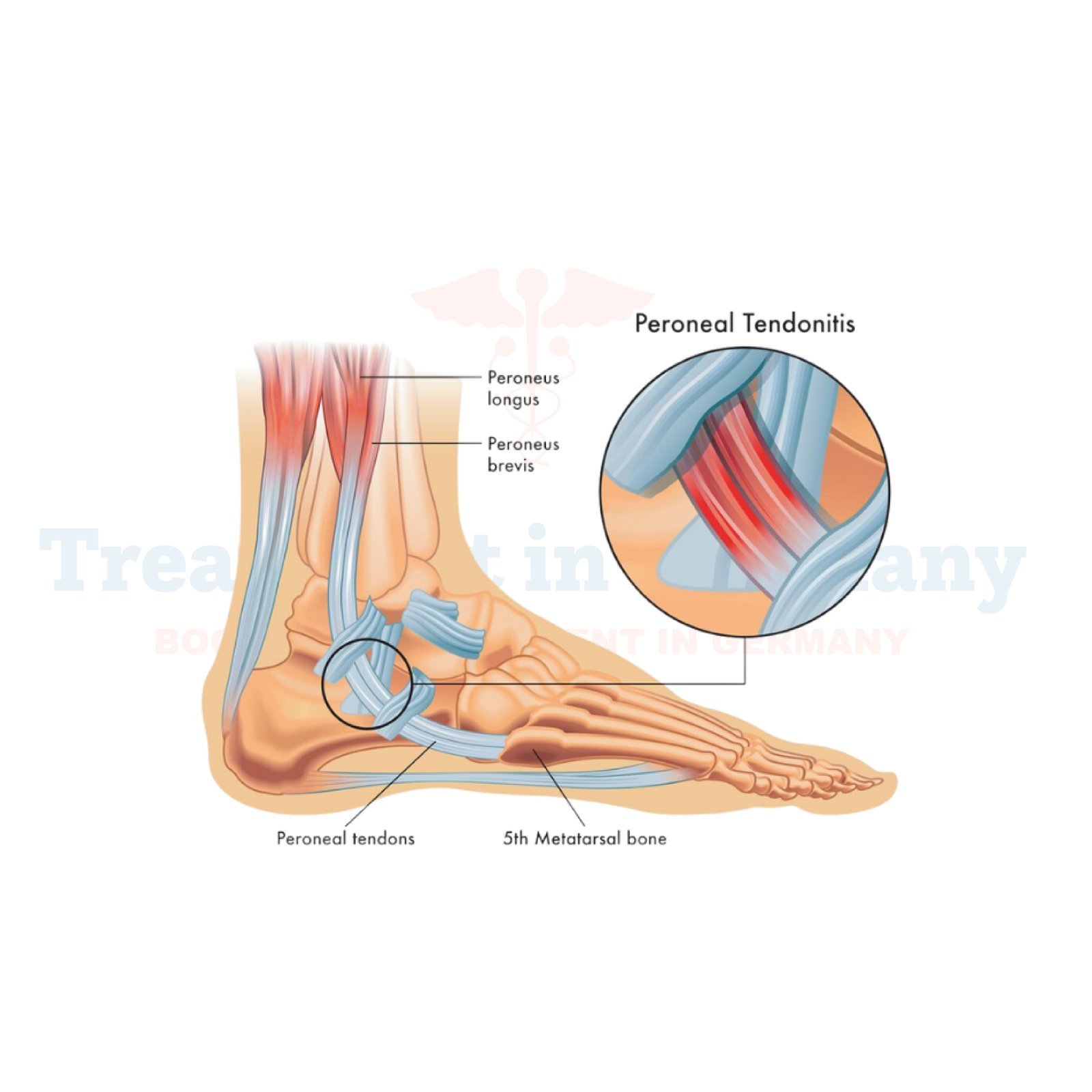
What is Peroneal Tendonitis:
Peroneal tendonitis is a condition characterized by inflammation or irritation of the peroneal tendons, which are located on the outer side of the lower leg. These tendons play a crucial role in stabilizing the foot and ankle during movement.
Peroneal tendonitis often develops gradually, typically due to overuse or repetitive stress on the tendons. It can cause pain, swelling, and discomfort along the outer part of the ankle and foot.
Side effects of Peroneal Tendonitis:
The symptoms of peroneal tendonitis can vary in severity but commonly include:
Pain along the outer side of the ankle or foot, especially during activities or when bearing weight.
Swelling and tenderness around the area of the affected tendon.
Difficulty or discomfort while moving the ankle or foot, particularly when trying to push off or walk on uneven surfaces.
Weakness or instability in the ankle, which may affect balance and mobility.
How is Peroneal Tendonitis diagnosed?:
Diagnosing peroneal tendonitis typically involves a thorough physical examination by a healthcare professional, where they will assess the patient's symptoms and medical history.
Imaging tests such as X-rays, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may also be ordered to visualize the tendons and rule out other possible causes of pain and discomfort.
Additionally, specialized tests such as the Thompson squeeze test or the peroneal tendon stress test may be performed to evaluate the integrity and function of the peroneal tendons.
Potential treatments of Peroneal Tendonitis:
Treatment for peroneal tendonitis aims to reduce pain, inflammation, and improve the strength and flexibility of the affected tendons. Depending on the severity of the condition, treatment options may include:
Rest and activity modification to avoid aggravating the tendons.
Ice therapy to reduce swelling and alleviate pain.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to help relieve pain and inflammation.
Physical therapy exercises and stretching techniques to improve flexibility and strengthen the muscles supporting the ankle.
Orthotic devices such as braces or shoe inserts to provide support and stability to the foot and ankle.
Corticosteroid injections may be considered in cases of severe pain and inflammation that do not respond to conservative measures.
In rare cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair or reconstruct the damaged peroneal tendons.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
