Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment in Germany
Peripheral Neuropathy (PN) is a condition affecting the peripheral nervous system, which transmits signals between the brain, spinal cord, and the rest of the body. It can result from various causes, including diabetes, infections, autoimmune diseases, and exposure to toxins. The symptoms range from mild numbness and tingling to severe pain, muscle weakness, and coordination problems. Germany is known for its cutting-edge medical treatments, including innovative therapies such as stem cell treatment, nerve regeneration techniques, and dendritic cell therapy.
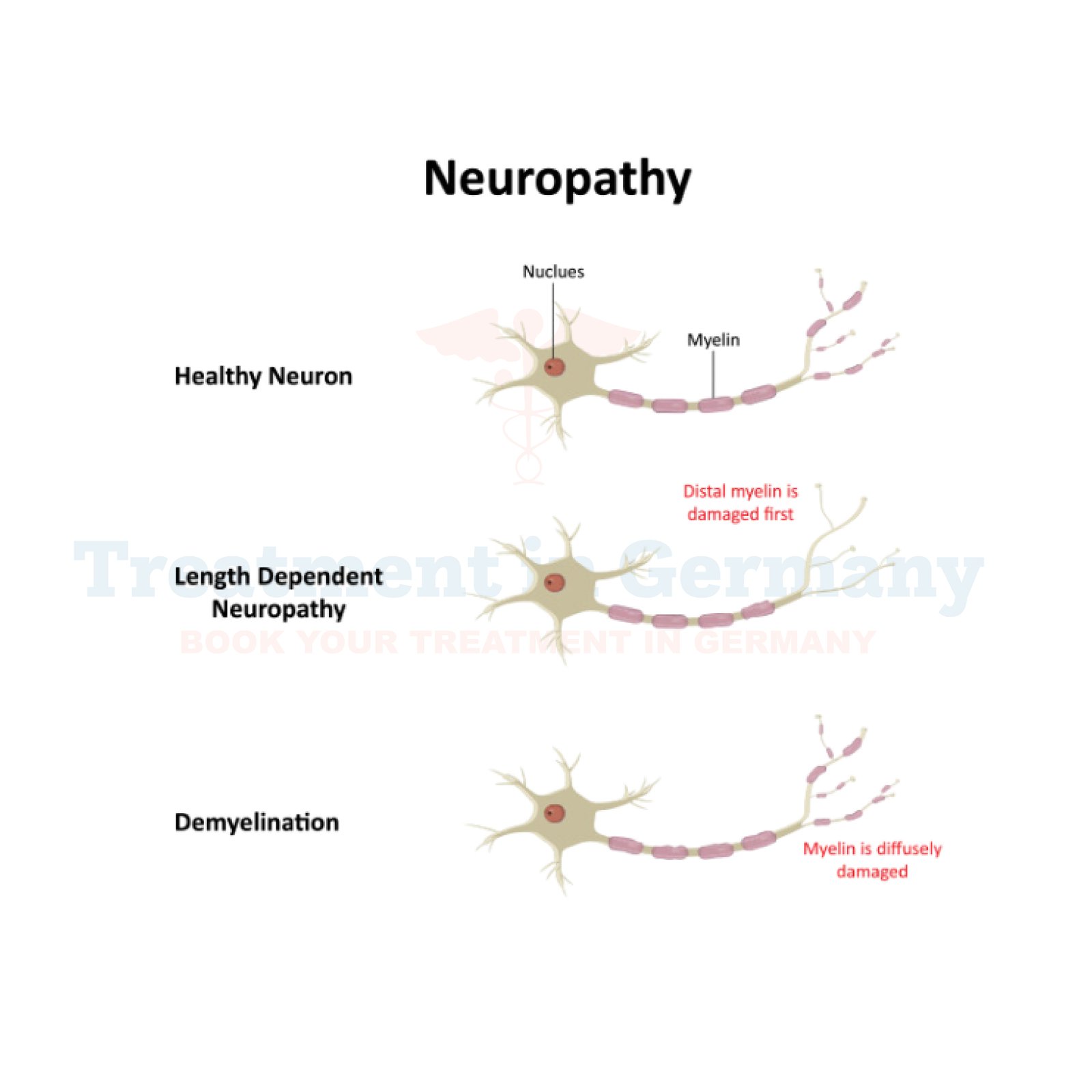
Peripheral Neuropathy occurs when the peripheral nerves are damaged or malfunction. It can affect sensory, motor, and autonomic nerves, leading to different symptoms depending on the type of nerves involved. The condition can be acute or chronic and may progressively worsen if left untreated.
Types of Peripheral Neuropathy
- Mononeuropathy: Damage to a single nerve, often due to trauma or prolonged pressure.
- Polyneuropathy: Affects multiple nerves, commonly seen in diabetes and autoimmune diseases.
- Sensory Neuropathy: Involves nerve damage affecting sensation, leading to tingling, numbness, and pain.
- Motor Neuropathy: Affects movement and muscle control, causing weakness and atrophy.
- Autonomic Neuropathy: Impairs involuntary functions like heart rate, digestion, and blood pressure.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Diabetes: The most common cause, leading to diabetic neuropathy.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Guillain-Barré syndrome.
- Infections: Such as Lyme disease, HIV/AIDS, and hepatitis.
- Vitamin Deficiencies: Deficiencies in B vitamins, especially B12.
- Toxins and Medications: Chemotherapy drugs, excessive alcohol consumption, and heavy metal exposure.
- Genetic Disorders: Some inherited conditions, such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.
- Trauma or Injury: Physical injuries causing nerve compression or damage.
- Obesity: Higher body mass index (BMI) contributes to nerve inflammation.
- High Cholesterol: Affects blood flow to nerves.
- Diabetes-Related Complications: Poor glucose control worsens nerve damage.
Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy
- Numbness and Tingling: Often starts in the hands and feet.
- Sharp, Burning Pain: Worsens at night or during rest.
- Muscle Weakness: Leads to difficulty walking or performing tasks.
- Loss of Coordination: Affects balance and motor skills.
- Autonomic Dysfunction: Causes dizziness, digestive problems, and abnormal sweating.
- Cold Sensitivity: Feeling extreme temperature changes in affected areas.
- Loss of Reflexes: Delayed reactions and poor mobility.
Diagnosis and Diagnostic Tools
Germany is at the forefront of neuropathy diagnostics, utilizing advanced tools such as:
- Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS): Measures electrical signals in nerves.
- Electromyography (EMG): Evaluates muscle response and nerve function.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Detects nerve compression and damage.
- CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: Helps rule out structural abnormalities.
- Blood Tests: Identifies underlying conditions like diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, and autoimmune diseases.
- Skin Biopsy: Examines nerve fiber density for small fiber neuropathy diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Peripheral Neuropathy in Germany
Germany offers world-class treatments for Peripheral Neuropathy, combining conventional and regenerative medicine approaches.
Medications and Pain Management
- Pain Relievers: NSAIDs, opioids (in severe cases), and topical treatments.
- Antidepressants: Such as amitriptyline or duloxetine, which help with nerve pain.
- Anticonvulsants: Like gabapentin and pregabalin to reduce nerve pain signals.
- Corticosteroids: Used for inflammatory neuropathies.
Regenerative and Advanced Therapies
- Dendritic Cell Therapy: Helps modulate the immune system and reduce inflammation.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Aims to regenerate damaged nerve cells and improve function.
- Plasma Exchange (Plasmapheresis): Used in autoimmune-related neuropathies.
- TACE (Transarterial Chemoembolization): Investigated for potential benefits in neuropathy treatment.
- Gene Therapy: Experimental techniques aiming to correct genetic nerve disorders.
Surgical and Physical Interventions
- Nerve Decompression Surgery: Relieves pressure on affected nerves.
- Physical Therapy: Enhances mobility, strength, and coordination.
- Occupational Therapy: Assists in regaining fine motor skills and daily function.
- Complementary Therapies: Acupuncture, massage, and alternative pain management techniques.
Why Choose Treatment in Germany?
State-of-the-Art Medical Facilities: Leading hospitals specializing in neurology and nerve regeneration.
- Expert Specialists: Neurologists, pain management experts, and surgeons with extensive experience.
- Innovative Therapies: Access to cutting-edge treatments not widely available elsewhere.
- Comprehensive Rehabilitation Centers: Providing holistic recovery plans.
- Personalized Care Plans: Tailored to each patient’s needs and condition severity.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: Collaboration between neurologists, physiotherapists, and regenerative medicine experts.
Prevention and Management
- Control Blood Sugar Levels: Essential for diabetic neuropathy prevention.
- Healthy Diet: Rich in vitamins B12, D, and antioxidants.
- Regular Exercise: Improves blood circulation and nerve health.
- Avoid Toxins: Limit alcohol and avoid exposure to harmful chemicals.
- Routine Check-ups: Early detection ensures better treatment outcomes.
- Stress Management: Reducing stress improves nerve function.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy BMI prevents nerve strain.
Conclusion
Peripheral Neuropathy is a complex condition requiring specialized care. Germany’s advanced medical facilities, expert neurologists, and innovative treatments offer hope for patients seeking effective management and potential recovery. With regenerative therapies like dendritic cell therapy and stem cell treatments, Germany continues to lead in neuropathy treatment, providing cutting-edge solutions for better nerve health and quality of life.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
