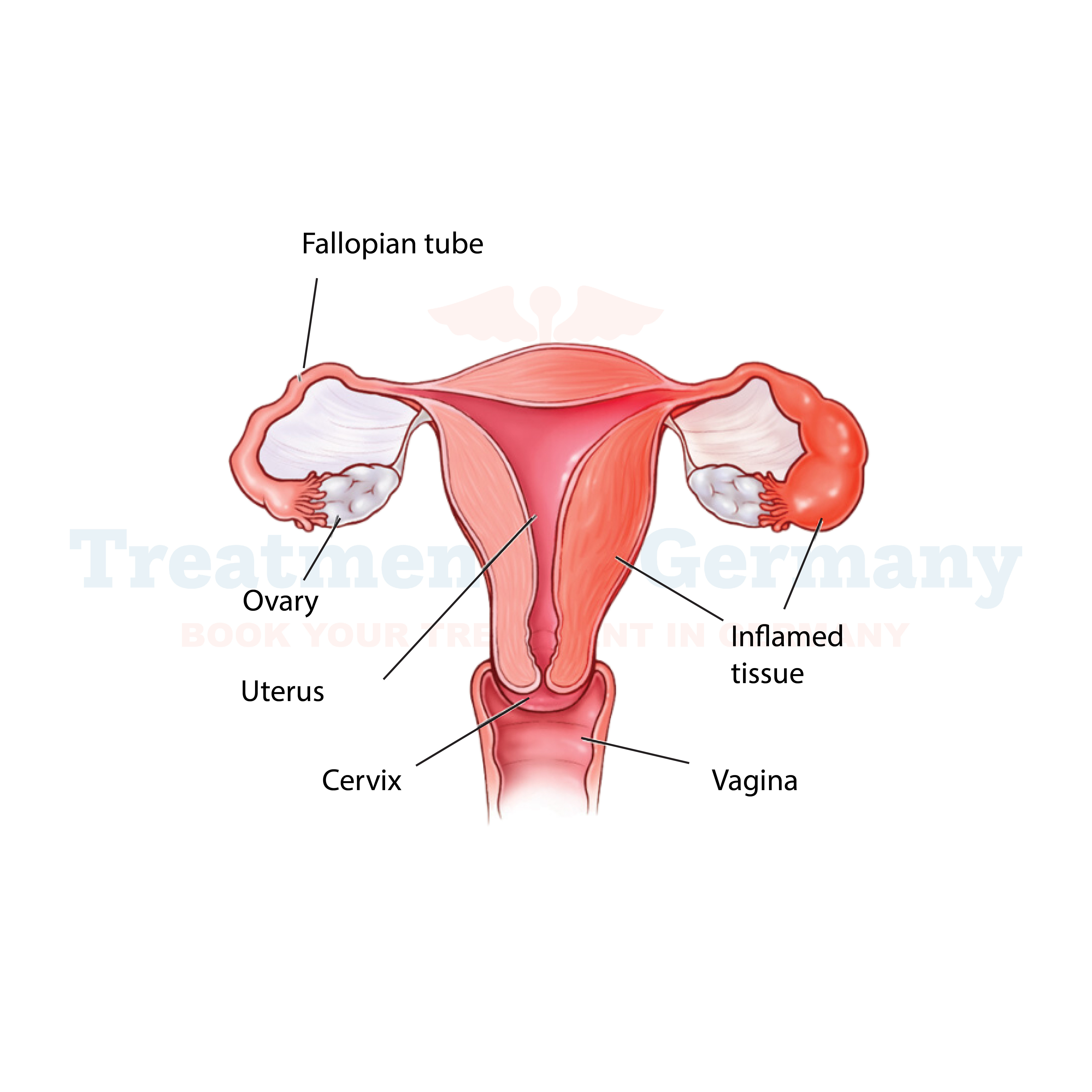
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) is an infection of a woman's reproductive organs. It typically occurs when sexually transmitted bacteria spread from the vagina to the uterus, fallopian tubes, or ovaries.
PID can cause serious complications if left untreated, including infertility, chronic pelvic pain, and an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Side effects of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID):
The symptoms of PID can vary in severity, but commonly include:
How is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) diagnosed?
Diagnosing PID typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Your doctor may:
Potential treatments of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID):
Treatment for PID typically involves a combination of antibiotics to eradicate the infection and relieve symptoms. In Germany, healthcare providers may prescribe antibiotics such as doxycycline or azithromycin to target the bacteria causing the infection.
It's essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve, to ensure the infection is fully eradicated.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
