What is Pernicious Anemia?
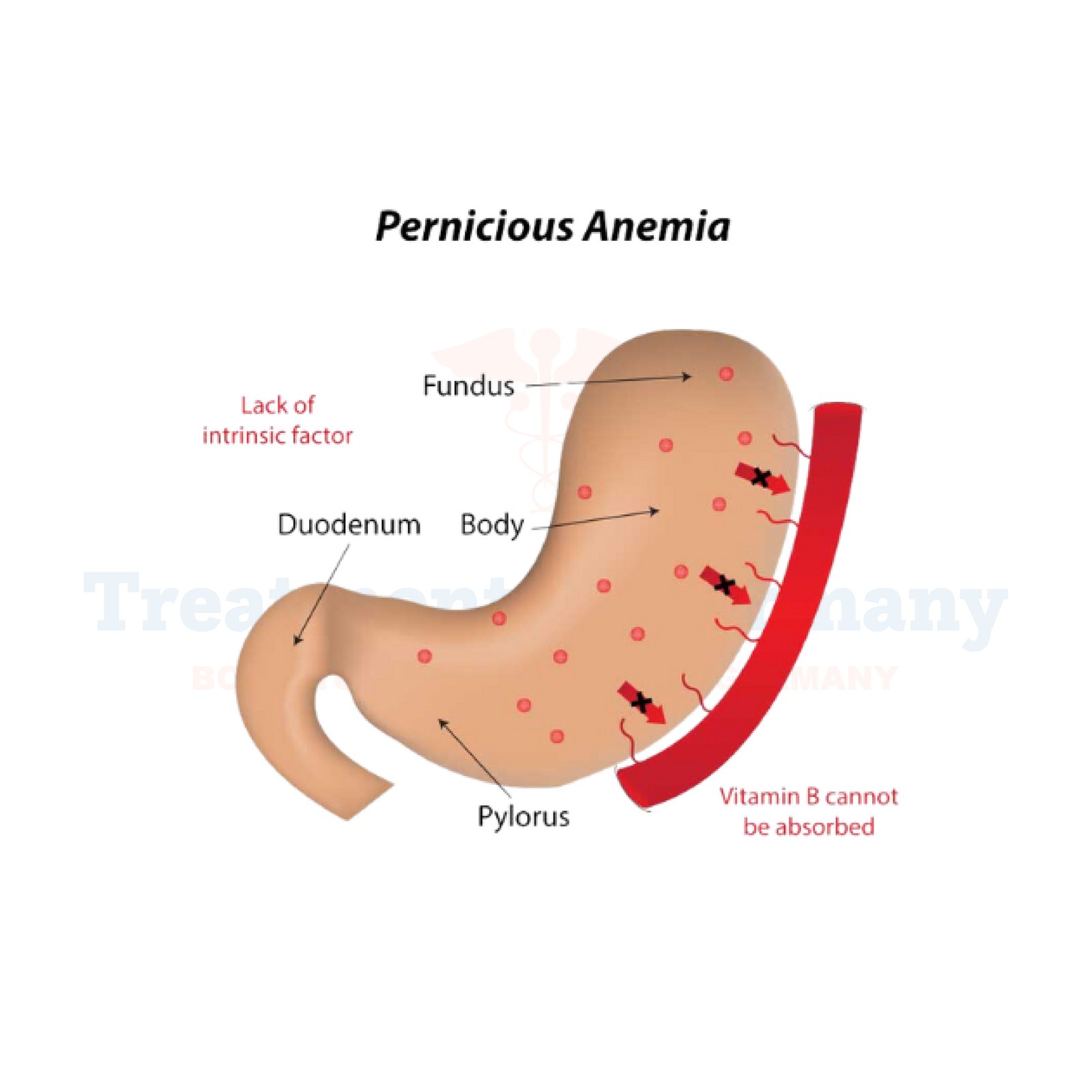
Pernicious Anemia is a type of anemia caused by the body's inability to absorb vitamin B12 from the gastrointestinal tract. In Germany, it is known as "Perniziöse Anämie."
This condition arises due to the lack of intrinsic factor, a protein produced in the stomach that is necessary for B12 absorption. Without adequate B12, the body cannot produce enough healthy red blood cells, leading to anemia.
Side Effects of Pernicious Anemia
The symptoms of Pernicious Anemia can vary but often include fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, pale or jaundiced skin, and a tingling or numbness in the hands and feet.
Patients may also experience difficulty walking, balance problems, and mood changes. If left untreated, Pernicious Anemia can lead to serious complications affecting the nervous system and potentially causing irreversible nerve damage.
How is Pernicious Anemia Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and specific blood tests. These tests measure levels of vitamin B12 in the blood and may also assess levels of folate and red blood cells.
Additionally, tests for antibodies to intrinsic factor and parietal cells are often performed to confirm the diagnosis of autoimmune Pernicious Anemia.
Potential Treatment of Pernicious Anemia
Treatment aims to replace the deficient vitamin B12 and manage symptoms effectively. In Germany, treatment options may include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
