Pituitary Tumor Treatment in Germany
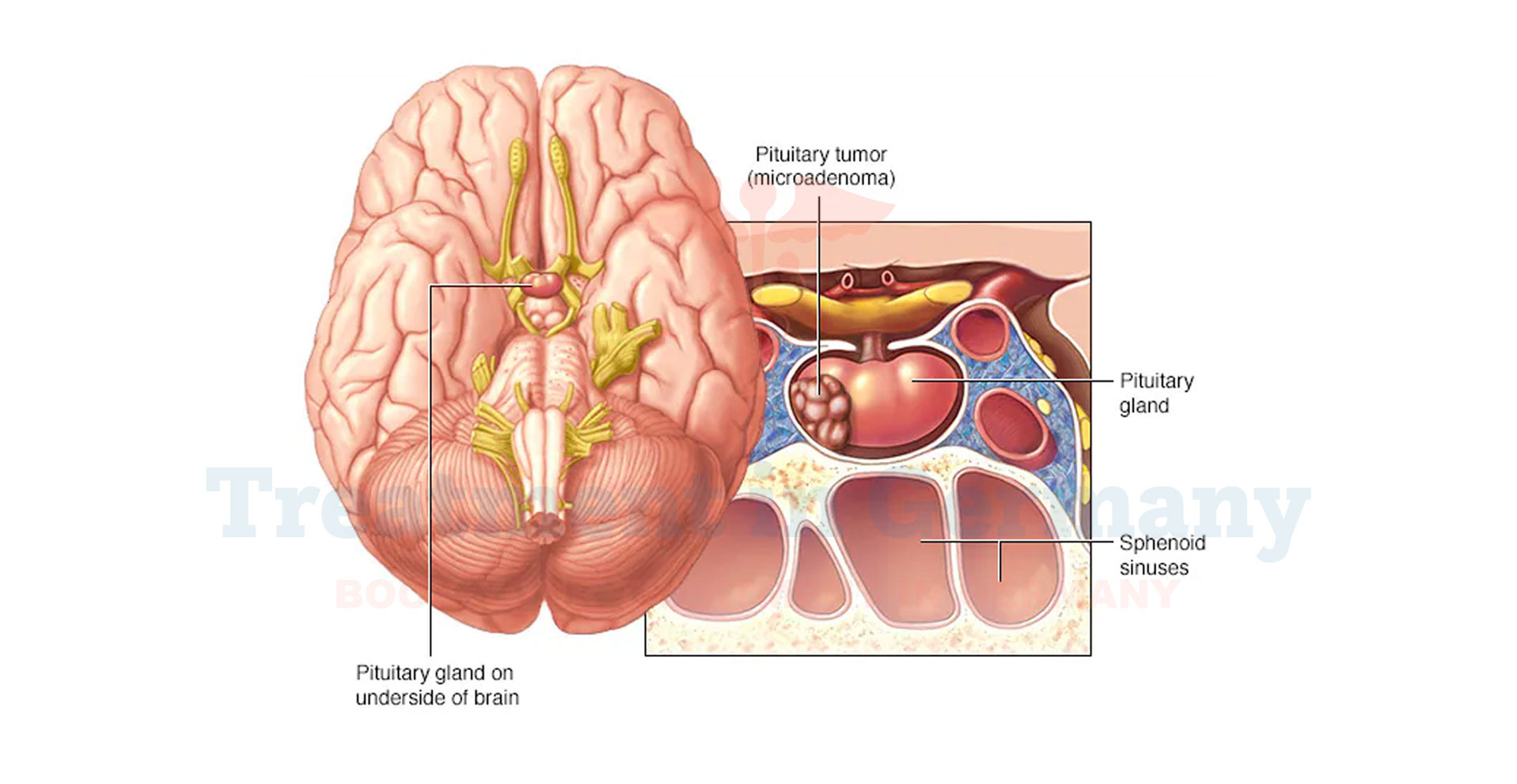
Pituitary tumors are abnormal growths in the pituitary gland, a vital organ at the base of your brain responsible for regulating hormones that impact your growth, metabolism, and overall health. While most pituitary tumors are benign (non-cancerous), they can significantly affect your quality of life. Early detection and reliable treatment are crucial for managing these growths effectively.
Germany is renowned for its world-class medical expertise and innovative treatment approaches for pituitary tumors. Specialists in Germany utilize cutting-edge diagnostic tools and advanced surgical techniques, including minimally invasive procedures, to ensure precise and effective treatment. With a focus on patient-centered care, Germany’s healthcare facilities provide personalized treatment plans tailored to each individual's condition, aiming for the best possible outcomes and a swift recovery.
Types of Pituitary Tumors
Understanding the type of pituitary tumor is essential for determining the most effective treatment plan.
- Functioning Tumors: These tumors release excess hormones, leading to symptoms such as Cushing’s disease, thyroid dysfunction, or infertility.
- Non-Functioning Tumors: Unlike functioning tumors, non-functioning ones do not produce hormones.
Symptoms of Pituitary Tumors
Recognizing symptoms early can help prevent complications. Common signs include:
- Persistent headaches: Headaches that do not improve with typical treatments.
- Vision issues: Blurred or impaired vision, double vision or loss of peripheral vision.
- Changes in body weight: Unexplained weight changes, either loss or gain, without an identifiable cause.
- Fatigue: Unexplained fatigue or weakness.
- Hormonal imbalances: Changes in menstrual cycles, libido, or physical appearance
What Causes Pituitary Tumors?
While exact causes remain unclear, certain signs seen in patients with pituitary tumor includes:
- Genetic Causes: Mutations in specific genes leading to abnormal cell growth in the pituitary gland.
- Sporadic Causes: Random development of pituitary tumors without any identifiable genetic or environmental factors.
- Potential Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain chemicals or radiation, though concrete evidence linking these to pituitary tumors is limited.
- Hormonal Dysregulation: Imbalances in hormone levels that may stimulate abnormal growth in pituitary cells.
Diagnosis and Diagnostic Tools
Accurate diagnostics play a vital role in managing pituitary-related conditions. Your specialist may recommend the following tests for precise analysis:
- Blood Tests: To measure hormone levels
- MRI or CT Scans: Detailed imaging tests to detect tumor size and location
- Vision Tests: Evaluates any loss of peripheral or overall vision
- Suppression/ Stimulation Hormone Testing: Helping to diagnose or manage pituitary disorders.
Treatment for Pituitary Tumors in Germany
Germany is a hub for advanced medical care, offering some of the most effective treatments for pituitary tumors worldwide. Here’s how Germany’s tailored approach to pituitary tumor care ensures improved outcomes:
Medications
- Dopamine Agonists: Medications like cabergoline and bromocriptine are commonly prescribed to shrink prolactin-secreting tumors (prolactinomas) and reduce prolactin levels.
- Somatostatin Analogs: Drugs such as octreotide and lanreotide help suppress the secretion of growth hormones in cases of acromegaly caused by pituitary tumors.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Necessary for patients experiencing hormone deficiencies due to the tumor or its treatment.
- Targeted Therapy: Investigative drugs or therapies aimed at blocking specific pathways in tumor growth for aggressive or resistant pituitary tumors.
Radiation Therapy and Surgeries
For inoperable tumors or residual tumor tissue post-surgery, targeted radiation therapy can deliver precise treatment for effective tumor management.
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS): A non-invasive procedure delivering highly focused radiation to target tumor tissue with minimal impact on surrounding structures.
- Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT): Advanced technology that adjusts radiation intensity to conform to the tumor shape, improving precision.
- Proton Beam Therapy: A treatment option that uses protons instead of traditional X-rays, reducing radiation exposure to healthy tissues.
Assistive Therapies
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Prescribed to restore hormonal balance when gland function is disrupted by surgery or radiation.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to aid recovery and improve mobility or strength after treatment.
- Nutritional Counseling: Guidance on maintaining a healthy diet to support physical recovery and overall well-being.
Why Choose Germany for Pituitary Tumor Treatment?
Germany offers an unparalleled combination of cutting-edge medical innovation and patient-centered care. Here’s why patients from around the world choose Germany for pituitary tumor treatment:
- World-Class Facilities: State-of-the-art hospitals equipped with advanced imaging, diagnostic, and surgical equipment.
- Expert Surgeons: Renowned neurosurgeons and endocrinologists with years of experience in handling complex pituitary tumor cases.
- Comprehensive Care: Patients receive holistic treatment plans, blending surgery, medications, and post-operative care.
- Innovative Research: Continuous advancement to introduce new therapies and medications.
Prevention and Management
While pituitary tumors may not always be preventable, maintaining regular check-ups and managing hormone levels effectively can mitigate risks. Patients recovering from treatment should follow these practices for long-term health:
- Regular Appointments: Attend regular follow-ups and imaging scans
- Follow Prescribed Medications: Stick to prescribed hormonal replacement therapies if needed
- Adapt to healthy lifestyle: Lead a healthy lifestyle with balanced nutrition and exercise
Conclusion
Pituitary tumors can pose significant health challenges, but Germany’s exceptional medical expertise provides patients with hope and effective solutions. With a combination of state-of-the-art technology, highly skilled specialists, and a patient-centered approach, Germany stands out as a top destination for pituitary tumor treatment. By delivering precise and compassionate care, it offers patients the best opportunity to manage their condition and enhance their overall well-being.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
