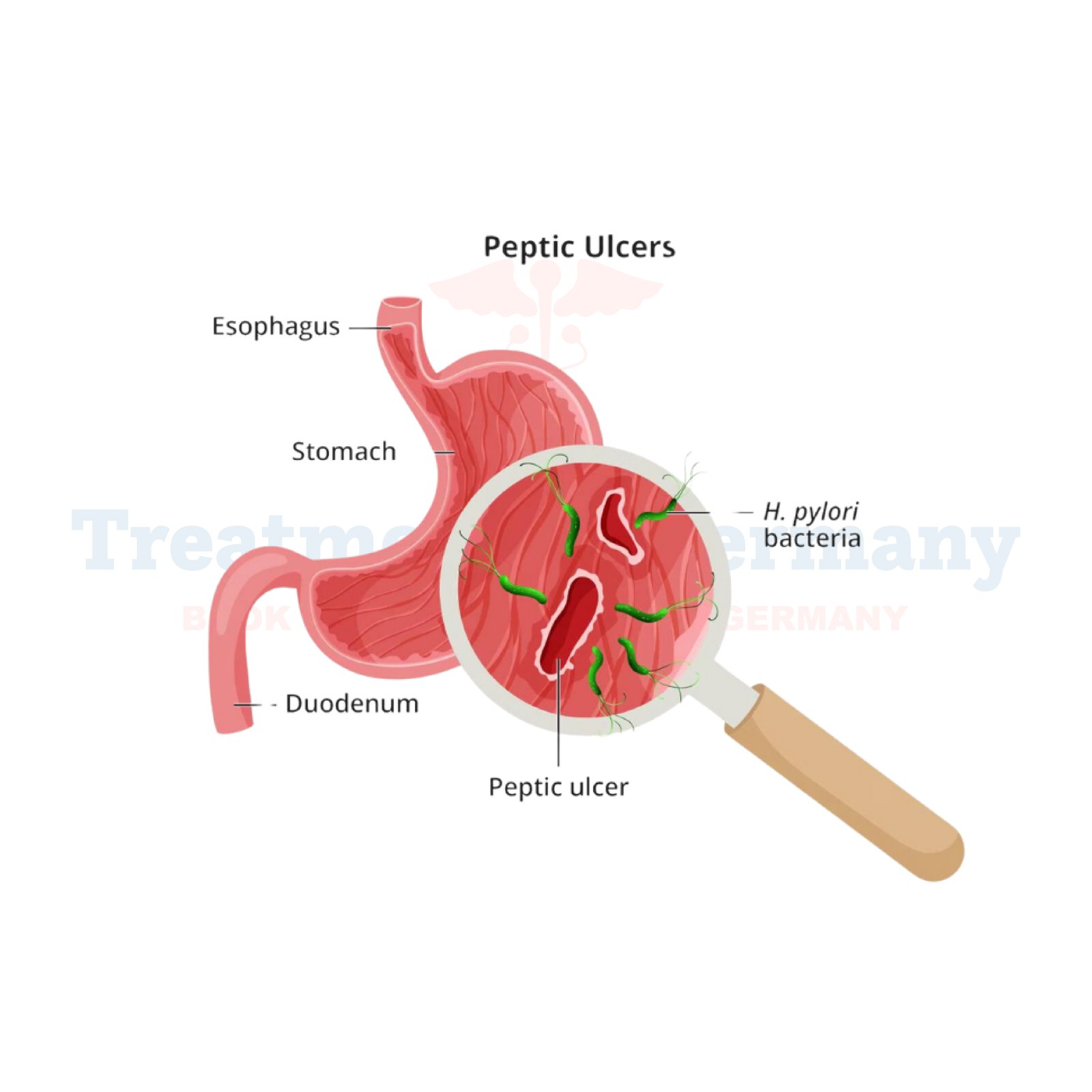
Understanding Peptic Ulcer Disease:
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) is a condition characterized by the development of open sores or ulcers in the lining of the stomach, upper small intestine, or esophagus. These ulcers occur when the protective mucous lining of the digestive tract is eroded, allowing stomach acid to cause irritation and damage to the underlying tissues.
Side Effects of Peptic Ulcer Disease:
The most common symptoms of PUD include abdominal pain, which can range from dull aches to sharp, intense pain, often occurring between meals or during the night. Other symptoms may include bloating, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, and unintended weight loss. In severe cases, complications such as internal bleeding, perforation of the ulcer, or obstruction of the digestive tract may occur, leading to serious medical emergencies.
Diagnosis of Peptic Ulcer Disease:
To Diagnose PUD, healthcare providers may perform a variety of tests, including:
- Endoscopy: A procedure in which a thin, flexible tube with a camera at its tip (endoscope) is inserted through the mouth and into the digestive tract to visually inspect the lining and identify ulcers.
- Upper GI Series: X-ray imaging of the upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract after consuming a contrast material to highlight any abnormalities or ulcers.
- Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) Testing: Blood, stool, or breath tests may be conducted to detect the presence of H. pylori bacteria, a common cause of peptic ulcers.
- Biopsy: During endoscopy, small tissue samples may be collected for further examination under a microscope to confirm the presence of ulcers and rule out other conditions.
Potential Treatments of Peptic Ulcer Disease:
Treatment for PUD aims to relieve symptoms, promote healing of ulcers, and prevent complications. Depending on the underlying cause and severity of the ulcers, treatment options may include:
- Medications: Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), histamine receptor blockers, and antacids are commonly prescribed to reduce stomach acid production and alleviate symptoms. Antibiotics may also be prescribed to eradicate H. pylori infection if present.
- Lifestyle Changes: Avoiding irritants such as spicy foods, alcohol, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), as well as adopting a healthy diet and managing stress, can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
- Endoscopic Therapy: In cases of severe bleeding or complications such as perforation, endoscopic procedures such as cauterization, injection therapy, or placement of clips or stents may be performed to stop bleeding or repair the ulcer.
- Surgery: In rare cases where ulcers do not heal with medication or endoscopic therapy, or if complications such as perforation or obstruction occur, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove the affected tissue or repair the digestive tract.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
