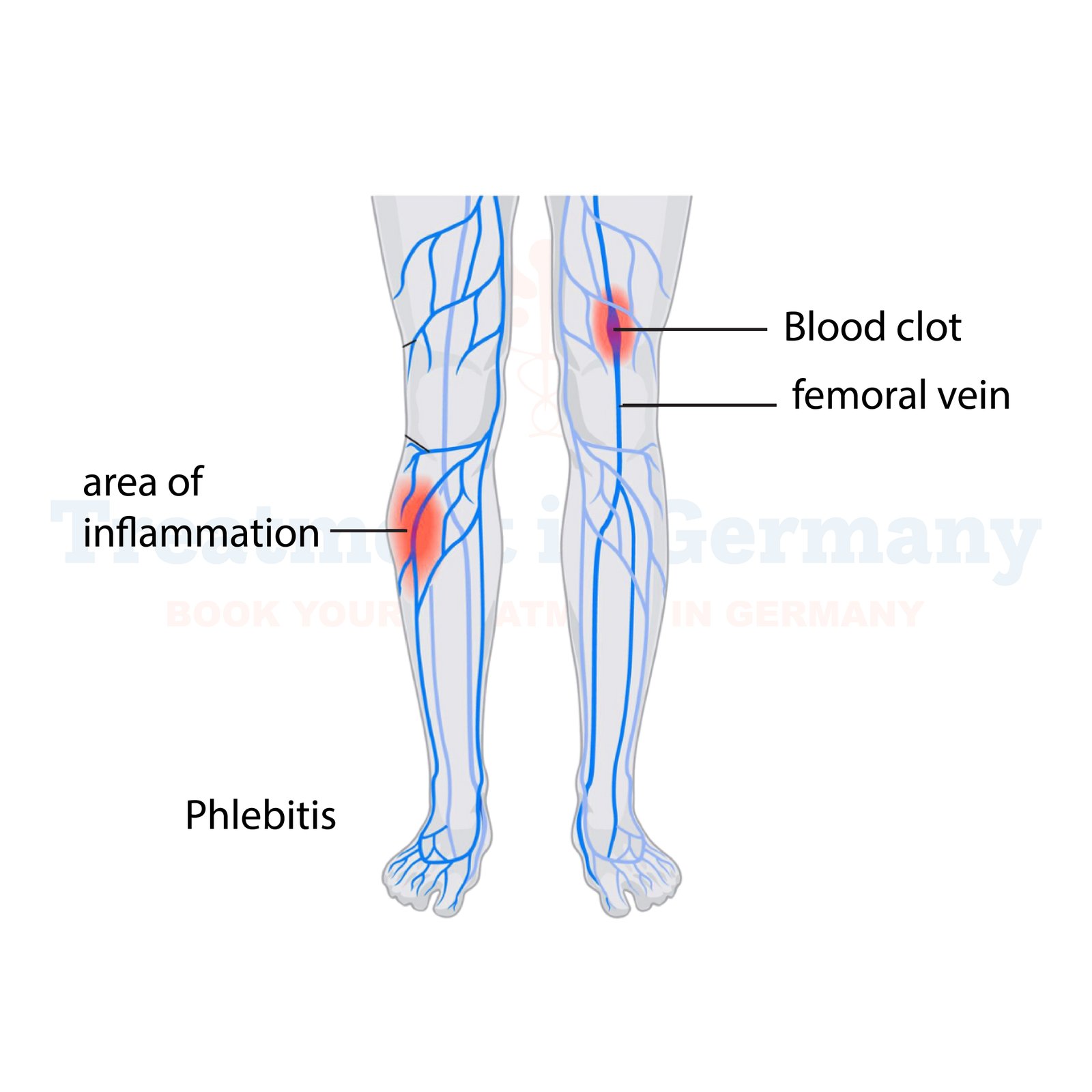
What is Phlebitis:
Phlebitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of a vein, often occurring in the legs. It can be painful and lead to complications if not treated promptly. Phlebitis typically occurs when a blood clot forms in a vein just beneath the skin's surface. This condition can affect both superficial veins (superficial phlebitis) and deeper veins (deep vein thrombophlebitis).
Side effects of Phlebitis:
The symptoms of phlebitis may vary depending on the severity and location of the inflammation. Common signs and symptoms include:
If left untreated, phlebitis can lead to more serious complications such as the development of blood clots, infections, or even a pulmonary embolism (a blood clot that travels to the lungs), which can be life-threatening.
How is Phlebitis diagnosed?
Diagnosing phlebitis typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional, who will assess your symptoms and medical history. In some cases, additional tests may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of the condition. These tests may include:
1. Ultrasound: This non-invasive imaging technique can help visualize blood flow and detect any blood clots in the affected vein.
2. Blood tests: Blood tests may be conducted to check for markers of inflammation and clotting factors.
3. Venography: In rare cases, a venogram may be performed, where a special dye is injected into the vein to make it visible on X-ray images.
Potential treatments of Phlebitis:
Treatment for phlebitis aims to relieve symptoms, prevent complications, and reduce the risk of blood clots. The appropriate treatment approach will depend on the type and severity of phlebitis. Common treatment options may include:
1. Compression Therapy: Wearing compression stockings or bandages can help improve blood flow and reduce swelling in the affected area.
2. Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or pain relievers may be prescribed to alleviate pain and inflammation. In some cases, anticoagulant medications (blood thinners) may be recommended to prevent blood clots from forming or getting larger.
3. Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the affected area can help soothe pain and promote circulation.
4. Elevation: Elevating the affected limb above heart level can help reduce swelling and discomfort.
5. Thrombolytic Therapy: In severe cases of deep vein thrombophlebitis, thrombolytic therapy may be considered to dissolve blood clots.
6. Surgery: Surgery may be necessary in rare cases of complicated phlebitis, such as when there is a risk of a blood clot breaking loose and traveling to vital organs.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
